Robb Read: Inside The World Of Bespoke Watchmaking
Why elite collectors often see elements of their supposed one-of-one on someone else’s wrist?
Related articles
“I made the mistake, no one else,” says former Hollywood power agent Michael Ovitz of the several dozen custom watches he commissioned from Patek Philippe about six or seven years ago. It was the first time Ovitz, who has been collecting for 35 years, placed a bespoke order, but his goal was ambitious: He requested several different references, each in a variety of metals, with one-of-a-kind dials. “They were terrific,” he says of Patek, “and accommodated everything I wanted.”
His regret is not foreseeing two problems. The first was misunderstanding his own psychology: Too afraid he’d bang up his special treasures by wearing them, he never even took some of them out of the packaging. In hindsight, he says he would stick to one version of each reference. “My second mistake was that I didn’t ask them for an exclusive on the design,” says Ovitz. “So I saw a lot of [Patek] watches showing up with my design, and I didn’t want that. I wanted unique pieces.” (Patek Philippe declined comment, citing clients’ privacy.)
Navigating the pitfalls of the world of bespoke watchmaking can be tricky, even for experienced collectors like Ovitz, who also has a major trove of modern and contemporary art. Commissioning can lead to the ultimate in bragging rights—influence over a genius creator’s oeuvre and legacy—or total dejection. Nearly every luxury firm is capable of taking customisation to the next level for those willing to spend whatever is required, which can run to millions, but when the client’s and the brand’s expectations are not aligned, the project can backfire.

Michael Ovtiz’s custom Patek Philippe Ref. 5004J-027 in yellow gold. Courtesy of Phillips
Ovitz’s response has been to part company with some of the Pateks, recognisable for his “MSO” initials discreetly placed at six o’clock. Several have quietly popped up on the market, both privately and publicly, through notable auction houses. In 2018, his 36mm Ref. 5004J, in 18-carat yellow gold with a perpetual calendar and split-seconds chronograph, fetched about $484,000 at Phillips’s Hong Kong Watch Auction: Seven. A Ref. 3940 in 18-carat rose gold with perpetual calendar and a Ref. 5059 in 18-carat yellow gold with retrograde perpetual calendar were sold through European Watch Company for undisclosed amounts. But despite the less-than-ideal outcome with his initial foray into bespoke, Ovitz says he has not soured on the concept. Asked if he’d try again, he replies, “Yes, but one-offs that I co-design and that are not duplicated.”
That can be easier said than done. Across the industry, this type of project requires not only a significant investment, with a hefty deposit paid upfront—it’s expensive to develop a new complication or rearrange elements on a dial—but also a certain level of blind trust in the watchmaker’s word. In some cases, collectors report having agreed to allow a company to create an ultra-limited handful of slightly tweaked versions of their originals but still ending up feeling burned.

Voutilainen Observatoire with a Peseux 260 movement inspired by a custom creation for a New York client. Voutilainen
One New York collector, who spoke on the condition of anonymity, recounts how he felt betrayed when a watchmaker began producing more and more pieces with his concept. They had entered into a loose agreement allowing for four additional versions to sell to other clients, which later grew by several and eventually resulted in an ongoing series. “At first, I thought it didn’t matter if he increased the production a little bit, because I got the watch that I wanted,” he says. “But the thing is, it was a little bit like pulling teeth to try to get him to do this thing, and ultimately, it put him on the map, and then he just started cranking them out. I was kind of bummed.” The collector was so disenchanted with his experience that he ended up selling it. The approx. $97,000 price was almost double what he had initially paid, but the piece was the first and last one he bought from that particular maker.
Not every collector minds seeing their ideas on other people’s wrists. The relationship between brand and client can be mutually beneficial. Occasionally, a bespoke commission is so inventive that it wields influence over the brand’s repertoire for years to come. That collector can serve as muse and visionary, investor, guinea pig and sounding board.

