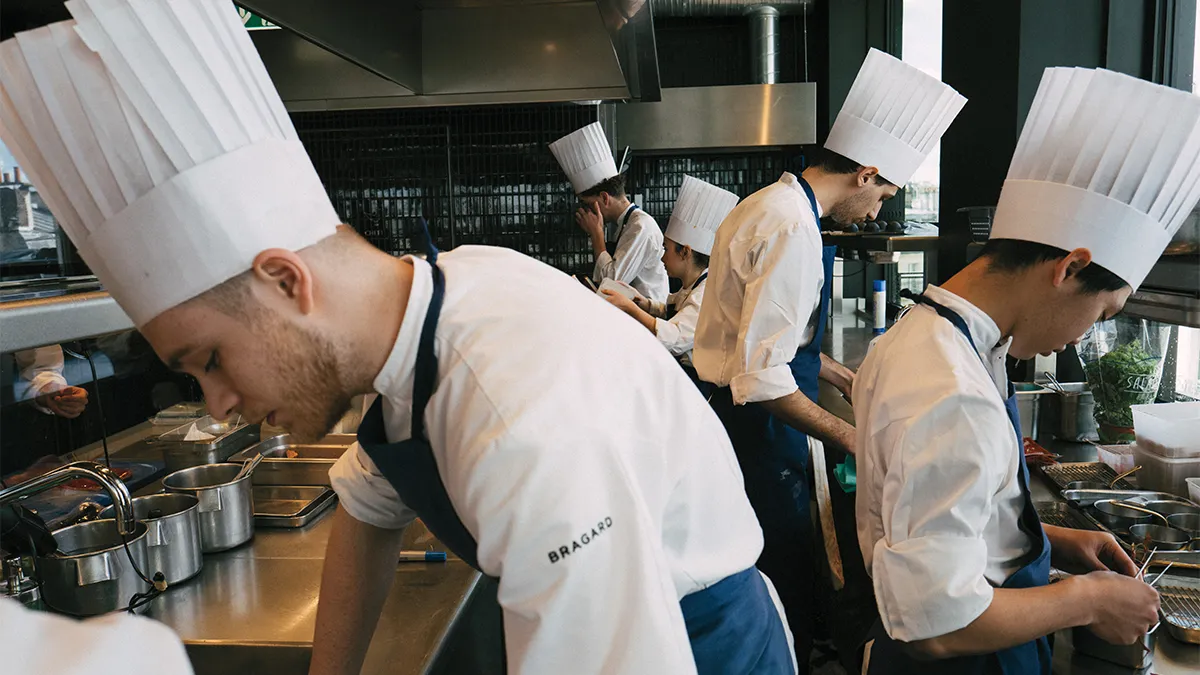
France’s 29 Best Restaurants – According To Michelin
Ahead of an anticipated summer sojourn – see which made the little red guide’s hallowed list.
Related articles
Michelin has almost become as emblematic of French fine-dining landscape as the cuisine itself. While today we may think of the guidebook as a comprehensive tastemaker, the Michelin Guide’s goal in 1900 when it launched was much simpler: to drive local tourism.
At a time when there were fewer than 3,000 automobiles in all of France, the Michelin Guide was designed to highlight hotels and restaurants in such a way that would encourage motorists to make the trek—presumably wearing out their tires in the process. In 1926 the guidebook began awarding stars, and by 1936, Michelin had adopted its criteria for the tiered ratings. One star indicates a “very good restaurant in its category,” two stars translate to”excellent cooking, worth a detour,” while the coveted three stars mean a restaurant offers “exceptional cuisine, worth a special journey. Those ratings have been inextricably linked to Gallic gastronomy.
Prior to the pandemic, the hallowed guide experienced upheaval to the old order. In 2019, Auberge de L’ill lost its third star after holding it for 51 years. And last year Paul Bocuse’s L’Auberge du Pont de Collonges was demoted two years after his death, sending shockwaves through the French culinary community. That continues this year as legendary chef Guy Savoy’s two-decade run with Michelin’s highest honour came to an end as his Parisian restaurant was demoted to two. It wasn’t all bad news as La Marine joined the ranks of Michelin three-star restaurants. Chef Alexandre Couillon can now be mentioned in the same breath as culinary legends from Anne-Sophie Pic to Alain Ducasse to Alain Passard. Here are France’s 29 Michelin three-star restaurants for 2023.
Alléno Pavillon Ledoyen, Paris, 8th Arrondissement
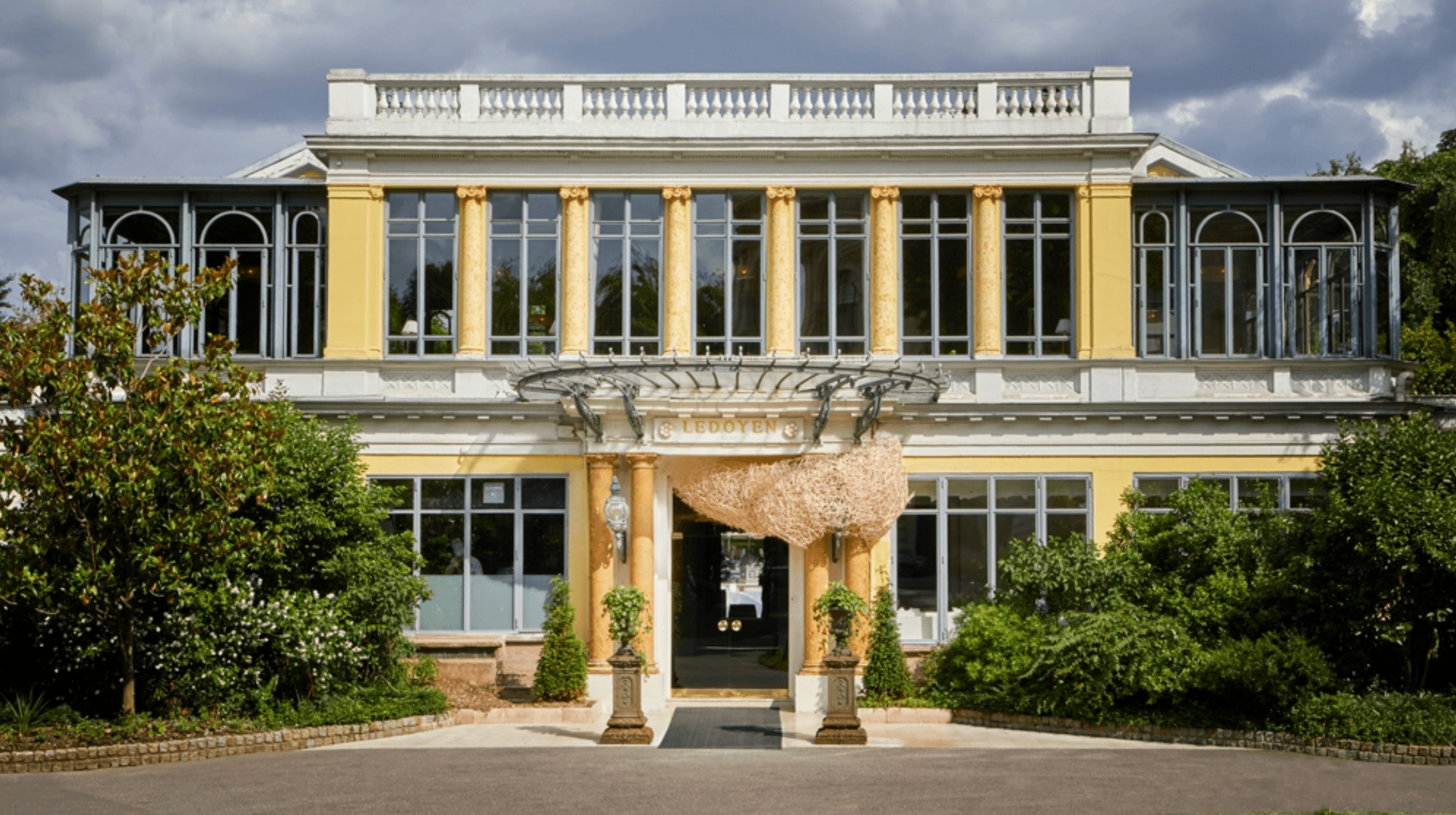
Pavillon Ledoyen’s deep Parisian roots date back to 1842, when the restaurant was first erected in the Champs-Elysées’ gardens. While you can catch a glimpse of the original painted mouldings and ceiling in the upstairs dining room, chef Yannick Alléno, who took over in 2014, brings a modern sensibility to the historic site, which earned the spot a third Michelin star just seven months after he started. Alléno’s pet technique for making sauces are “extractions.” This entails first extracting liquids from ingredients and then reducing them using a technique called cryoconcentration, which involves a combination of sub-zero temperatures and centrifugal force. Diners can enjoy the fruits of this methods in dishes like a dessert that features a coffee-flavoured fir-tree extraction jelly.
Am par Alexandre Mazzia, Marseille

Chef Alexandre Mazzia’s eponymous restaurant draws inspiration not just from the produce and seafood available in France’s Cote d’Azur, this 24-seat restaurant boasts influences from beyond its Marseille home. Mazzia spent his first 14 years living in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and before his culinary career, the chef was professional basketball player. His restaurant opened in 2014, earning its first star soon after. He’s become known for unique, globally inspired compositions that have made him beloved in the chefs world, like his scorched mackerel satay with tapioca, wasabi sorbet, red métis; or his marinated egg yolk with lemon panais, combawa mais granité and tarragon.
Arpège, Paris, 7th Arrondissement

Today, there are few chefs quite as influential as Alain Passard, but back in 1986 he was simply trying to fill his mentor Alain Senderens’ big shoes. That’s the year Passard took over Senderens’ restaurant Archestrate. Passard renamed his new venture, Arpège, the French word for arpeggio, a name that like the establishment’s original name (which means orchestra en francais) pays tribute to his second love: music. Before arriving at Arpège, Passard cut his teeth at the Duc d’Enghien at the Casino of Enghien and the Carlton in Brussels, where he was awarded his first Michelin stars. Arpège earned its third in 1996 and has held onto them ever since—even after adopting a plant-centric menu in 2001. Guests can sample the signature dishes that put Passard on the map, such as his famous l’arpège egg—the hot-cold, hard-soft boiled amuse bouche you’ll now find tributes to at fine-dining restaurants around the globe.
Assiette Champenoise, Tinqueux

Chef Arnaud Lallement’s fate as a chef seemed predestined. As a child, he watched his father Jean-Pierre, who ran the family restaurant starting in 1975. Then, after studying under culinary legends, like Roger Vergé and Michel Guérard, Lallement took over at the helm in 1998. There, he won L’Assiete its second Michelin star in 2005 and its third in 2014. The menu boasts classic dishes (such as grated foie gras served over fois gras toast), as well as unique novel ones (milk-fed veal sweetbreads), but always with a focus on bringing out the pure flavours of the ingredients with just the right balance of acidity (Lallement’s mantra is “mangez vrais,” which translates to, “eat true”). And, as you’d expect from the region, there are more than a thousand champagnes in the cellar for you to sip with your meal.
Auberge du Vieux Puits, Fontjoncouse

Chef Gilles Goujon rise to Michelin stardom is the stuff of heartwarming movies. In 1990, he bought L’Auberge de Vieux Puits in the small village of Fontjoncouse for 34,000 euro, after its previous three owners had failed to turn a profit. For five years he struggled to attract diners. But his fortune turned in 1996 when he won the “Best Worker of France,” a prestigious award given out every four years to artisans in different categories. Shortly after, he snagged his first Michelin star in 1997. He won his second star in 2001 and his third in 2010.
Epicure, Paris, 8th Arrondissement

While many Michelin-star-winning chefs could be considered culinary royalty, Epicure’s chef Eric Frechon bears an additional, extra-official-sounding honourarium. He was decorated as a Knight of the Order of the “Légion d’Honneur” by Nicolas Sarkozy in 2008—just a year before he was first awarded three Michelin stars. The self-described “control freak” prides himself on his ability to elevate simple—even cheap—ingredients into Michelin-star-worthy fare. Though, there’s no shortage of decadence on his menu. You’ll find classic French cuisine, such as whole roast chicken cooked in a pig’s bladder (a signature dish) and black truffle, artichoke, and foie-gras stuffed macaroni.
Flocons de Sel, Megève

Nestled in the French Alps, Flocons de Sel offers a taste of the mountains. Chef Emmanuel Renaut scours the hillsides for herbs and mushrooms to adds to his dishes. He also takes a twice-yearly sojourn with award-winning cheesemaker Jacques Dubouloz through local farms and pastures in pursuit of the very best cheese. Just don’t expect to see fussily prepared cheese dishes at Folcons de Sel: When it comes to le fromage, Renaut is a purist. You’ll find all 20 of the menu’s hand-selected cheeses in their natural state. “I don’t like to cook with cheeses. I think it’s a waste,” he once remarked.
Georges Blanc, Vonnas

Going on 38 straight years of three Michelin stars, Georges Blanc—both the chef and the restaurant—is a French culinary fixture. While Blanc sharpened his technique in restaurants in France and abroad (as well as during a stint as a military cook) it’s hard not to think that some of his talent might be hereditary. Three generations of cooks preceded him, including his grandmother, who was once named the “best cook in the world,” by a food writer. Blanc took the reins from his mother in 1968, before turning the family business into a luxury hotel in the ‘70s.
Kei, Paris, 1st Arrondissement

The newest Michelin three-star recipient in the City of Lights is also the first ever Japanese chef to nab the honour in France. Kei Kobayashi was born in Nagano before moving to France to cook. He’s serving dishes like foie gras with green apple jelly; potato gnocchi with truffle, parmesan emulsion and Iberian ham; and salmon with a bitter sorrel cream with raw and cooked vegetables. While his menu has an influence from his Japanese roots, he’s quite taken with modern French cuisine.
La Marine, Ile de Noirmoutier

When La Marine joined the ranks of three-star restaurants in 2023, Michelin’s inspectors said that chef Alexandre Couillon’s ocean-focused cuisine, which spotlights seafood and edible coastal plants, asserted La Marine as one of the very best restaurants in all of France. The guide called his style of cooking both striking and bold, calling out his “braised artisanally fished mackerel, beetroot and parsley foam” and the “crispy buckwheat dessert, caramel mousse, candied citrus fruit and sea lettuce sorbet.”
L’Ambroisie, Paris, 4th Arrondissement

Abandoned by his parents and placed in an orphanage at 13, chef Bernard Pacaud found salvation in the kitchen of Eugénie Braizer’s Col de la Luère. The three-star-winning Lyonnais chef took Pacaud under her wing, providing him with both a roof over his head and a place to learn the craft. First nabbing his own third star in 1988, Pacaud has been holding onto the stellar Michelin rating for longer than any of Paris’s other three-star restaurants. L’Ambroisie lives up to its name which means “food of the gods” with its lavish, stunningly plated dishes like sea bass and artichoke served atop caviar. And even if the gods don’t literally dine there, some pretty powerful mortals do: In 2015 presidents Barack Obama and Francois Hollande enjoyed a working dinner at L’Ambroisie.
L’Oustau de Baumanière, Baux-de-Provence

When the Michelin Guide bestowed its third star on the restaurant at L’Oustau de Baumanière, it said of chef Glenn Viel that “organic vegetables from the garden of Baumanière, along with lamb, chicken and pork, each ingredient of the rich local produce finds its meaning and its true flavours in the hands of the chef.” Viel is merging local ingredients and traditional technique with modern flourishes like serving frog’s leg with puffed rice.
La Vague d’Or, Saint-Tropez

Arnaud Doncklele’s impressive resume includes apprenticeships in the kitchens of Alain Ducasse and Michel Guérard, so it’s hardly a surprise that the young chef achieved three Michelin Stars by the time he turned 35. La Vague D’Or offers three tasting menus, including the seven-course “Balade Epicurienne” for adventurous diners and a five course vegetarian option. There’s also two à la carte menus: one inspired by land and one inspired by the sea—which happens to be within view of restaurant’s umbrella-lined terrace, by the way.
La Villa Madie, Cassis

Joining the ranks of the three-stars in 2022, La Villa Madie has focused on Mediterranean fare under the leadership of Dimitri and Marielle Droisneau since 2013. Tucked in the south of France, overlooking the pristine blue waters, the local seafood and flora take centre stage. When it comes to Dimitri’s cooking, the guide is effusive: “From one dish to another, it makes its presence felt—light, subtle, tasty, fresh and aromatic, punchy when necessary, and always surprising and original.”
Le 1947 at Cheval Blanc, Courchevel

Yannick Alléno has performed the chef’s equivalent of a hat trick, having earned three triple-star Michelin restaurants over the course of his career. Ten years after his three-star win at Le Meurice, and three years after earning three stars at Pavillon Ledoyen, Michelin awarded him stars for Le 1947 at Cheval Blanc in 2017. The Alpine outpost’s sleek, modern surroundings—which include a perforated sphere through which diners can watch the chefs work—set the tone for the nine-course menu that puts a creative spin on French cuisine. Le 1947 is named for Château Cheval Blanc’s most renowned vintage and aims to provide guests with an experience just as covetable.
Le Cinq, Paris, 8th Arrondissement

From within the Four Seasons Hotel George V, chef Christian le Squer combines nostalgic French flavours with ambitious new techniques. “My cooking is like a Chanel suit worn over a pair of jeans,” he once said. You can taste this amalgam in dishes like his Parisian-style gratinated onions or line-fished sea bass served with caviar and buttermilk (a nod to growing up near the Morbihan sea in Brittany). “His signature is all over the superb dishes, mastered to perfection and demonstrating exceptional skills and a deep knowledge of the very best produce,” the former director of the Guide, Michael Ellis, said when the 2016 Michelin Guide was released. “Each of Christian Le Squer’s dishes is a true work of art, a shining example of the best of French gastronomy.” Prior to racking up stars at Le Cinq in 2016, Le Squer enjoyed 12 consecutive years of three-star glory at Pavilion Ledoyen.
Le Clos des Sens, Annecy-le-Vieux

Perched near Lake Annecy in the French Alps not far from the Swiss border, Le Clos des Sens is a manor built back in 1866. Laurent Petit leads the Michelin three-star restaurant inside the inn and he draws heavily on the region around him. His food features the crayfish, arctic char and other seafood from the surrounding lakes, including Annecy. As well as ingredients from the garden he’s built at the manor. His culinary education began early, as Petit grew up the son of a butcher and as a young chef cooked for the legendary Michel Guérard, a founder of nouvelle cuisine.
Le Louis XV—Alain Ducasse à l’Hôtel de Paris, Monte Carlo

The first hotel restaurant to secure three Michelin stars, Alain Ducasse’s Le Louis XV has become as much a fixture in Monte Carlo as any casino. But the Riviera mainstay has undergone changes in recent years. In 2007 Franck Cerutti assumed the role of executive chef and was joined by Ducasse’s protege, Dominique Lory, in 2011. Then, the space underwent a more physical transformation in 2015, trading its opulent, 19th-century-inspired wall hangings and sculptures for a more modern vision of luxury. Along with it, the menu got a little facelift, moving to even lighter, more nuanced fare. “Creating a menu is like writing good music,” Ducasse told The New York Times. “Loud and strong contrasts with soft and gentle. In a world where people zap away from anything they don’t instantly love or understand, gastronomic luxury happens when a dish is so well conceived it wins the time to seduce with subtlety.”
Le Petit Nice, Marseille

Chef Gérald Passédat says he inherited his taste for beauty and appreciation for things well done from his family of artists and chefs, while he honed his technique in the kitchens of the Troisgros brothers and Michel Guérard. It all came together in 2008 when Le Petit Nice first ascended to three stars. Passédat’s cuisine leans heavily on the abundance of fish in the sea the restaurant overlooks. In a year, he estimates at least 65 different Mediterranean species make their way onto his plates. An updated take on classic bouillabaisse, anemone fritters, seafood carpaccio, and a delicately prepared sea bass named for the chef’s opera star grandmother are a few of the signature dishes that grace Passédat’s menu.
Le Pré Catelan, Paris, 16th Arrondissement

In one respect Frédéric Anton, one of France’s most admired chefs, is an utter failure: As a child he aspired to become a cabinetmaker. Alas, his cabinet-making dreams were put on hold when he began his career as a chef in 1983, and further left in the dust when he proceeded to cook under some of fine-dining’s biggest names—including serving as Joël Robuchon’s chef de cuisine. Anton’s impressive pedigree eventually landed him at Le Pré Catelan in 1997, where he earned two Michelin stars by 1999 and was elevated to a third in 2007.
Les Prés d’Eugénie—Michel Guérard, Eugénie des Bains

If one were to erect a Mount Rushmore of French gastronomy, Michel Guérard’s inclusion would be a foregone conclusion. One of the so-called founding fathers of French nouvelle cuisine, Guérard got his first taste of Michelin stardom at Pot-au-Feu, which won its second star in 1971. He opened Le Prés d’Eugénie in 1974, and his cuisine was awarded its first star almost immediately, with a second star arriving in 1975 and a third following in 1977. Today, he’s focused on balancing the hedonistic delights of food with healthy eating.
Maison Lameloise, Chagny

This Burgundian restaurant has been a gastronomic institution since Michelin’s inception. It appeared in Michelin’s very first guide in 1900 and earned its first star in 1926. Maison Lameloise enjoyed its first three-star streak between 1979 and 2004, which picked back up again in 2007. Many of the restaurant’s most successful years occurred under Jacques Lameloise, who took over for his father in 1979. In 2008, Lameloise passed the torch to then up-and-comer Eric Pras, who has kept its three-star rating going strong ever since. Pras has made his mark on the mainstay’s menu with technically precise dishes that put a fresh spin on Burgundian cuisine.
Mirazur, Menton

It was a career-defining year for chef Mauro Colagreco in 2019. Mirazur finally ascended to three stars and five months later it World’s 50 Best crowned it the top restaurant in its annual rankings. The chef has cooked at Mirazur in the South of France since 2006 after working with titans Alain Passard and Alain Ducasse. He incorporates ingredients around the French Riviera and merges them with inspiration from his Argentinian-Italian heritage for dishes like squid with artichokes and bagna cauda.
Pic, Valence

Pic’s Michelin-star-studded history dates back to the early 20th century. Andre Pic opened in Valence in 1935 and earned three Michelin stars by 1939. Later years proved to be rockier, with the restaurant dropping to two stars in 1946 and to one in 1950. Under the leadership Andre’s son Jacques, Pic ascended again to two stars in 1959 and three in 1973, before falling back to two in 1995, just a few years after Jacques’ death. Then, Jacques’s daughter, Anne-Sophie, took over the illustrious dining spot in 1998 with no formal training. Less than a decade later, chef Pic, the only woman in France with three Michelin stars (and just the fourth women ever to receive the honour), restored Pic to three-star glory in 2007. She describes her cuisine as simple, sophisticated and pointedly feminine, which you’ll see reflected in the menu, as well in the decor. “All my emotions are feminine, so I have this feminine way in my cooking. I think some men are able to make very feminine cuisine, but they are perhaps more focused on technique, less on developing the emotional part,” she told CNN in 2012.
Pierre Gagnaire, Paris, 8th Arrondissement

Credited with pioneering the French fusion movement, Pierre Gagnaire’s philosophy in the kitchen is, “tourné vers demain mais soucieux d’hier”—or “facing tomorrow, but respectful of yesterday.” His own culinary past is a mix of formal training and familial connections. Pierre Gagnaire learned the ropes from his Michelin-star-winning chef father, as well as in the kitchens of the highest calibre French chefs of the era, including Paul Bocuse. Gaugnaire took these lessons and started his own restaurant in his hometown of Saint Etienne in 1980, which received three Michelin stars in 1993, but struggled financially. Then, in 1996, Gagnaire opened his eponymous establishment. By 1998 he had his three Michelin stars again.
Plénitude—Cheval Blanc, Paris, 1 Arrondissement

Well, chef Arnauld Donckele wasted no time. For many chefs, bringing their restaurant to the Michelin three-star level can be a career-spanning effort. In Plénitude’s first year of eligibility, the restaurant rocketed to the top of Michelin’s rankings, earning tres etoiles right out of the gate in 2022. Of course, as the chef of three-star La Vague d’Or in Saint-Tropez, Donckele and the guide are quite familiar with each other. Located inside a an LVMH hotel in the heart of Paris, the 26-seat Plénitude connects cuisine from across French regions, drawing inspiration from Normandy, the south of France and Paris. When awarding Plenitude its third star, Michelin called Donckele an “ingenious master creator of sauces,” which is about as high of praise you can give a French toque.
Régis et Jacques Marcon, Saint Bonnet le Froid

Named for the father-son team that runs the restaurant, Régis et Jacques Marcon offers a seasonal taste of the Haute-Loire region—with a special reverence for the local mushrooms (Régis has even written a book on his beloved champignons). Régis took over his family’s inn in 1979, eventually moulding it into the restaurant it is today. He earned his first Michelin star in 1990, his second in 1997, and his third in 2005, just a year after his son, Jacques, joined him in the kitchen.
René et Maxime Meilleur, Saint Martin, Saint Martin de Belleville

René and Maxime Meilleur, the self-taught, father-son chef duo behind their eponymous restaurant, have been cooking together since 1996. The pair’s cuisine pays tribute to the surrounding Savoie region, with ingredients like crozet pasta, raclette, and Saint Martin goat’s milk, and first earned its third star in 2015. “The dishes are precise, generous and remarkably creative. “La bouitte” may mean small house in the local dialect, but the fare offered by René, Maxime and their spouses is of the highest calibre,” Ellis said when awarding La Bouitte its third star.
Troisgros—Le Bois sans Feuilles, Ouches

Holding onto its three-star rating for half a century, La Maison Troisgros—and the family dynasty behind it—has long been a driving force in French cuisine. In 1930 Jean-Baptiste Troisgros opened the restaurant near Lyon. Later, his sons Jean and Pierre took the reins, shaping it into the triple-starred establishment it is today with their nouvelle cuisine. Now Pierre’s son Michel runs the empire, alongside his wife Marie-Pierre and son César. César credits the restaurant’s continued success to his mother’s intuition (she’s pioneered much of Troisgros’s growth) and his father’s culinary sensibilities, which César describes as “tangy, vibrant, fresh, and measured.” Meanwhile, as the youngest Troisgros, César brings youthful perspective, flavours inspired by his travels through Spain and California (he also worked at Thomas Keller’s French Laundry), and “a thing for hot peppers.” The dish he says most encapsulates the restaurant’s ethos today is the cosa croquante: a salad made with shaved carrots that have been lightly fried and seasoned with herbs from the family garden.
Subscribe to the Newsletter
Recommended for you
Watch This Space: Mike Nouveau
Meet the game-changing horological influencers blazing a trail across social media—and doing things their own way.
By Josh Bozin
July 22, 2024
5 Lounge Chairs That Add Chic Seating to Your Space
Daybeds, the most relaxed of seating solutions, offer a surprising amount of utility.
July 22, 2024
You may also like.
You may also like.
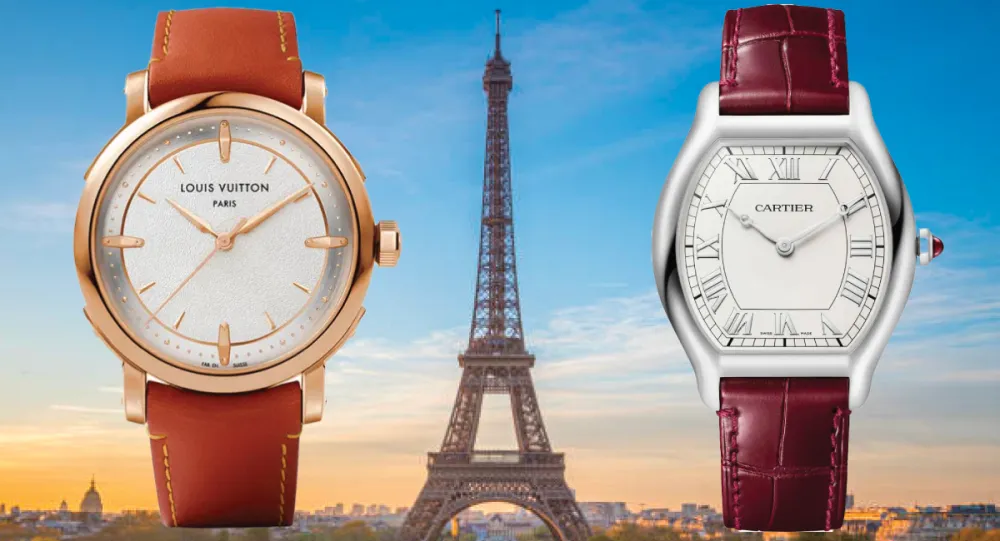
8 Trés Chic French Watches Perfect for Commemorating the Olympics, from Breguet to Cartier
Chanel, Cartier, Louis Vuitton, Breguet, and more make up quite a stellar list of French watches perfect for remembering the Paris Olympics for decades to come.
The opening ceremony for the 2024 Olympic Games takes place in Paris on July 26th. Whether or not you’re attending the games, one way to celebrate the start of the world’s biggest sporting event, and to show some espirit de corps with your fellow Francophiles, is by treating yourself to a French watch. Of course, you could go for the very Swiss Omega Speedmasters that came out to commemorate the Paris Olympics earlier this year, and that would be a tasty choice, but perhaps something more French is in order.
Also, if you’re going to be in Paris for the games (or anytime really) we have an excellent guide to the best watch boutiques in Paris for you, as well.
While not all of the timepieces highlighted below were made in France (so few watches are anymore), they each have deep connections to Paris, French watchmaking and/or Gallic style. And, as we’ve written elsewhere, French watchmaking has a long-standing and powerful influence on Swiss watchmaking. In fact, it was in Paris the Louis Cartier perfected the Tank that would go on to make wearing a watch on the wrist popular in the first place, this during the 1920s and 30s. And, of course, Cartier watches are all the rage these days, including the rather tiny Tank Mini, which made big waves at Watches and Wonders this year, as well as the Tortue, which made our best-of list this year.