An Audemars Piguet VIP client recently requested a prominent minute-repeater slide on his Royal Oak Grande Complication, similar to this one. Diode SA – Denis Hayoun
Take, for instance, Bovet’s Récital timepiece (top image), an ultra-high-complication design that has received multiple accolades, including several Grand Prix d’Horlogerie de Gèneve awards (the GPHG, the highest honour in watchmaking). Its origins date to 2006, when one of the brand’s biggest collectors came to owner Pascal Raffy asking for a tourbillon timepiece that featured a hefty seven days of power reserve along with a crown positioned at three o’clock in a pure and simple design. “He asked me, ‘How do you imagine the dial?’” says Raffy. “I said, ‘The tourbillon is the tank of the timepiece. It is the power, the energy, the generosity. Extending from its cage, let’s design a beautiful and simple blackened Côtes de Gèneve finishing.’” Together, they gave birth to the first Récital in 2007.
The collector was so pleased with the outcome that he suggested Bovet do other iterations, according to Raffy. The prototype was then presented to select retail partners and VIPs. “We were happy if we could sell a few of them,” says Raffy. “It would be a gift [to us] from the collector. That week, 50 models were sold.” The piece has spawned 22 editions to date and has become one of Bovet’s most recognisable designs.

Watchmaker François-Paul Journe in his atelier. F. P. Journe
Collaborations such as these have sometimes been so crucial they have lifted a watchmaker out of relative obscurity. When Kari Voutilainen ventured out on his own after honing his craft behind the bench under master watchmaker Michel Parmigiani at Parmigiani Fleurier, a single client’s wish propelled him into the spotlight. Before he began making his own movements, a client came to him wanting an old Peseux 260 calibre—an observatory-competition movement used by brands for entries in chronometry competitions—in a time-only watch with straight lugs.
It took a year of negotiating and waiting to source the movement before it was delivered as a unique piece. The collector then brought it to the Besançon Observatory in Besançon, France, to be officially tested and certified as an observatory chronometer. The test goes a step further than the standard COSC certification, widely used in the industry, in that it inspects the entire watch for high-level accuracy rather than just the interior movement. The unusual piece went on to spawn not only a newly established Besançon Observatory chronometer certification but also Voutilainen’s coveted Observatoire series, which now encompasses 50 iterations of the original.

The F. P. Journe Centigraphe was the result of a request from a VIP customer who wanted an exceptional chronograph with three hands. F. P. Journe
The Observatoire is not a singular story at Voutilainen’s workshop; other client requests have spawned series. “It has happened many, many times,” says the watchmaker. “One customer wanted to have a GMT but something a little unusual. He said, ‘Make me a watch where the whole dial is turning at six o’clock. That will be cool because it is like it’s living and changing its face all the time.’” So Voutilainen set about redesigning the second time zone to be replaced with a rotating disc integrated into the small seconds, with an arrow to read the GMT time. After the client shared photos on a watch forum, Voutilainen was inundated with requests. “That was purely the idea of our customer, and actually, I myself didn’t even believe that it could be so successful,” says Voutilainen, who has since produced 25 GMTs with the same function. As for the man who came up with the idea in the first place, he adds, “it wasn’t an issue for the customer at all. He has a unique piece with an engraved dial.”
Duplication is not the only drawback of bespoke commissions that serve as research and development for small independent brands. Allen, a San Francisco collector who spoke on the condition of not using his surname, says that sometimes the complex new technology simply doesn’t work. “We’re basically the beta testers,” he explains. “These are not big manufacturers that are able to do all sorts of testing to make sure they are running smoothly before they deliver them. If there’s a problem, we have to send it back.”

London-based collector Michael Hickcox (left) with a timepiece at the Salon International de la Haute Horlogerie. Ben Gierig
Even at major companies, such as Audemars Piguet, which produces about 40,000 watches a year at its sprawling manufacture in Le Brassus, Switzerland, complex customisations remain rare but influential. Despite making only unique pieces until 1951, the brand says this level of attention is now reserved for the very elite few. “Capacity is always the issue, because of the amount of hand-finishing we do,” says Michael Friedman, head of complications. “It’s a long back-and-forth process, because you still have to keep a balance between the design language of the brand and what the client wants.”
Currently on the docket: a larger, easier-to-activate minute-repeater slide for a client’s Royal Oak Grande Complication. “That’s a cool idea, and it’s something we very well could propose in the future, perhaps not his exact design,” says Friedman. “It’s a customisation which we hadn’t considered yet on the Royal Oak.” But it won’t be as simple to execute as it sounds. The entire piece will have to be re-engineered to adjust the pocket where the lever is activated and still meet its water-resistance standards.
Similarly, Vacheron Constantin—the third member, along with Audemars and Patek, of the “holy trinity,” horology’s anointed crème de la crème—has produced custom pieces for centuries. Its clients, however, usually have high expectations for their commissions to remain singular creations. The company’s Les Cabinotiers atelier builds one-off complications from the ground up for its bespoke watches, many of which remain out of the public eye in private hands.