Indeed, the Parisian horological roots run deep, but it’s not all Cartier. From Louis Erard’s whimsical collaboration with French interior-designer-turned-watchmaker Alain Silberstein to the dreamy, avant-garde designs of Paris-based Trilobe, there’s something for everyone in this mix.
Of all the watches Cartier introduced at Watches and Wonders Geneva this year, the Tortue re-edition was the most talked-about. Even older than the Tank, the tortoise-shaped model (born in 1912) is now available in a monopusher chronograph as well as the simpler “hours and minutes” platinum version shown here. Limited to 200 pieces, the stylish and shapely Tortue, which comes out in September, makes clear that even though Cartier manufactures all of its watches in Switzerland, the Paris-based brand is French to its core. $54,770.
Breguet Classique Double Tourbillon “Quai de l’Horloge” 5345
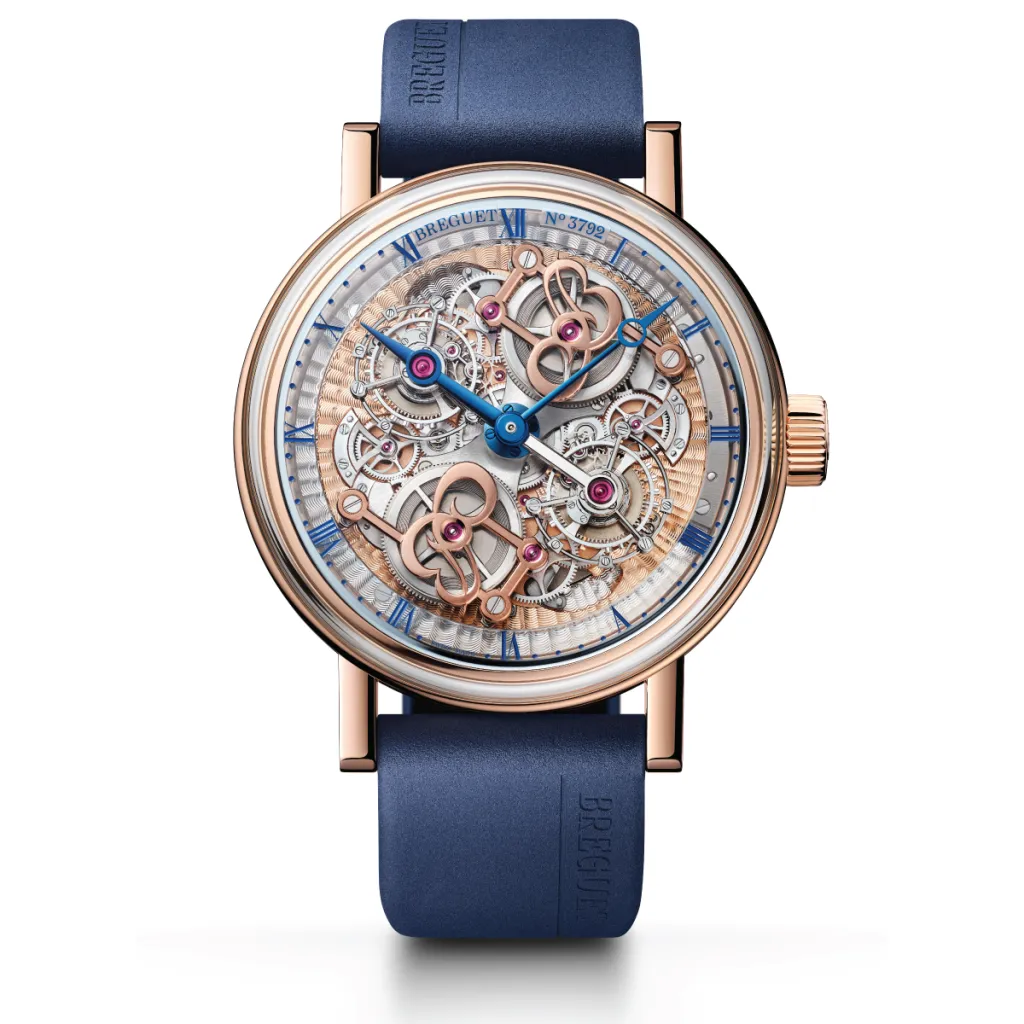

Although Breguet is now based in Switzerland, its namesake, Abraham-Louis Breguet, inventor of the tourbillon as well as the now-ubiquituous Breguet hands and numerals, made his mark on horology in Paris, where he maintained a workshop at 39 Quai de l’Horloge. The brand pays tribute to that history with its latest tourbillon, a 46 mm rose gold wristwatch equipped with not one, but two of the whirling mechanisms. Be sure to admire the engraving on the back of the movement, which depicts an aerial view of the workshop. C’est magnifique! Price on request.
Trilobe Les Matinaux L’Heure Exquise Dune Edition
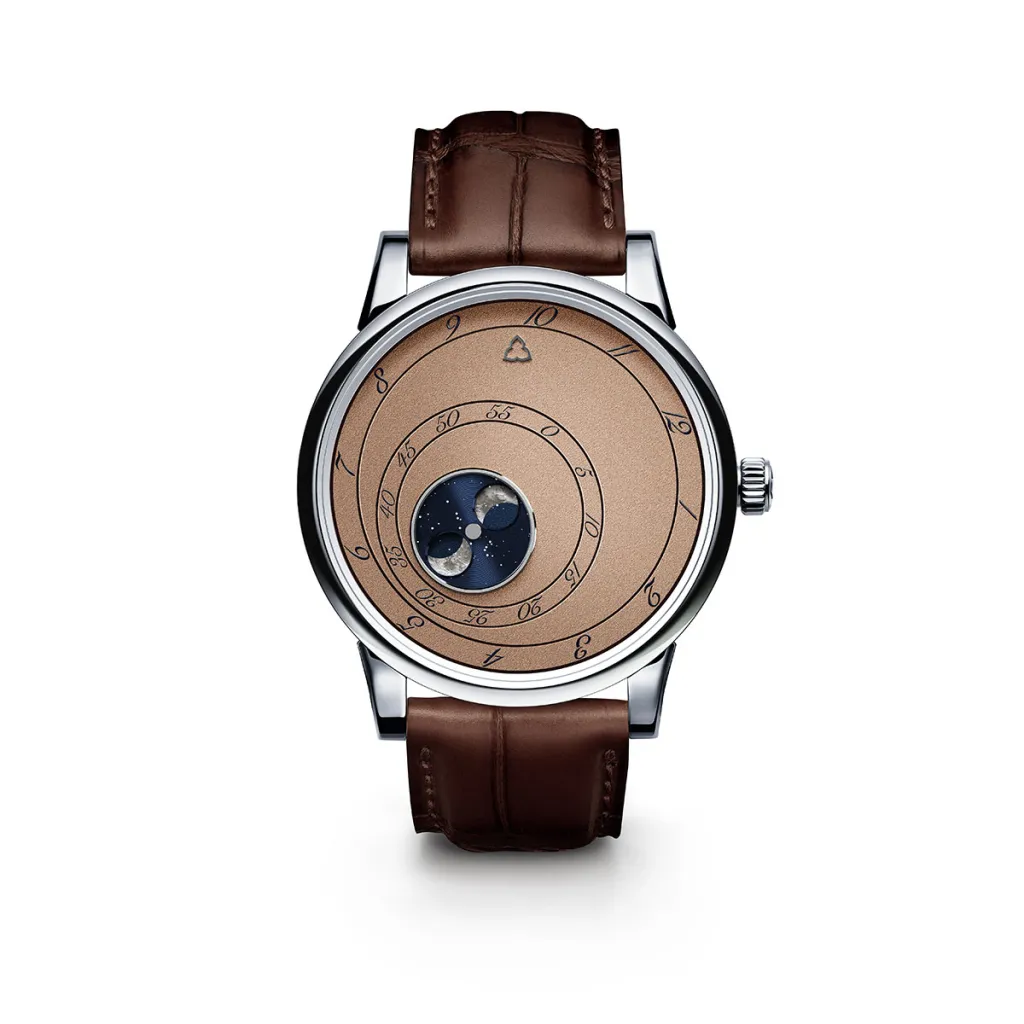

In 2018, Paris-based Trilobe introduced its Les Matinaux (“The Morning”) collection, and with it, a new way of telling the time. Employing a wandering display, the watch used three discs that rotated counterclockwise and three fixed pointers to indicate the hours, minutes and seconds. Named after a collection by the midcentury French poet René Char, the series recently spawned a new sand-colored Dune edition that marks the brand’s entrée into the world of complications. Limited to 100 pieces, the model, dubbed L’Heure Exquise (“The Exquisite Hour”), features a moonphase complication that evokes the orbit of the Moon around the Earth against the backdrop of a starry night sky. $21,995
Chanel Monsieur de Chanel Édition Superleggera Intense Black
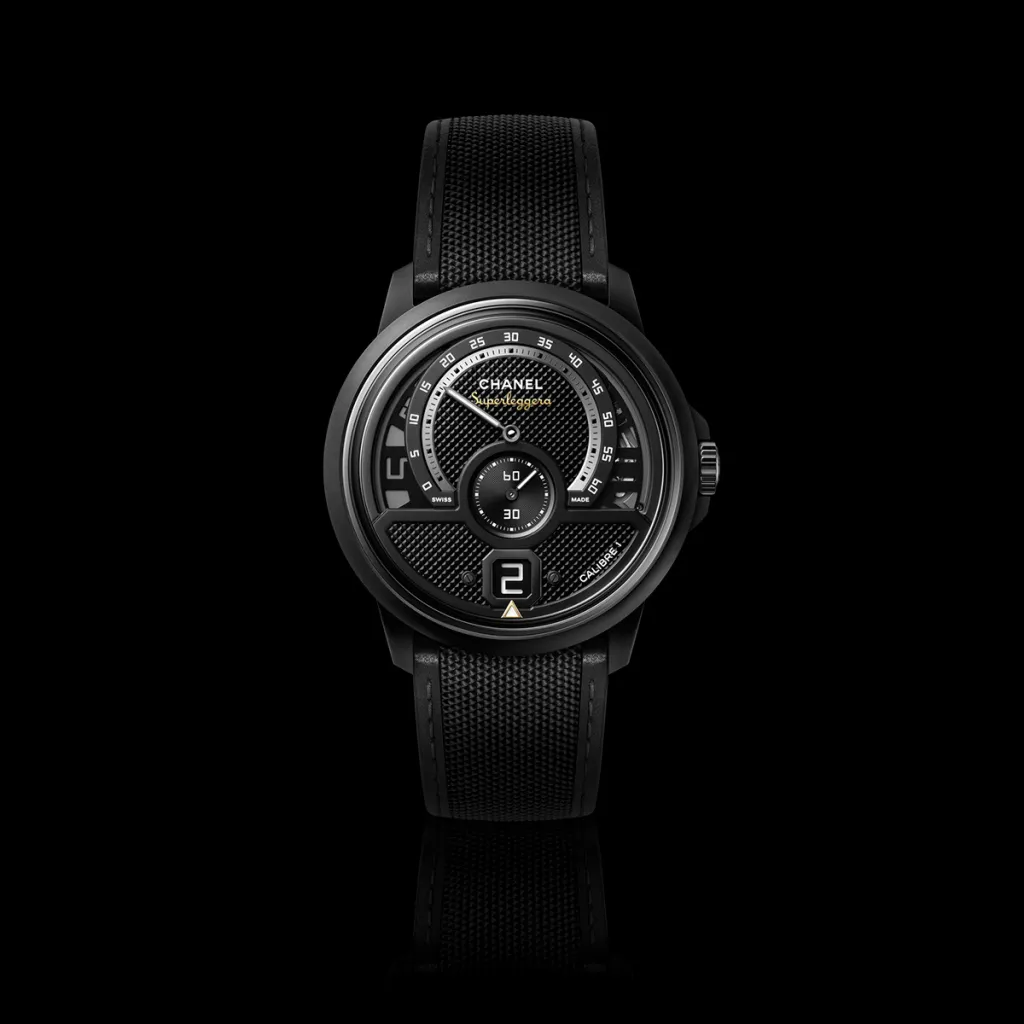