Voutilainen’s GMT-6 timepiece was based on an original commission from a private client. Voutilainen
But for independents, which lack the infrastructure of vast facilities and armies of employees, the time and resources required to create complex bespoke projects add up to significant investments. To make the math work, they may have little choice but to repeat innovations. In the case of Voutilainen, who makes only about 60 watches a year and is intent on building movements in-house, committing to a one-off piece is an enormous personal sacrifice as well. “The time is missing, but also it’s my personal time,” says Voutilainen, who just bought a new building to expand his workshop and house a few more employees to work on bespoke pieces. “During all these past years, I’ve been doing the casing, finishing of the hands and fabricating some components for the hands myself.” It takes him an entire day to complete one set of hands, meaning he dedicates 50 to 60 days of his year solely to that task. He says he spends more than half his time on the bench, working well into the evenings most days.
As a result, a custom order from an independent can take longer than earning a college degree. Hickcox, the London collector, says he waited five years to receive his customized open-dial Roger W. Smith Series II timepiece after commissioning it in 2012. By the time it was ready, he had lost interest. He had also had some temporary financial reversals and so decided to sell the Series II to dealer Silas Walton, owner of the high-end vintage-watch e-tailer A Collected Man, rather than pay the balance and take delivery. “Silas made sure it went to a deserving client, so Roger was pleased with where it ended up.” (Smith declined to comment on the record.)
Smith makes just 12 watches a year, and they are highly coveted, enabling Hickcox to easily unload his for about 30% more than the roughly $163,000 he says he paid. “It worked out really well from a financial point of view for me, even though I’m not a watch speculator or investor,” says Hickcox.

Collector Gary Getz inspects a watch through a loupe.
The five years Hickcox waited is nothing compared to what some clients with extraordinary wish lists endure. When F. P. Journe revealed his first Centigraphe model in 2008, about a dozen years had elapsed since the initial request from a mathematician, who had come to him asking for an exceptional chronograph with three hands: The first would make one revolution in a second, another would turn in 20 seconds and a third would do a 360 every 10 minutes. “I could never figure out how to do it,” Journe says, “until one day, I visited the Scuderia Ferrari, where I finally figured out how to have three hands turning at three different speeds.” The client passed away long before he could ever see his concept come to fruition.
Journe is notorious for doing as he pleases. He works on his own clock, so to speak, and often declines projects he considers beneath him. Rushing to find a solution simply to satisfy an impatient client is not an option, and he will never build a watch by adding complications or modules on top of a basic movement. “It’s too easy,” says Journe. “It’s like cars built with these communal platforms. That’s called industry, and that is not the kind of work I do. I always do what I want. Very often I refuse absurd requests or things I do not find interesting.”

Getz gave design input for this Petermann Bédat Dead Beat Second watch. Petermann Bédat
The right of refusal remains firmly in the hands of the maker, a power imbalance that can surprise some collectors, who tend to be accustomed to getting their own way in life. Even an offhand comment about where you plan to wear your six- or seven-figure watch could land your project dead in the water. Bovet’s Raffy recalls a time in 2013 when he had agreed to create a bespoke minute-repeater tourbillon for a client, which, in addition to its haute horlogerie mechanics, would feature hand-engravings and an enamel painting. But the collector made a grave mistake when he informed Raffy he was going to be very proud to take it swimming in his balmy locale. Plans for the creation were promptly extinguished. “For me, this is absolutely something you cannot do,” says Raffy. “I said, ‘I’m sorry. I will not do it.’ He thought it was a joke. This gentleman thought I would not refuse an order of two million Swiss francs [about $2.8 million]. I said, ‘Thank you. You have my respect, but this is not the image of the house of Bovet.’”
Questions of aesthetics can also kill a project. Requesting motifs that he considers kitschy is a no-no chez Voutilainen. “I like very classical and technical-looking watches,” he says. You wouldn’t, say, ask Lamborghini to outfit the seats of your Huracán supercar in floral chintz.
Keeping control of the visual design is especially important for independents like Voutilainen, who typically do not or cannot spend a dime on marketing. Collectors act as walking advertisements. But that’s not to say watchmakers have a monopoly on visionary ideas. On the contrary, sometimes it’s the companies seeking out the collectors for their ideas and insights. The industry, like most today, relies on social-media influencers, and in some cases, the mutually beneficial relationship has catapulted both watchmaker and collector to rock-star status.

Vienna-based Breitling collector and consultant Fred Mandelbaum. The Image Gate
Silicon Valley collector Gary Getz, who frequently posts about his collection under the Instagram handle @garyg_1 and writes about it regularly on the site Quill & Pad, recalls Petermann Bédat cofounder Gaël Petermann approaching him and a friend at an auction preview in November 2019. “I didn’t know him,” Getz says, “but he recognized me and he asked to show us their watch and asked us for feedback.” Petermann unpacked an early version of his Dead Beat Second, which had a blue dial and gold Roman numerals. Getz, after asking permission to be frank, called the dial “boring” and suggested Petermann add some flare.
Petermann and his partner, Florian Bédat, took the advice to heart. The steel-and-sapphire dial of the finished Dead Beat Second features a cutaway between one and four o’clock that reveals a front-facing glimpse of its manual-winding mechanical movement. In November of 2020, it took home the Horological Revelation prize at the GPHG. Getz didn’t receive a dime for his advice, but Bédat thanked him from the stage. “My friends and I are more than delighted to be asked for our inputs and really pleased to see these independent makers succeed,” Getz says.

The AVI Ref. 765 1953 re-edition Mandelbaum helped conceive for Breitling. Breitling
Status and recognition are significant ego-strokers, but the ultimate accolade is landing a full-time, paid consulting gig. One of the first people Breitling CEO Georges Kern called as he was preparing to take over the brand in 2017 was Vienna collector Fred Mandelbaum, whose popular Instagram account, @watchfred, has 54,000 followers. Not long after, Kern was on a plane to Austria to woo him for an official role. “They call me the guardian of heritage,” says Mandelbaum, who was tapped to help conceive a line of re-editions based on the brand’s vintage models. The new pieces include the Ref. 806 and AVI Ref. 765, both modern replicas of the 1959 and 1953 originals, respectively. He also consults on design generally, when it comes to tapping into the brand’s history. Why? Mandelbaum’s deep knowledge comes in part from the fact that his collection of vintage Breitlings is more extensive than the brand’s own archive. Over the past decade he has acquired one of each “relevant,” as he puts it, Breitling chronograph ever produced. “I think it’s safe to say that my scope of expertise about the brand heritage is something that wasn’t available when Georges took over,” says Mandelbaum. Many of the heritage models referenced on Breitling’s website and in its catalog are in fact his. So far, Mandelbaum has proved his Midas touch. Both re-editions sold out quickly to retailers and distributors, and a third is in the works for this year.
Collaborating at this level is not for novices. It’s a years-long process with serious money at stake on both sides. But when it works, Mandelbaum insists, more than watches are built. “There is a lot of support, goodwill and friendship that evolves in these circles,” he says. “Ultimately, it is a gentleman’s sport.”