Arguably the Frenchiest brand on our list, Chanel made a name for itself as a high-end (as opposed to fashion) watchmaker in 1999, when it introduced its signature timepiece, the J12 (in unusual-for-the-time ceramic, no less). At Watches and Wonders Geneva in April, the brand upped the ante with its latest Monsieur timepiece, the Superleggera Intense Black, a limited edition of 100 pieces inspired by car racing. Housed in a matte black ceramic and steel case, the watch features a matte black guilloché dial and comes on a black nylon strap with black calfskin leather trim and lining. $69,651
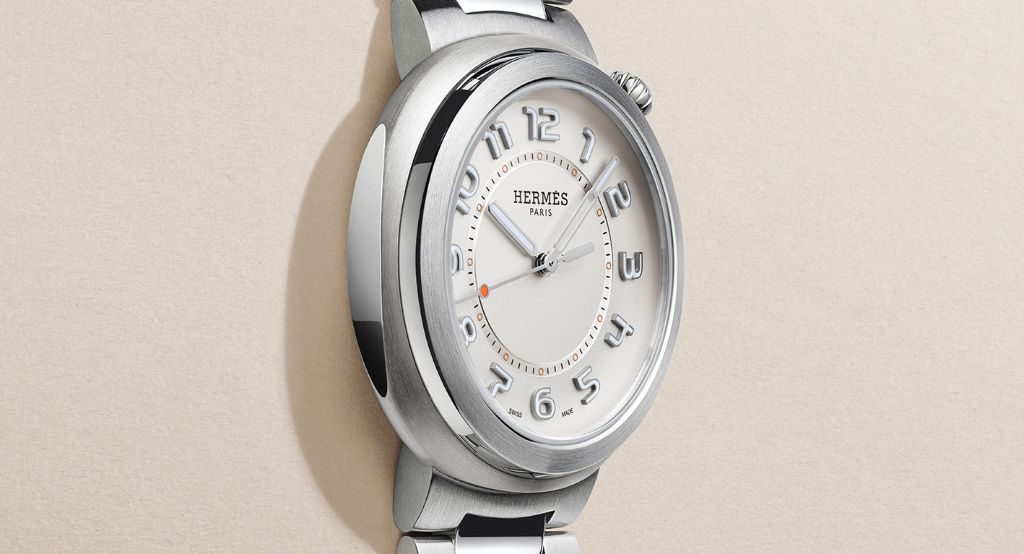
Hermès Arceau Grand Tralala Brides et Mors
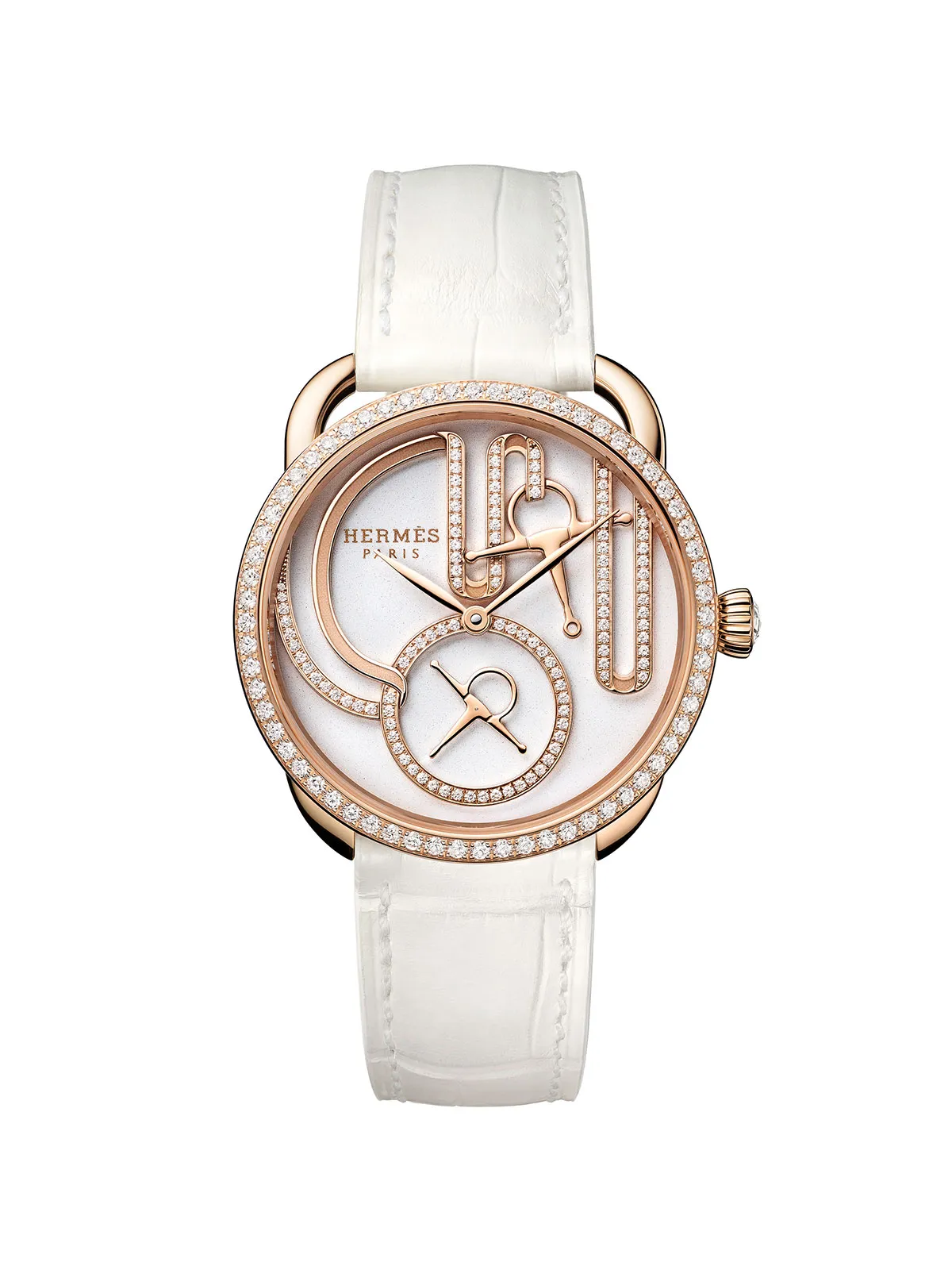

Like so many of Hermès’s most sought-after watches, the new 34 mm Arceau Grand Tralala Brides et Mors traces its design to another Hermès product, in this case the Grand Tralala silk scarf created by French artist Virginie Jamin. Patterned after the prestigious harnesses worn by the Royal Hungarian Bodyguard in the 19th century, the graphic design evokes the look of intertwined bridles and bits within a rose gold frame. Note the bit-shaped seconds hand! $72,172
Louis Erard x Alain Silberstein Smile-Day
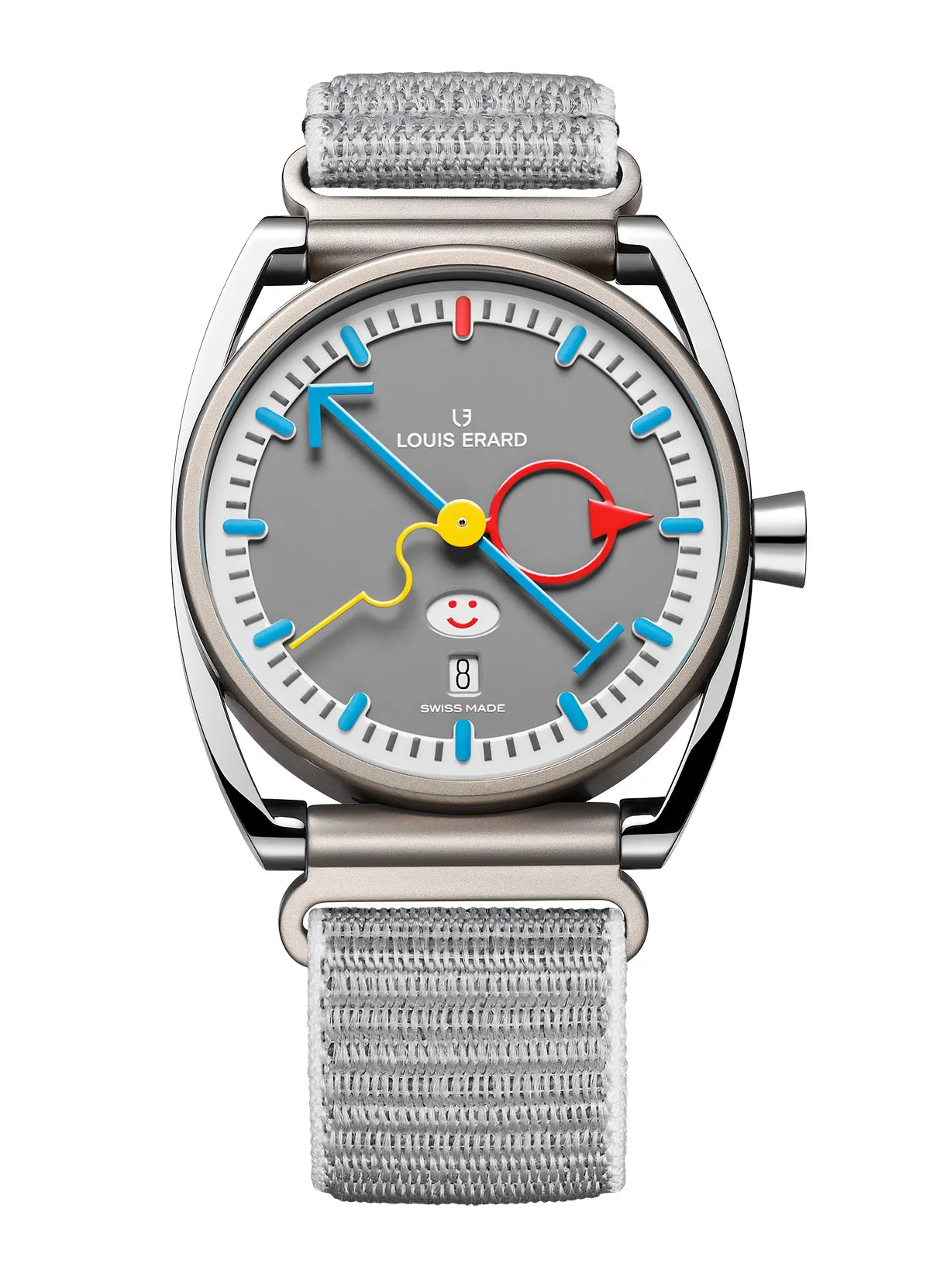

Imagine if Rolex’s much-talked-about emoji watch of 2023 had a child with the Memphis Group, a collective of Milan-based architects and designers who became known in the 1980s for their use of bright primary colors and bold patterns. That’s a quick way to describe the new 40 mm Smile-Day limited edition in titanium from Swiss watchmaker Louis Erard, whose latest collaboration with the iconoclastic French watchmaker Alain Silberstein reflects his signature whimsy. Silberstein was trained in graphic design and architecture in Paris by former members of Germany’s Bauhaus faculty, and he takes his whimsy very seriously. Between the aperture at six o’clock featuring a sliding carousel of seven emojis, the yellow squiggly seconds hand and the nostalgic color scheme, the piece is an instant classic. $8,019
Louis Vuitton Escale
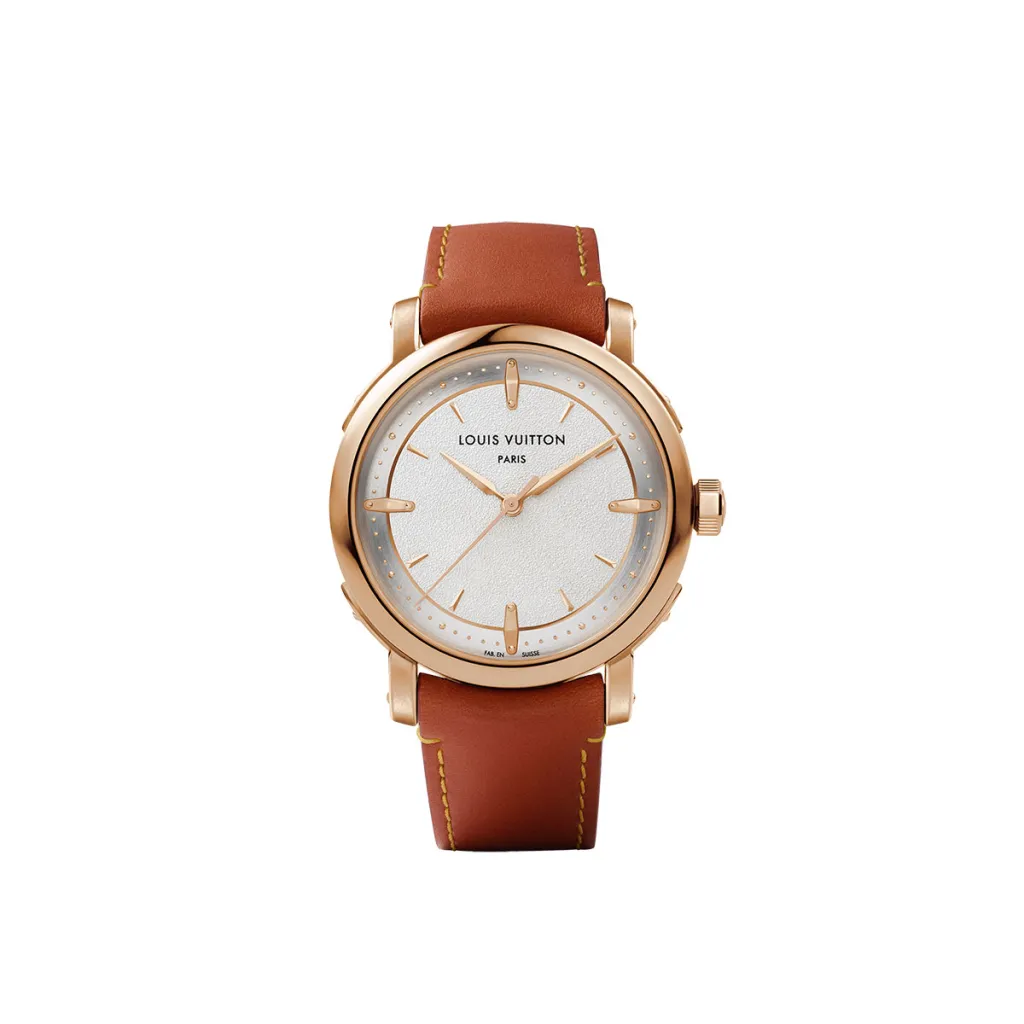

The dress watch revival continues with the new Escale by Louis Vuitton, an elegant timepiece honoring the 10th anniversary of the Escale collection (its first time-only, three-hand watch). Of the four new models in the line, two come in rose gold (like the 39 mm automatic model shown here), while the other two come in platinum. The former feature textured dials designed to evoke the suppleness and tactility of the Louis Vuitton Monogram canvas on metal. Equipped with a chronometer-certified movement with 50 hours of power reserve, the rose-gold Escale comes on a calf-leather strap. In a press release, the brand made sure to emphasize the model’s roots: “Just below the 12 o’clock hour marker, under the Louis Vuitton logo, is one word that encapsulates everything there is to be known about the Escale’s creative rebirth: Paris.” $40,324
Bell & Ross BR 03 Diver Full Lum
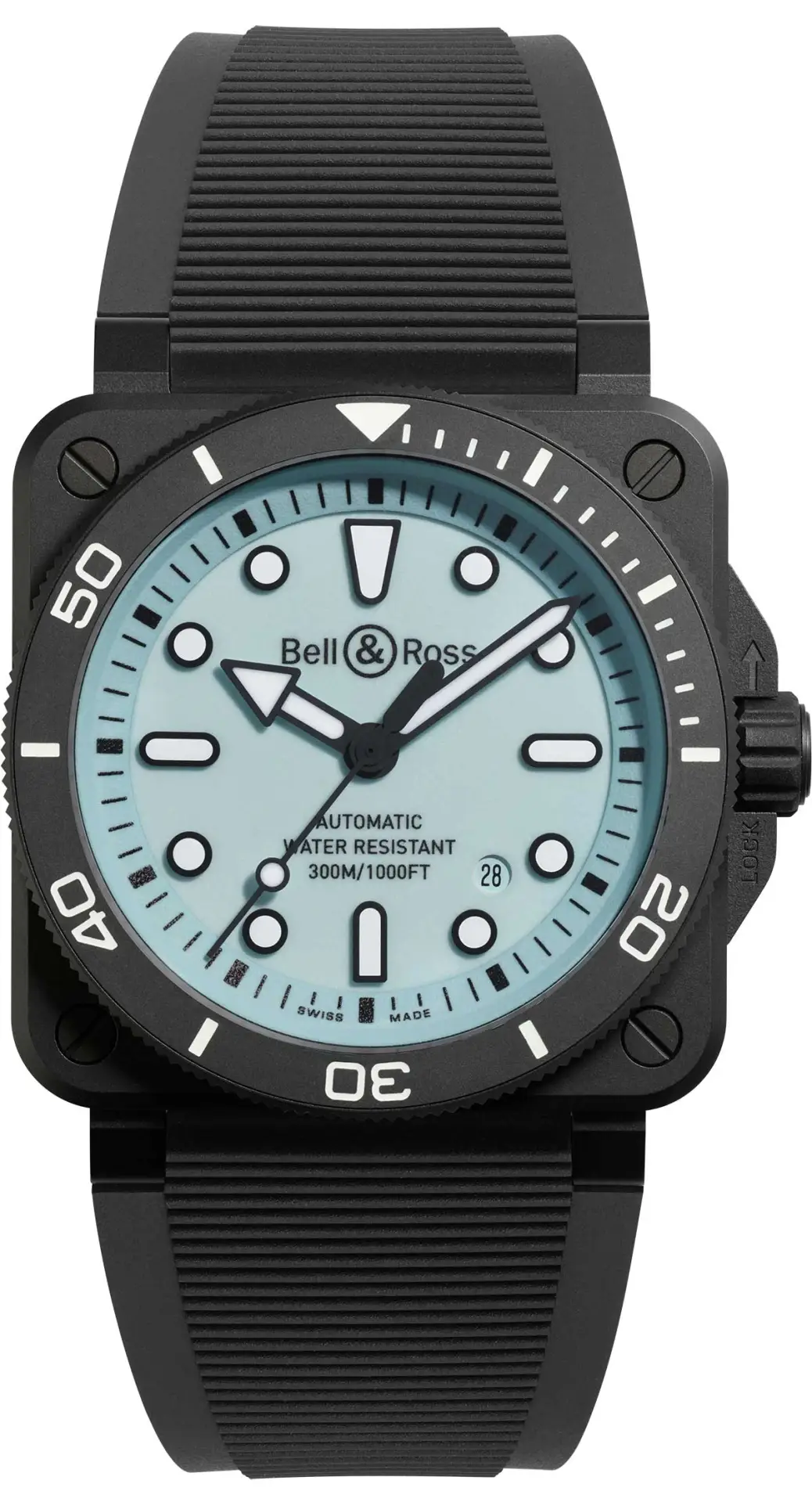

The BR03 Diver from Paris-based Bell & Ross celebrates its seventh anniversary this year. Recognised as the first square diving watch, the 2024 edition is new in more ways than one. Composed of five new models, including the full lume version with a pale blue dial shown here, the series is equipped with an improved automatic movement boasting 54 hours of power reserve, new typography, redesigned hands for optimal legibility and a new adaptable strap. $8,248
You may also like.
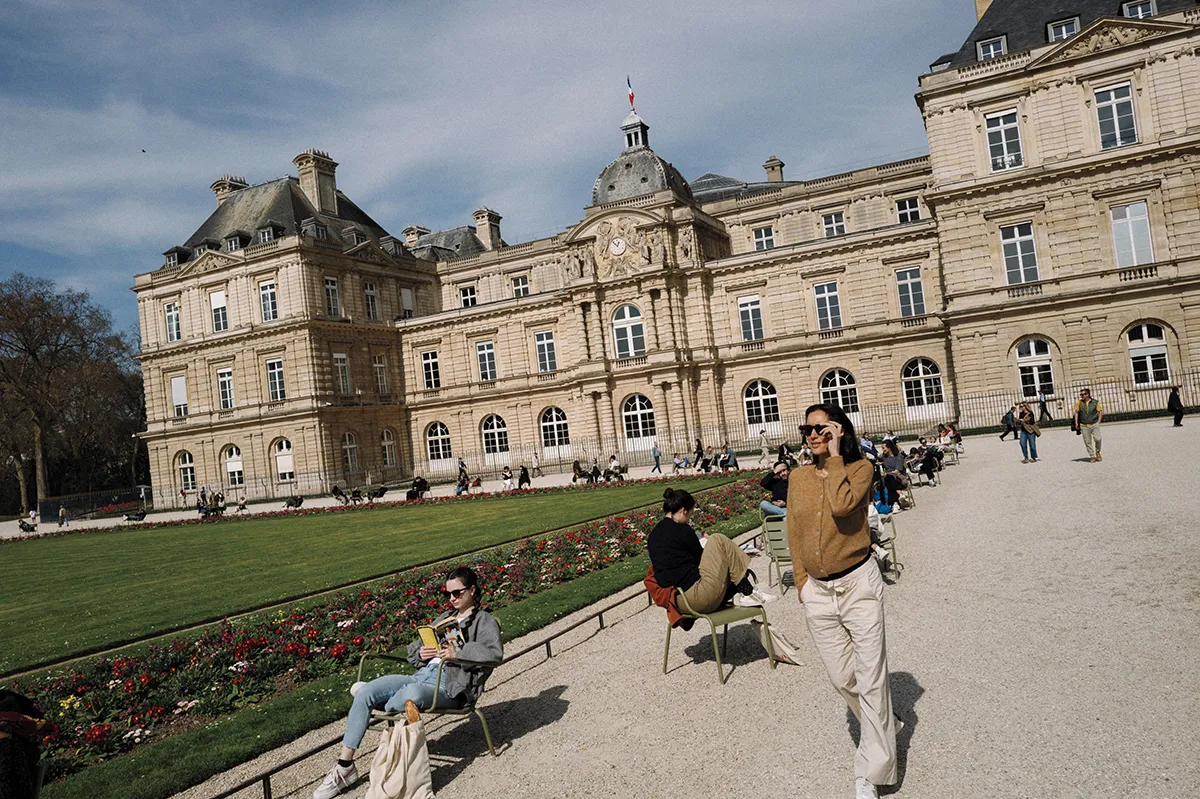
How Paris’s Dining, Hotel and Art Scene Got Their Groove Back — Just in Time for the Olympics
The French capital’s cultural life was already on the upswing. Mix in a major global sporting event, and it’s now ready to go toe to toe with any city in the world.
Host cities of modern-day Olympic Games have gotten into the competitive spirit by trying to stage the most spellbinding, over-the-top opening ceremony on record. Beijing enlisted 2008 drummers. London featured James Bond escorting Queen Elizabeth II. All Rio needed to wow the crowd was Gisele, who turned the stadium into her personal catwalk, strutting the length of the field solo. But only Paris could make the unprecedented gamble that the city itself is spectacular enough to be the star of the show.
If all goes according to plan when the Summer Olympics alight in Paris this July, the opening ceremony will play out like a Hollywood epic: timed to coincide with the sinking of the sun, an open-air flotilla of boats will ferry the athlete delegations on the Seine, sailing toward the sunset as hundreds of thousands of spectators cheer from either side of the river’s banks and the bridges above, all bathed in the amber afterglow.

Nico Therin
It will mark the first time the ceremony will be held outside a stadium, let alone on a waterway. So too many of the events themselves, instead of being mounted in mostly generic stadiums on the outskirts of the city, will take place in the heart of Paris, reframing the French capital in a way that locals and visitors alike have never experienced—and that’s sure to dial up the promise of pageantry and emotion.
The Eiffel Tower’s latticed silhouette will serve as the backdrop for beach volleyball at Champs de Mars. Place de la Concorde, where more than a thousand people (including Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette) had their heads lopped off during the French Revolution, will be the site of newly admitted Olympic sports such as skateboarding and breakdancing. And though Olympic swimmers have raced in pools since 1908, this year’s athletes are slated to compete in the river itself. (Competitions will also take place in cities across France, from Lyon to Marseille, and Tahiti in French Polynesia will host the surfing event.)
The specs are ambitious and inventive, and in some ways could restore the city’s reputation for audacity. Because while the City of Light may be known as the cradle of fashion, culture and gastronomy, not too long ago it was also regularly accused of slipping into a lazy, even smug, complacency—stuck in its ways, resting on the laurels of its storied past.
In the food world, those doldrums translated into controversial snubs from the influential World’s 50 Best Restaurants list, known for flushing out avant-garde chefs. The French Michelin Guide, once considered the ultimate arbiter of fine dining, suddenly seemed staid and irrelevant. London and Berlin took Europe’s centre stage in art and design. Even President Emmanuel Macron described his fellow countrymen as resistant to change, much to the ire of those fellow countrymen—and countrywomen.

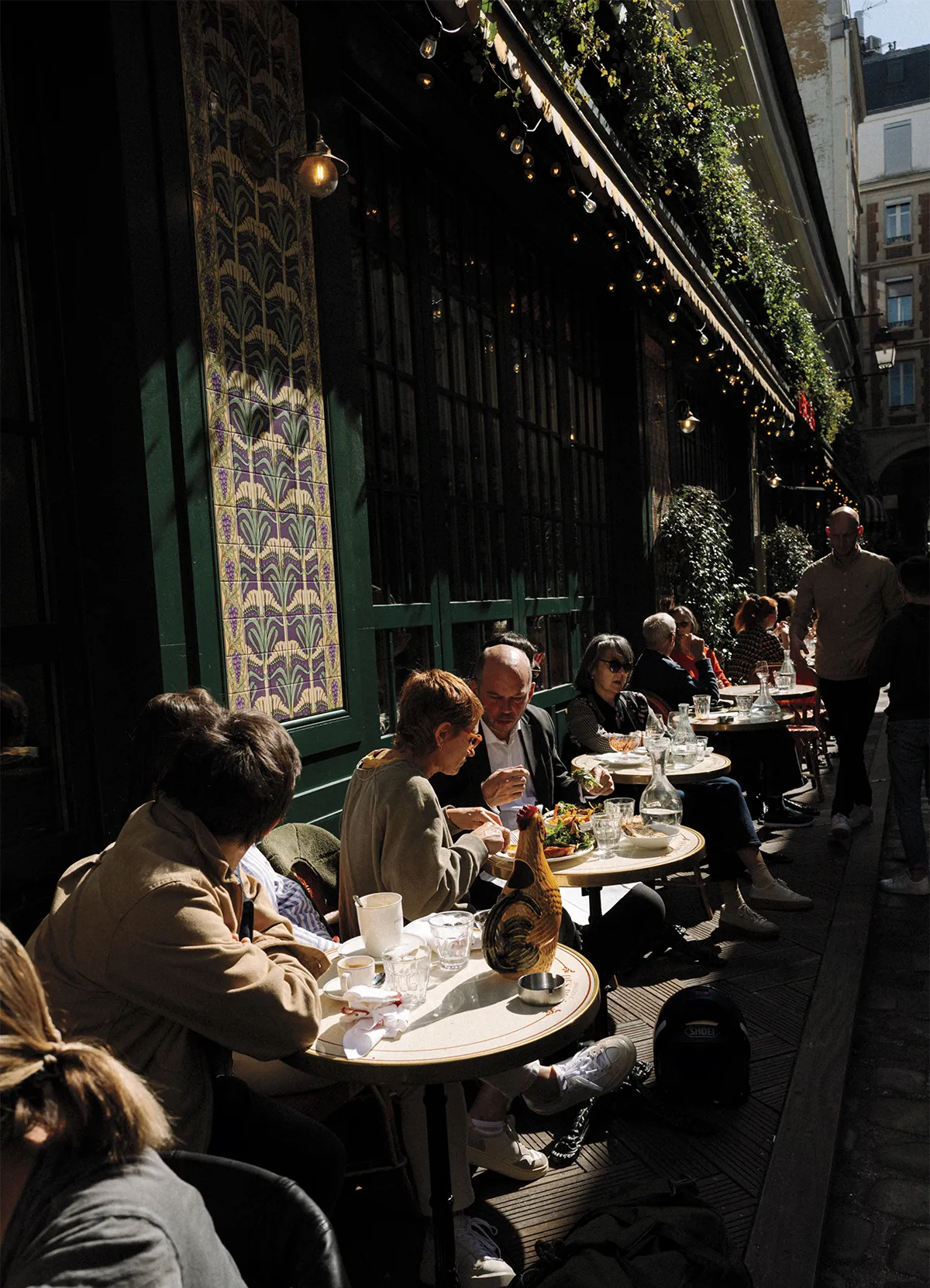
But influential creatives and Parisians say that in the years leading up to the Games, and particularly since the pandemic, something has shifted. “I really think that during the last 10 years, Paris opened itself to more new things, for different trends,” says Hélène Darroze, the acclaimed chef whose six restaurants include Michelin two-star Marsan in Paris and her three-star namesake at The Connaught in London. “Paris is happier than before, more joyful than before.”
There’s a giddy sense of anticipation, says the illustrator Marin Montagut, who has collaborated with Le Bon Marché and the Ritz Paris and owns an eponymous boutique in Saint-Germain-des-Prés where he sells hand-painted glassware and porcelain decor. “It feels like Paris is trying to look very, very pretty for a very important evening. She’s been getting some plastic surgery and is trying to get ready in time,” he says with a chuckle. “There’s just a lot of effervescence in the city.”