Subscribe to the Newsletter
Recommended for you
Watch of the Week: the Piaget Altiplano Ultimate Concept Tourbillon
The new release claims the throne as the world’s thinnest Tourbillon.
By Josh Bozin
April 19, 2024
The Boldest, Most Exciting New Timepieces From Watches & Wonders 2024
Here are the highlights from the world’s biggest watch releases of the year.
You may also like.
18/04/2024
17/04/2024
You may also like.
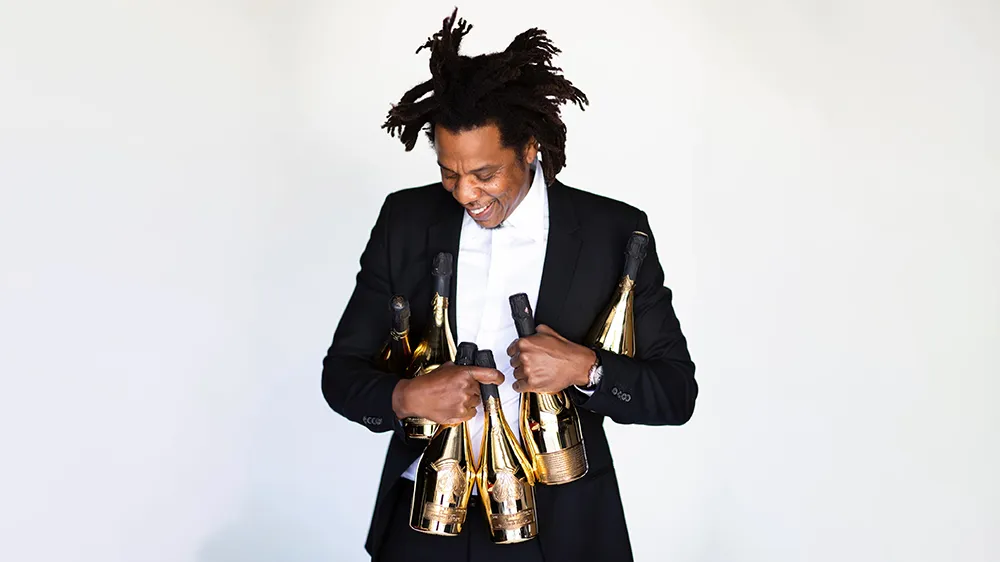
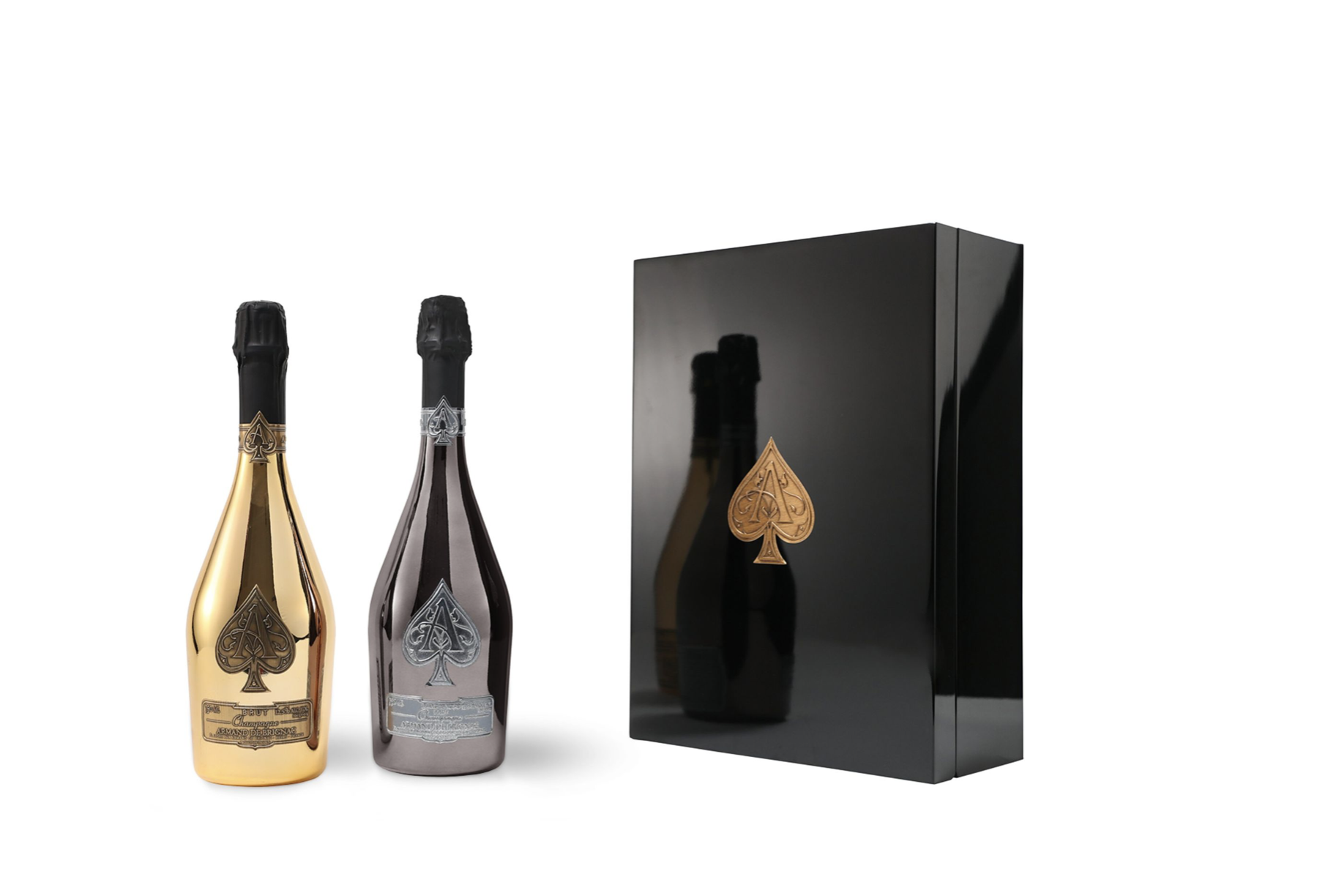
Here’s What Goes Into Making Jay-Z’s $1,800 Champagne
We put Armand de Brignac Blanc de Noirs Assemblage No. 4 under the microsope.
In our quest to locate the most exclusive and exciting wines for our readers, we usually ask the question, “How many bottles of this were made?” Often, we get a general response based on an annual average, although many Champagne houses simply respond, “We do not wish to communicate our quantities.” As far as we’re concerned, that’s pretty much like pleading the Fifth on the witness stand; yes, you’re not incriminating yourself, but anyone paying attention knows you’re probably guilty of something. In the case of some Champagne houses, that something is making a whole lot of bottles—millions of them—while creating an illusion of rarity.
We received the exact opposite reply regarding Armand de Brignac Blanc de Noirs Assemblage No. 4. Yasmin Allen, the company’s president and CEO, told us only 7,328 bottles would be released of this Pinot Noir offering. It’s good to know that with a sticker price of around $1,800, it’s highly limited, but it still makes one wonder what’s so exceptional about it.
Known by its nickname, Ace of Spades, for its distinctive and decorative metallic packaging, Armand de Brignac is owned by Louis Vuitton Moët Hennessy and Jay-Z and is produced by Champagne Cattier. Each bottle of Assemblage No. 4 is numbered; a small plate on the back reads “Assemblage Four, [X,XXX]/7,328, Disgorged: 20 April, 2023.” Prior to disgorgement, it spent seven years in the bottle on lees after primary fermentation mostly in stainless steel with a small amount in concrete. That’s the longest of the house’s Champagnes spent on the lees, but Allen says the winemaking team tasted along the way and would have disgorged earlier than planned if they’d felt the time was right.
Chef de cave, Alexandre Cattier, says the wine is sourced from some of the best Premier and Grand Cru Pinot Noir–producing villages in the Champagne region, including Chigny-les-Roses, Verzenay, Rilly-la-Montagne, Verzy, Ludes, Mailly-Champagne, and Ville-sur-Arce in the Aube département. This is considered a multi-vintage expression, using wine from a consecutive trio of vintages—2013, 2014, and 2015—to create an “intense and rich” blend. Seventy percent of the offering is from 2015 (hailed as one of the finest vintages in recent memory), with 15 percent each from the other two years.