Nico Therin
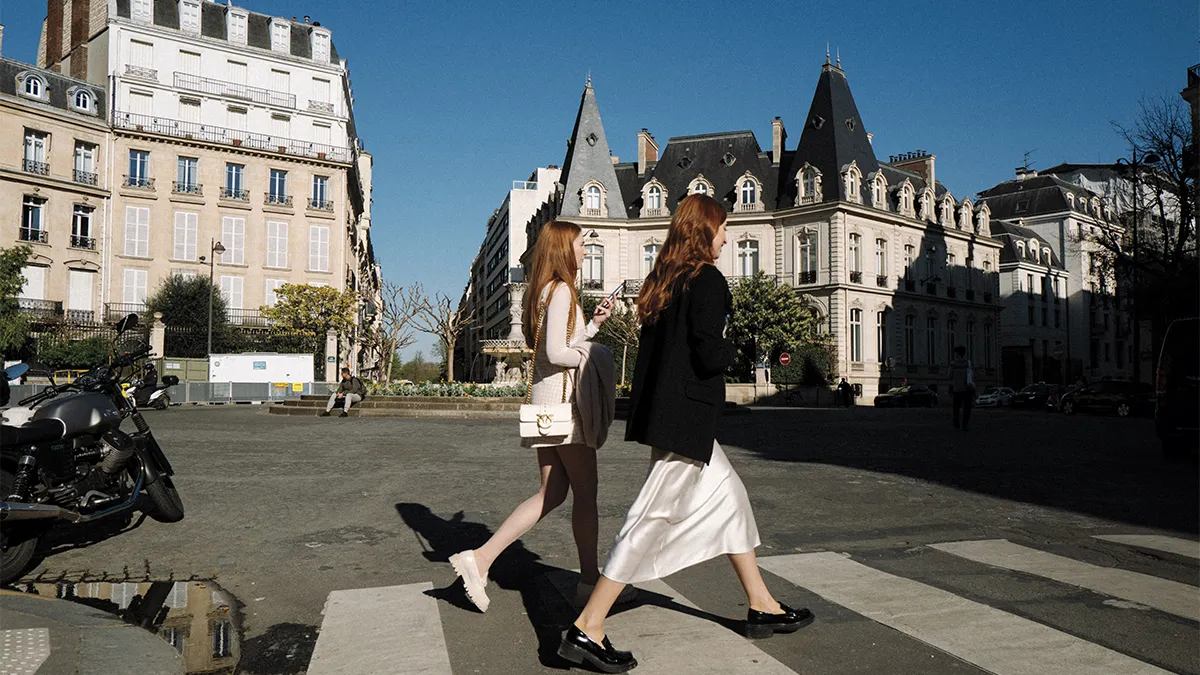
For better or for worse, some of the credit for that renewed vitality belongs to the light-as-soufflé Netflix series Emily in Paris, which quickly became the collective escapist fantasy for viewers around the world who were grounded by the Covid-19 virus. Another part of that newfound energy, though, can be traced to the frenzied building of luxury hotels, restaurants, galleries, museums and boutiques over the past few years, including Montagut’s own Paris-themed shop, which he opened in 2020.
In the past three years alone, 25 new five-star hotels debuted across the city, bringing the total to 101. Noteworthy newcomers include Madame Rêve, Kimpton St. Honoré Paris, Château des Fleurs, Maison Proust, LVMH’s Cheval Blanc Paris, and Chopard’s first boutique hotel here, 1 Place Vendôme. The dual autumn 2023 openings of Le Grand Mazarin and La Fantaisie hotels marked the Paris debut of Swedish designer Martin Brudnizki, whose playfully modern, maximalist and flamboyant aesthetic injected colour and character into Paris’s elite hotel scene.
In parallel with the growth of traditional hotels, new players in the luxury rental market are emerging, joining the likes of Le Collectionist and Belles Demeures. Founded in 2020, Highstay rents out luxury serviced apartments equipped with kitchens and living spaces. The firm’s current portfolio includes 36 apartments in areas such as the Champs-Élysées and Saint-Honoré, and another 48 are under construction—all of which it owns. There is no check-in (guests are sent digital access codes) and all concierge requests, including housekeeping and travel reservations, are made via live chat on a dedicated guest portal. “The goal is that guests get the real Parisian experience and feel like an insider, like a city dweller,” says general director Maxime Lallement.
The idea of making Paris as welcoming as a second home is also what drives the luxury real-estate market for foreign buyers, particularly Americans, says Alexander Kraft, CEO of Sotheby’s International Realty France-Monaco. He sees 2024 as a “transition year” and says that the local market is moving at two different speeds: while demand for properties between roughly $1.5 million and $8.5 million has cooled, high-end properties between about $17 million and $85 million continue to sell fast among buyers from the Middle East. Kraft predicts the market will pick up in 2025 following the US presidential election. “Paris is one of those real-estate markets that is eternally popular,” he says. “Contrary to other international cities, it really has broad appeal.”
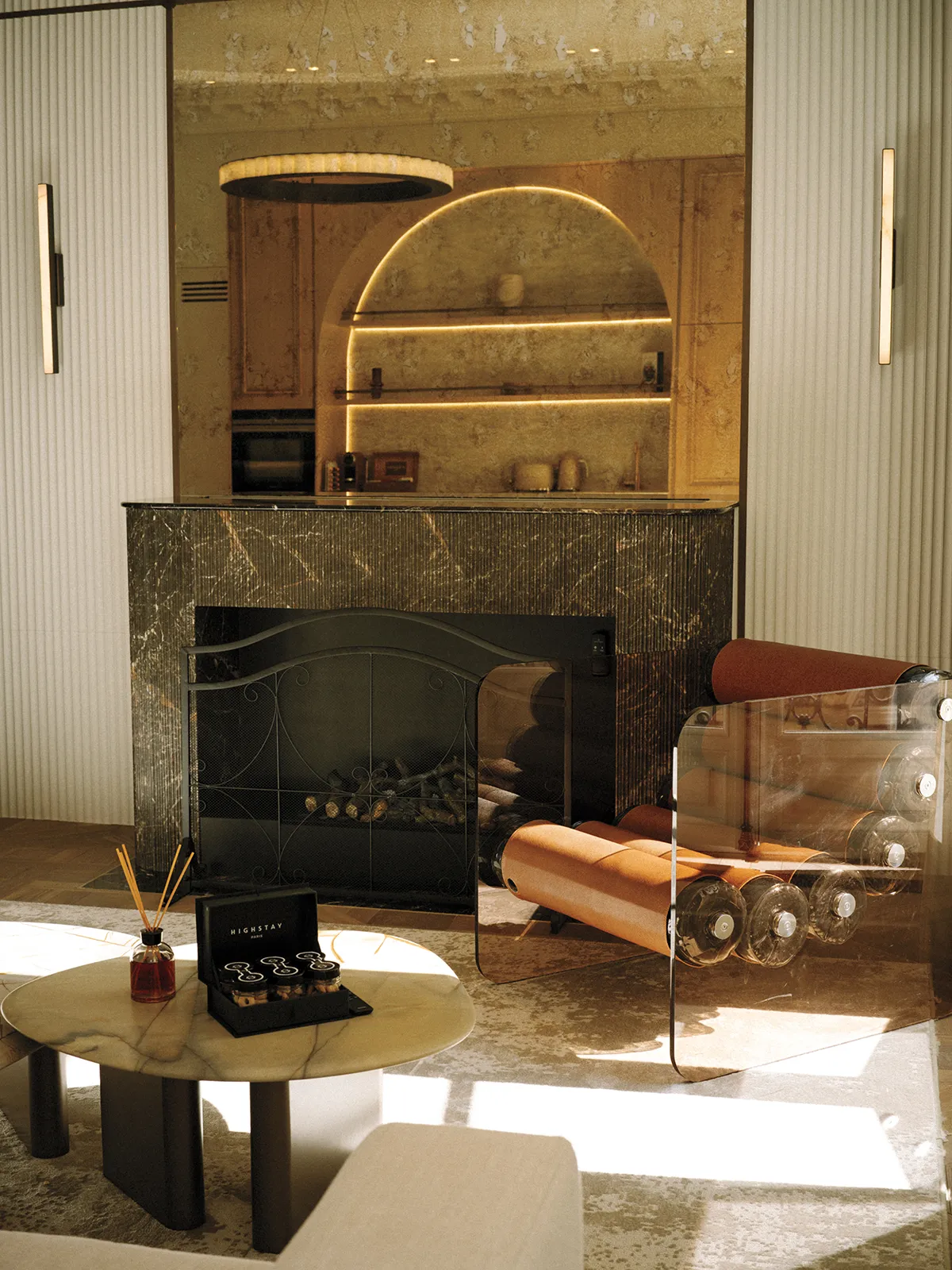

Nico Therin
Montreal-born, New York–based interior designer Garrow Kedigian is one of those frequent visitors who decided to take the leap and buy his own pied-à-terre in Paris a few years ago, after a lifetime of travelling back and forth for both work and pleasure.
As a part-time resident, Kedigian says he too has noticed a palpable shift in the city’s vibe, which he attributes to a renewed appreciation for tourists following their absence during the pandemic, as well as an “international flair” that has given the city a fresh spark. “There’s a lot more cultural diversity than there was before,” he says. “In that respect it’s a bit like New York. And I think that now the interface between Paris’s unique flavour and the international populace is a little bit smoother.”
For Montagut, one of the best examples of this synergy can be found in Belleville, in the city’s east end, where independent artists, musicians and other urban creatives rub shoulders in Chinese, African, and Arab restaurants and businesses. “There’s a social and cultural diversity here, and for me this is really important,” Montagut says. “If Paris was just the 6th arrondissement, it would be boring.”
The eastern edge of Paris is also one of the preferred neighbourhoods of Michael Schwartz, the marketing and communications manager for Europe at French jewellery house Boucheron. A recent New York City transplant, he is drawn to the burgeoning number of gastronomic gems far from the madding tourist crowds.
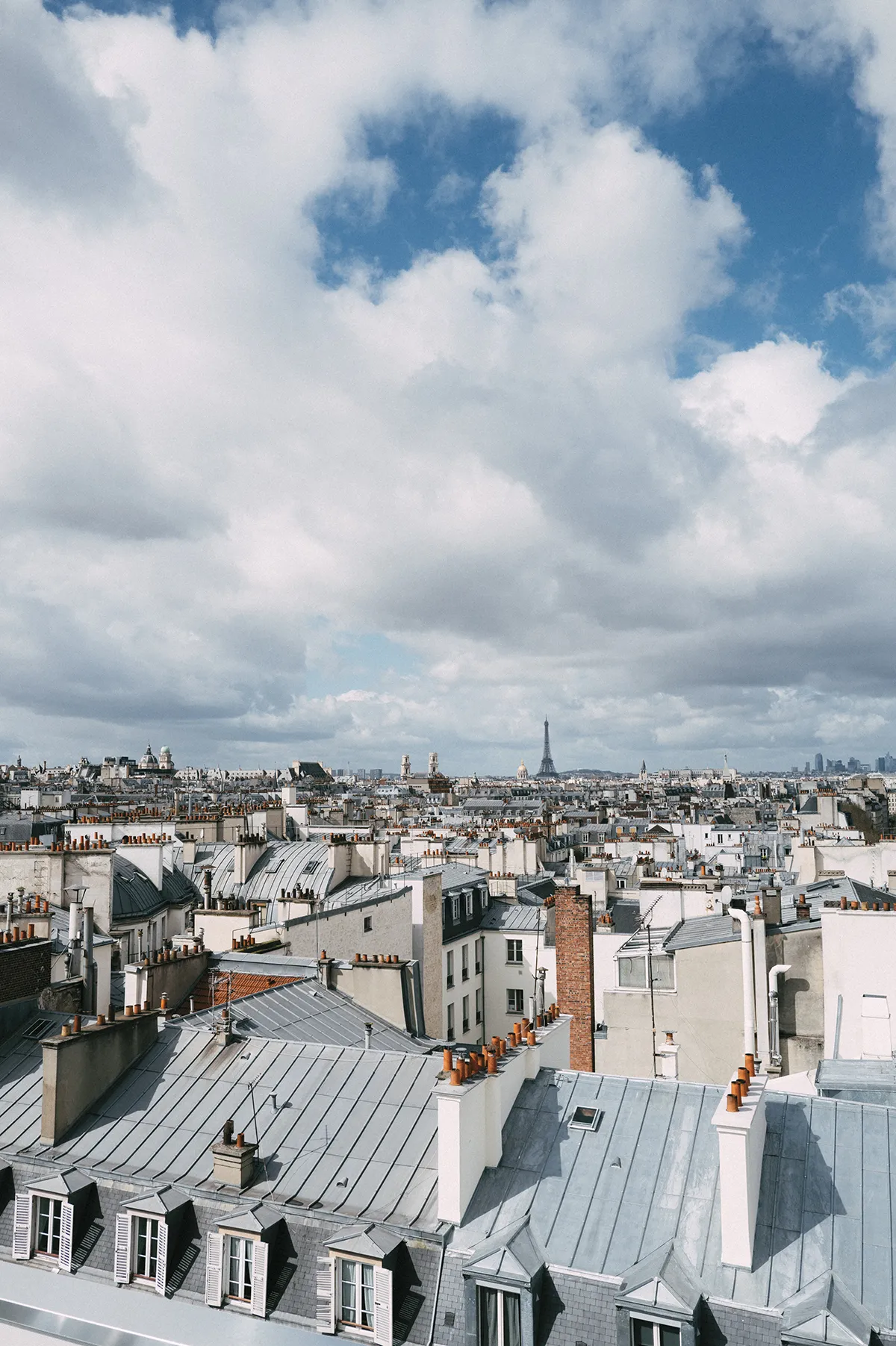

Nico Therin
He points to sister restaurants Caché and Amagat (the names mean “hidden” in French and Catalan, respectively), discreetly located at the end of a cobblestoned cul-de-sac, as favourites. With backgrounds in fashion and advertising, the Italian duo who run them have attracted equally fashionable locals to this hitherto quiet part of town. Caché serves up fresh Mediterranean seafood dishes, while next door, Amagat specialises in Catalan tapas.
Then there’s Soces, a corner seafood bistro on rue de la Villette, where you might find Jean-Benoît Dunckel, who co-wrote the score to Sofia Coppola’s film The Virgin Suicides when he was part of the electronic-music duo Air (Dunckel’s recording studio is in the area), or the French designers behind the Coperni fashion line, Sébastien Meyer and Arnaud Vaillant. “This is a really special restaurant,” says Schwartz. “It’s frequented by really cool creatives, designers and musicians, and it’s kind of a destination restaurant for most people because it’s not central.”
What makes Paris’s dining scene so exciting now, according to Stéphane Bréhier, editor in chief of French restaurant guide Gault& Millau, is a sense of fearlessness among younger chefs who reject the traditional trajectory that begins with a lowly stage in a Michelin-star kitchen. What’s more, visitors are likewise foregoing Michelin establishments in favour of newer, more experimental dining spots. “Over the last few years, there’s been a profusion of young chefs who don’t want to work for other people and are daring to set up their own shop,” Bréhier says. “The gastronomic scene is booming in Paris.”

Nico Therin
These bold, emerging chefs feel less bound not only to their elders but also to French cuisine itself. “It has changed a lot,” says Hélène Darroze, who opened Marsan, her first Parisian restaurant, 25 years ago. “The new generation travelled a lot—in South America, for example, in Asia—before opening a restaurant or being a head chef somewhere. They opened themselves to other cultures. This is why the culinary scene at the moment is very interesting in Paris; because it’s a mix of very famous chefs with Michelin stars but also young chefs who don’t care about Michelin stars—they just want to explore so many fields.”
The ever-growing importance of social media and its insatiable hunger for envy-inducing images is driving another major trend in the dining scene: rooftop spots, including Mun and Girafe in the Golden Triangle, the area bordered by avenues Montaigne and George V and the Champs-Élysées. “A lot of rooftops have opened in Paris, where before they were pretty much nonexistent apart from the Eiffel Tower and the Montparnasse Tower,” says Dimitri Ruiz, head concierge at Hôtel Barrière Fouquet’s Paris on the Champs-Élysées.
Five-star Right Bank hotels SO/ and Cheval Blanc Paris have watering holes that offer sweeping vistas of the Seine. But perhaps the most coveted perch during the opening ceremony will be the Champagne bar at La Tour d’Argent restaurant, which boasts unobstructed views of the Notre-Dame Cathedral and the Seine. (And yes, someone already had the idea to book it for a private event.) Famous for its signature pressed duck as well as for hosting monarchs and heads of state, the historic restaurant recently underwent a major renovation that included the addition of the aerie, which opened late last summer. “It’s only been in the last 10 years or so that Paris has been developing rooftops, and it’s really taking off like wildfire,” says third-generation owner André Terrail.
Paris’s venerated fashion industry has also found ways to innovate, with fresh faces keeping their fellow couturiers on their toes and the shopping options enticing. In 2022, for example, Simon Porte Jacquemus opened his first boutique in the city on avenue Montaigne—home to Gucci, Chanel, and Prada, among other venerable names—and in March, at the age of 34, became France’s youngest fashion designer to be named a Chevalier de l’Ordre des Arts et des Lettres for his contributions to the field. That kind of success has a ripple effect in the creative community.
“Almost every street has the name of an artist or a politician,” says Charaf Tajer, the Parisian-born creative director behind the London-based Casablanca sportswear line. “So the city reminds me always that the people who came before me, who walked those streets, created the future in a way. As much as [Paris] seems stuck in time visually, you can also feel the energy of people creating the present.”
Interior designer David Jimenez, whose 2022 book Parisian by Design compiles his Francophile projects, moved to the city in 2015 and spent his first few years living near the Champs-Élysées, which he says has undergone a noticeable revival. Along with Jacquemus’s arrival, new luxury openings or expansions—including Burberry, Saint Laurent, Bottega Veneta, and Panerai—and city-led greening efforts are bringing Parisians back to the 8th arrondissement, long dismissed as an overcrowded tourist trap where fast-food and fast-fashion chains had colonised the once glamorously luxe avenue. Now, Dior’s captivating Peter Marino–designed museum draws legions of fans, while the city has been busy planting more trees, renovating gardens and repairing damaged sidewalks as part of a long-term embellishment plan. And on the first Sunday of every month, the entire length of the Champs-Élysées becomes a pedestrian-only promenade. “It’s an exciting evolution in a part of the city that seemed sleepy and perhaps lost its way a little bit,” Jimenez says. “Now there’s a thrust forward.”

Nico Therin
The thriving fashion houses are responsible for more than maintaining the city’s unparalleled reputation for chic. To a large degree, they have also helped revive its status as an art capital. The billions generated by LVMH (parent of Louis Vuitton, Dior and Berluti, among others) and Kering (Alexander McQueen, Gucci, Bottega Veneta, et al.) funded the extraordinary contemporary art collections amassed by their founders, Bernard Arnault and François Pinault, respectively. The rivals rewarded their hometown with two museums, Fondation Louis Vuitton and Bourse de Commerce, that have helped make it a leader in contemporary art.
Also lending a hand: Brexit, which persuaded many international galleries to brush up on their French. One of the most talked-about recent additions is the powerhouse Hauser & Wirth, which opened in a 19th-century hôtel particulier near the Champs-Élysées last year. David Zwirner arrived in 2019, Mariane Ibrahim in 2021, and Peter Kilchmann the following year, all joining long-established Parisian galleries including Perrotin and Thaddaeus Ropac. The City of Light even snagged its own coveted annual installment of Art Basel: Paris+, which now runs every October in the Grand Palais.
“Quite frankly, Paris has been putting up some of the most incredible exhibitions in institutions in Europe,” says Serena Cattaneo Adorno, senior director at Gagosian. “And a lot of private collectors have also decided to open spaces in the city, creating a great dynamic between public and private galleries.”

The always-savvy Gagosian, on rue Ponthieu, has hit upon an authentic tie-in with the Games: a summer exhibition featuring Olympic posters created over the years by celebrated artists from Picasso on up to Warhol, Hockney and Tracey Emin. “Once you start digging, you find that a lot of artists have reflected on sports and the engagement of the body,” Cattaneo Adorno says. “It’s just a really pure and beautiful message about how art and sports have dialogues that can be somewhat surprising.”
A few months out from the festivities on the Seine, interior decorator Jimenez sums up the mood of many locals, saying (only half-jokingly), “I think for most Parisians, there’s a sense of curiosity, optimism, excitement—and an exit plan, in that order.”
While polling shows that nearly half of Parisians intend to vacate the city during the games, Jimenez notes that he will be watching the opening ceremony with friends who live in an apartment overlooking the Seine. “I want to be part of the excitement. I want to see as much as I can and be energised by this very special and unique moment,” he says. “It’s a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity, and I am deeply grateful to be able to experience it first-hand as an American living in Paris.”
Additional reporting by Lucy Alexander and Justin Fenner.
You may also like.
Watches & Wonders 2024 Showcase: Hermès
We head to Geneva for the Watches & Wonders exhibition; a week-long horological blockbuster featuring the hottest new drops, and no shortage of hype.
With Watches & Wonders 2024 well and truly behind us, we review some of the novelties Hermès presented at this year’s event.
—
HERMÈS
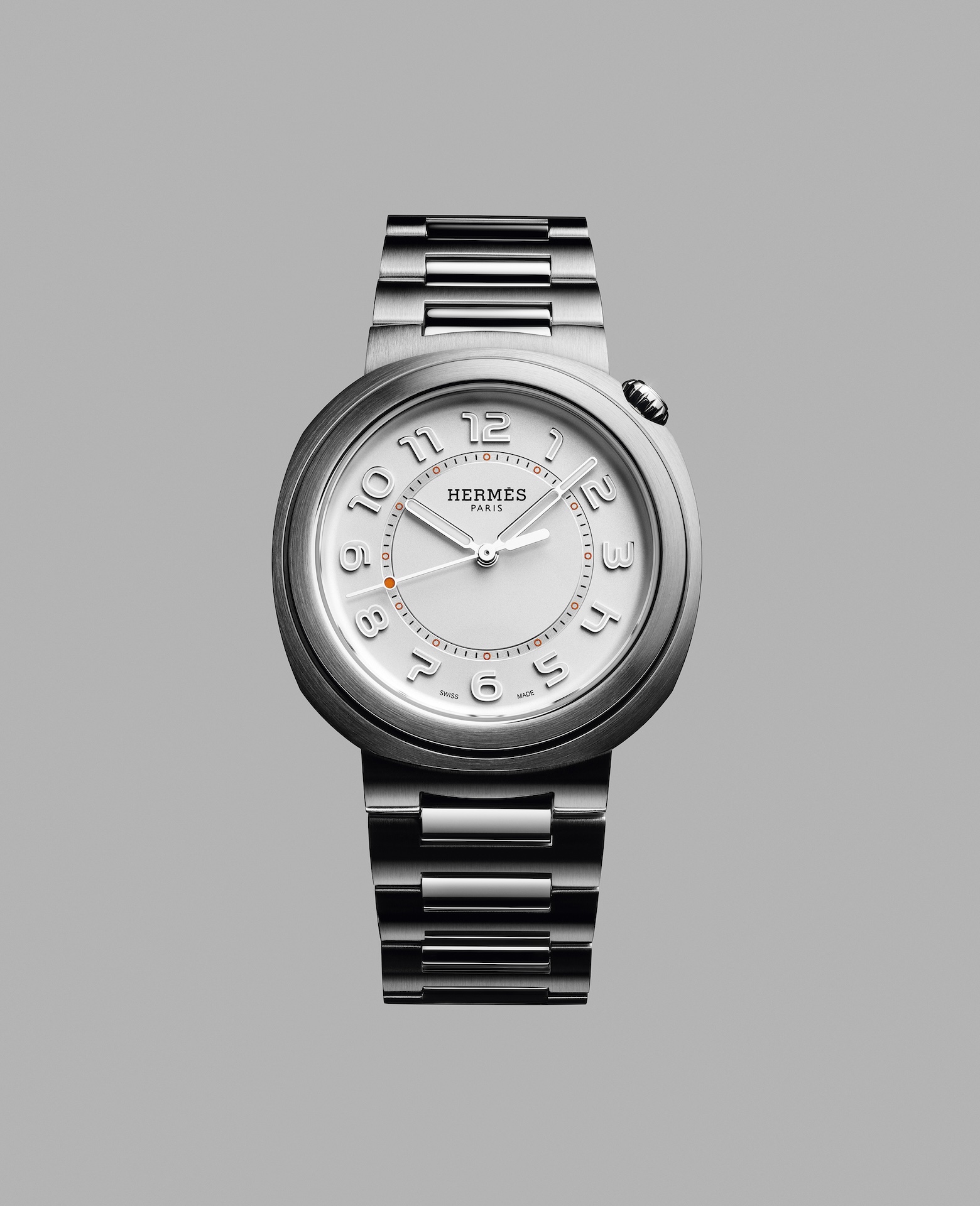

Moving away from the block colours and sporty aesthetic that has defined Hermès watches in recent years, the biggest news from the French luxury goods company at Watches & Wonders came with the unveiling of its newest collection, the Hermès Cut.
It flaunts a round bezel, but the case middle is nearer to a tonneau shape—a relatively simple design that, despite attracting flak from some watch aficionados, works. While marketed as a “women’s watch”, the Cut has universal appeal thanks to its elegant package and proportions. It moves away from the Maison’s penchant for a style-first product; it’s a watch that tells the time, not a fashion accessory with the ability to tell the time.
Hermès gets the proportions just right thanks to a satin-brushed and polished 36 mm case, PVD-treated Arabic numerals, and clean-cut edges that further accentuate its character. One of the key design elements is the positioning of the crown, boldly sitting at half-past one and embellished with a lacquered or engraved “H”, clearly stamping its originality. The watch is powered by a Hermès Manufacture movement H1912, revealed through its sapphire crystal caseback. In addition to its seamlessly integrated and easy-wearing metal bracelet, the Cut also comes with the option for a range of coloured rubber straps. Together with its clever interchangeable system, it’s a cinch to swap out its look.
It will be interesting to see how the Hermès Cut fares in coming months, particularly as it tries to establish its own identity separate from the more aggressive, but widely popular, Ho8 collection. Either way, the company is now a serious part of the dialogue around the concept of time.
—
Read more about this year’s Watches & Wonders exhibition at robbreport.com.au
You may also like.
Watch This Space: Mike Nouveau
Meet the game-changing horological influencers blazing a trail across social media—and doing things their own way.
In the thriving world of luxury watches, few people own a space that offers unfiltered digital amplification. And that’s precisely what makes the likes of Brynn Wallner, Teddy Baldassarre, Mike Nouveau and Justin Hast so compelling.
These thought-provoking digital crusaders are now paving the way for the story of watches to be told, and shown, in a new light. Speaking to thousands of followers on the daily—mainly via TikTok, Instagram and YouTube—these progressive commentators represent the new guard of watch pundits. And they’re swaying the opinions, and dollars, of the up-and-coming generations who now represent the target consumer of this booming sector.
—
MIKE NOUVEAU
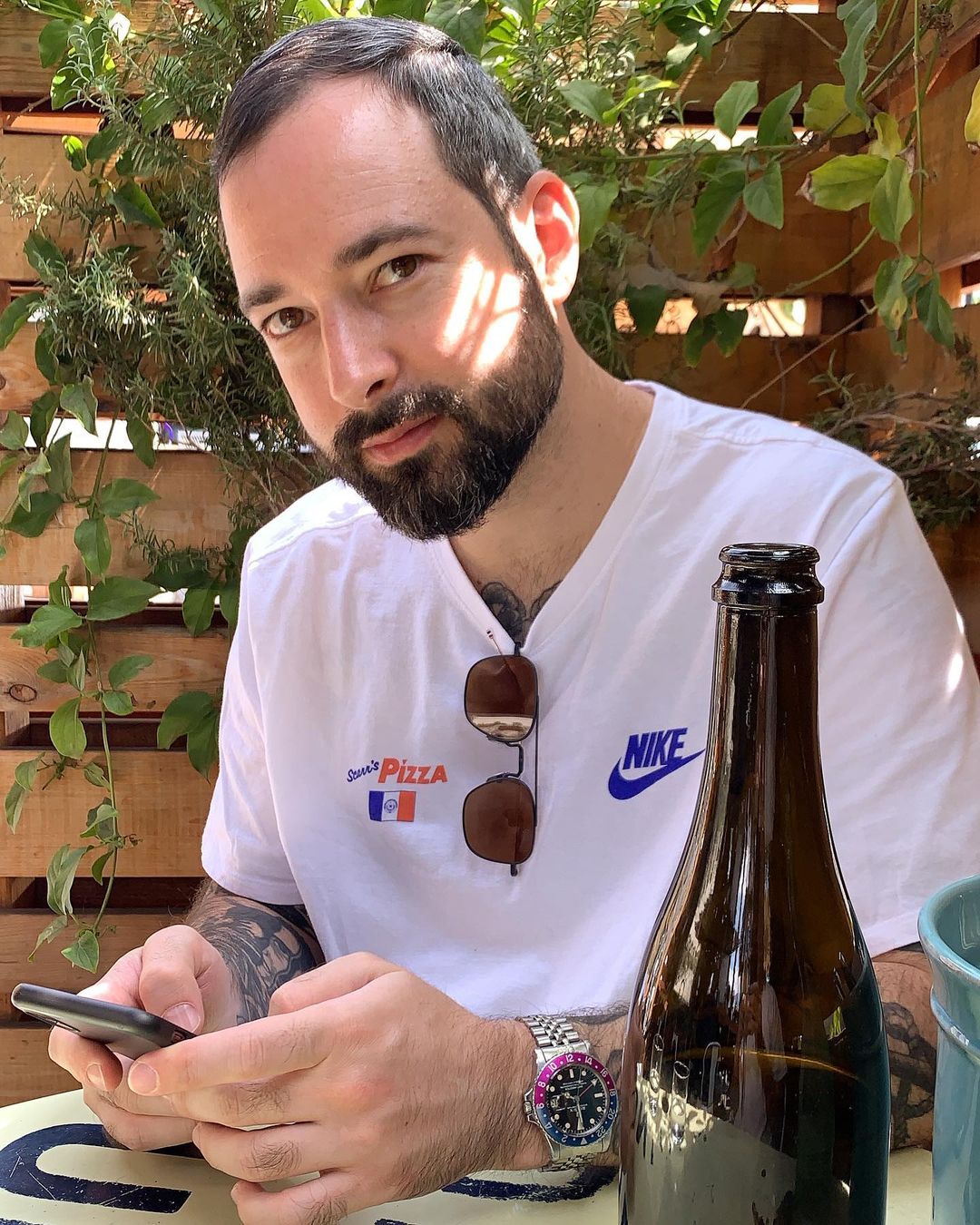

Can we please see what’s on the wrist? That’s the question that catapulted Mike Nouveau into watch stardom, thanks to his penchant for highlighting incredibly rare timepieces across his TikTok account of more than 400,000 followers. When viewing Nouveau’s attention-grabbing video clips—usually shot in a New York City neighbourhood—it’s not uncommon to find him wrist-rolling some of the world’s rarest timepieces, like the million-dollar Cartier Cheich (a clip he posted in May).
But how did someone without any previous watch experience come to amass such a cult following, and in the process gain access to some of the world’s most coveted timepieces? Nouveau admits had been a collector for many years, but moved didn’t move into horology full-time until 2020, when he swapped his DJing career for one as a vintage watch specialist.
“I probably researched for a year before I even bought my first watch,” says Nouveau, alluding to his Rolex GMT Master “Pepsi” ref. 1675 from 1967, a lionised timepiece in the vintage cosmos. “I would see deals arise that I knew were very good, but they weren’t necessarily watches that I wanted to buy myself. I eventually started buying and selling, flipping just for fun because I knew how to spot a good deal.”
Nouveau claims that before launching his TikTok account in the wake of Covid-19, no one in the watch community knew he existed. “There really wasn’t much watch content, if any, on TikTok before I started posting, especially talking about vintage watches. There’s still not that many voices for vintage watches, period,” says Nouveau. “It just so happens that my audience probably skews younger, and I’d say there are just as many young people interested in vintage watches as there are in modern watches.”
View this post on Instagram
Nouveau recently posted a video to his TikTok account revealing that the average price of a watch purchased by Gen Z is now almost US$11,000 (around $16,500), with 41 percent of them coming into possession of a luxury watch in the past 12 months.
“Do as much independent research as you can [when buying],” he advises. “The more you do, the more informed you are and the less likely you are to make a mistake. And don’t bring modern watch expectations to the vintage world because it’s very different. People say, ‘buy the dealer’, but I don’t do that. I trust myself and myself only.”
—
Read more about the influencers shaking up horology here with Justin Hast, Brynn Wallner and Teddy Baldassare.
You may also like.
5 Lounge Chairs That Add Chic Seating to Your Space
Daybeds, the most relaxed of seating solutions, offer a surprising amount of utility.
Chaise longue, daybed, recamier, duchesse brisée—elongated furniture designed for relaxing has a roster of fancy names. While the French royal court of Louis XIV brought such pieces to prominence in fashionable European homes, the general idea has been around far longer: The Egyptian pharaohs were big fans, while daybeds from China’s Ming dynasty spurred all those Hollywood Regency fretwork pieces that still populate Palm Beach living rooms. Even Mies van der Rohe, one of design’s modernist icons, got into the lounge game with his Barcelona couch, a study of line and form that holds up today.
But don’t get caught up in who invented them, or what to call them. Instead, consider their versatility: Backless models are ideal in front of large expanses of glass (imagine lazing on one with an ocean view) or at the foot of a bed, while more structured pieces can transform any corner into a cozy reading nook. Daybeds may be inextricably linked to relaxation, but from a design perspective, they put in serious work.
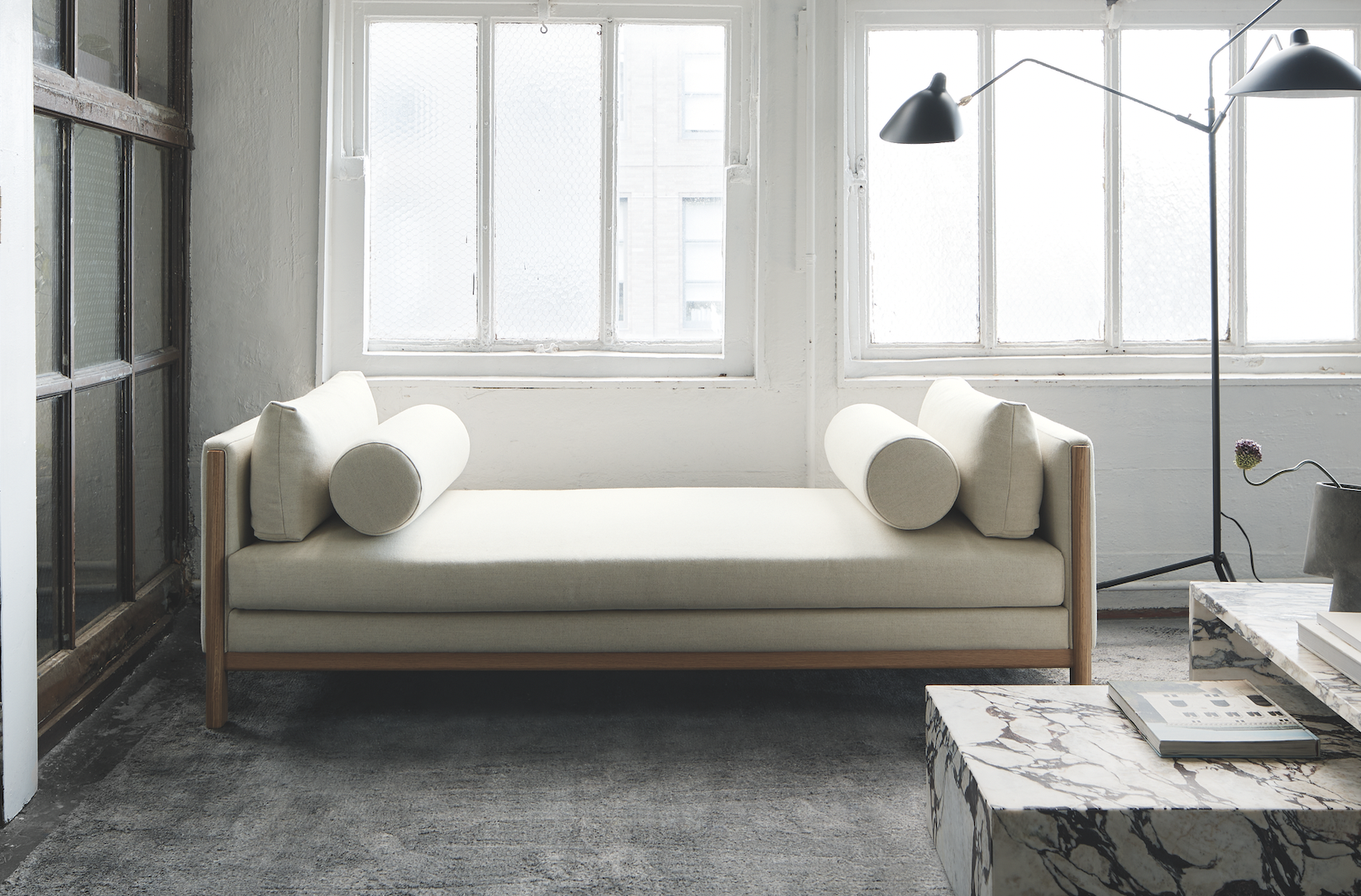

Emmy, Egg Collective
In designing the Emmy chaise, the Egg Collective trio of Stephanie Beamer, Crystal Ellis and Hillary Petrie, who met as students at Washington University in St. Louis, aimed for versatility. Indeed, the tailored chaise looks equally at home in a glass skyscraper as it does in a turn-of-the-century town house. Combining the elegance of a smooth, solid oak or walnut frame with the comfort of bolsters and cushioned upholstery or leather, it works just as well against a wall or at the heart of a room. From around $7,015; Eggcollective.com
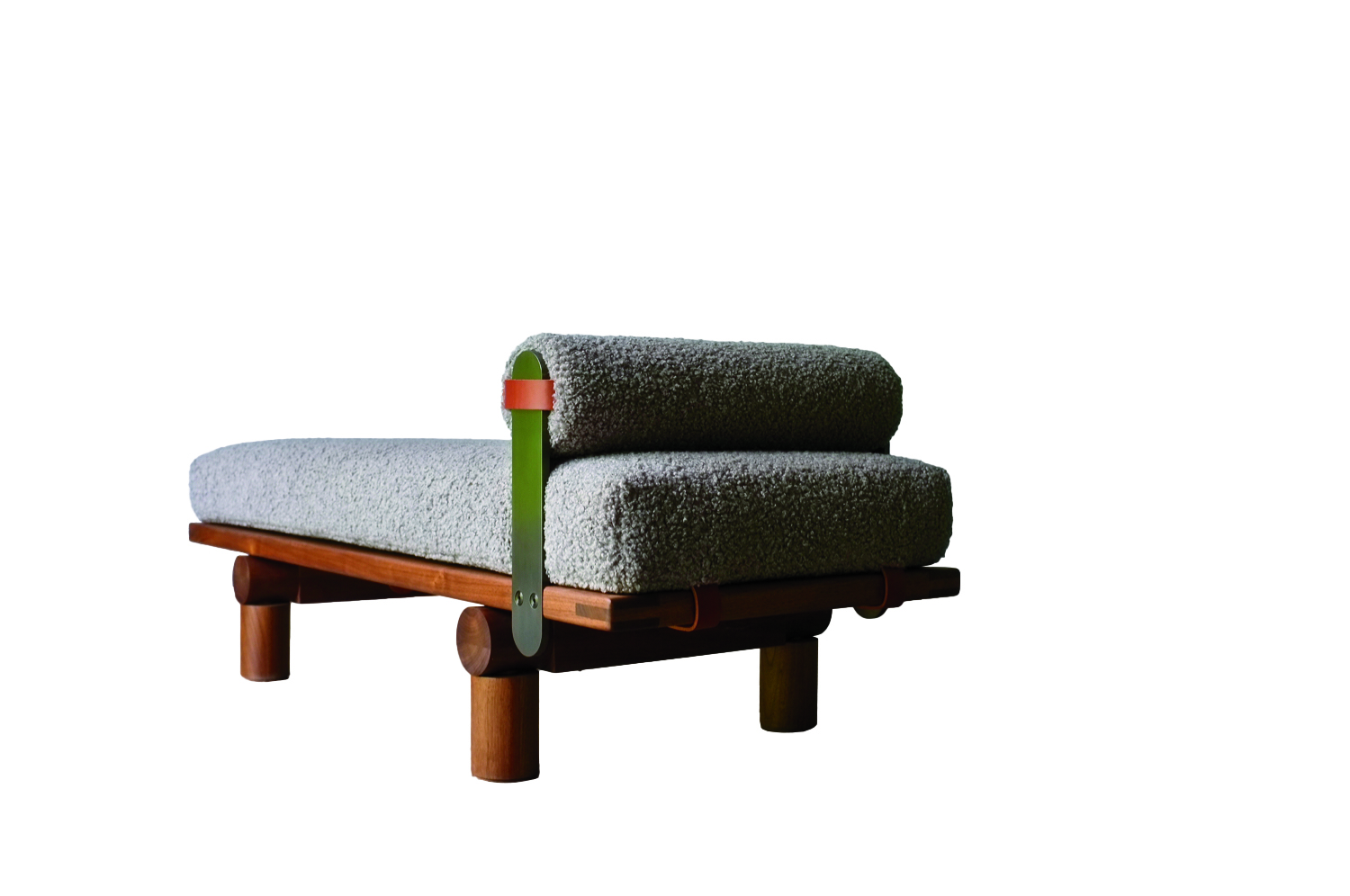 Plum, Michael Robbins
Plum, Michael Robbins
Woodworker Michael Robbins is the quintessential artisan from New York State’s Hudson Valley in that both his materials and methods pay homage to the area. In fact, he describes his style as “honest, playful, elegant and reflective of the aesthetic of the Hudson Valley surroundings”. Robbins crafts his furniture by hand but allows the wood he uses to help guide the look of a piece. (The studio offers eight standard finishes.) The Plum daybed, brought to life at Robbins’s workshop, exhibits his signature modern rusticity injected with a hint of whimsy thanks to the simplicity of its geometric forms. Around $4,275; MichaelRobbins.com
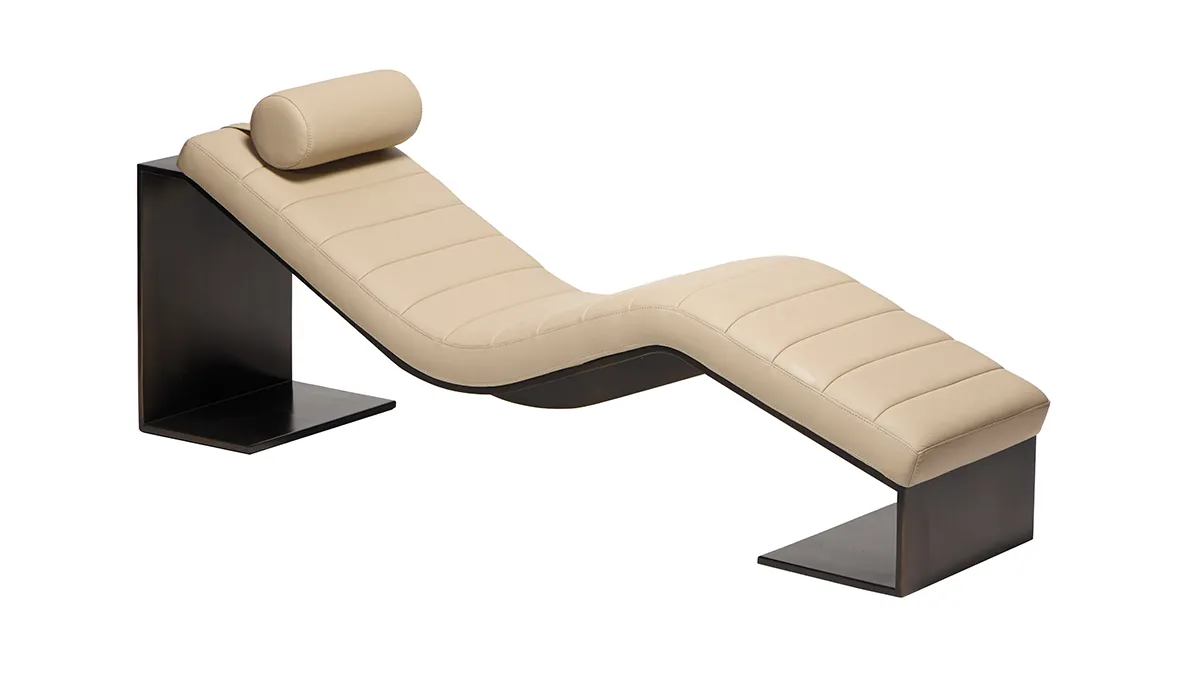

Kimani, Reda Amalou Design
French architect and designer Reda Amalou acknowledges the challenge of creating standout seating given the number of iconic 20th-century examples already in existence. Still, he persists—and prevails. The Kimani, a bent slash of a daybed in a limited edition of eight pieces, makes a forceful statement. Its leather cushion features a rolled headrest and rhythmic channel stitching reminiscent of that found on the seats of ’70s cars; visually, these elements anchor the slender silhouette atop a patinated bronze base with a sure-handed single line. The result: a seamless contour for the body. Around $33,530; RedaAmalou
Dune, Workshop/APD
From a firm known for crafting subtle but luxurious architecture and interiors, Workshop/APD’s debut furniture collection is on point. Among its offerings is the leather-wrapped Dune daybed. With classical and Art Deco influences, its cylindrical bolsters are a tactile celebration, and the peek of the curved satin-brass base makes for a sensual surprise. Associate principal Andrew Kline notes that the daybed adeptly bridges two seating areas in a roomy living space or can sit, bench-style, at the foot of a bed. From $13,040; Workshop/ APD
Sherazade, Edra
Designed by Francesco Binfaré, this sculptural, minimalist daybed—inspired by the rugs used by Eastern civilizations—allows for complete relaxation. Strength combined with comfort is the name of the game here. The Sherazade’s structure is made from light but sturdy honeycomb wood, while next-gen Gellyfoam and synthetic wadding aid repose. True to Edra’s amorphous design codes, it can switch configurations depending on the user’s mood or needs; for example, the accompanying extra pillows—one rectangular and one cylinder shaped— interchange to become armrests or backrests. From $32,900; Edra
