This precisely crafted Champagne uses only the tête de cuvée juice, a highly selective extraction process. As Allen points out, “the winemakers solely take the first and freshest portion of the gentle cuvée grape press,” which assures that the finished wine will be the highest quality. Armand de Brignac used grapes from various sites and three different vintages so the final product would reflect the house signature style. This is the fourth release in a series that began with Assemblage No. 1. “Testing different levels of intensity of aromas with the balance of red and dark fruits has been a guiding principle between the Blanc de Noirs that followed,” Allen explains.
The CEO recommends allowing the Assemblage No. 4 to linger in your glass for a while, telling us, “Your palette will go on a journey, evolving from one incredible aroma to the next as the wine warms in your glass where it will open up to an extraordinary length.” We found it to have a gorgeous bouquet of raspberry and Mission fig with hints of river rock; as it opened, notes of toasted almond and just-baked brioche became noticeable. With striking acidity and a vein of minerality, it has luscious nectarine, passion fruit, candied orange peel, and red plum flavors with touches of beeswax and a whiff of baking spices on the enduring finish. We enjoyed our bottle with a roast chicken rubbed with butter and herbes de Provence and savored the final, extremely rare sip with a bit of Stilton. Unfortunately, the pairing possibilities are not infinite with this release; there are only 7,327 more ways to enjoy yours.
You may also like.
Bill Henson Show Opens at Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery
Dark, grainy and full of shadows Bill Henson’s latest show draws on 35 mm colour film shot in New York City in 1989.
Bill Henson is one of Australia’s best-known contemporary photographers. When a show by this calibre of artist opens here, the art world waits with bated breath to see what he will unveil.
This time, he presents a historically important landscape series that chronicles a time in New York City that no longer exists. It’s a nostalgic trip back in time, a nocturnal odyssey through the frenetic, neon-lit streets of a long-lost America.
Known for his chiaroscuro style, Henson’s cinematic photographs often transform his subject into ambiguous objects of beauty. This time round, the show presents a mysterious walk through the streets of Manhattan, evoking a seedy, yet beautiful vision of the city.
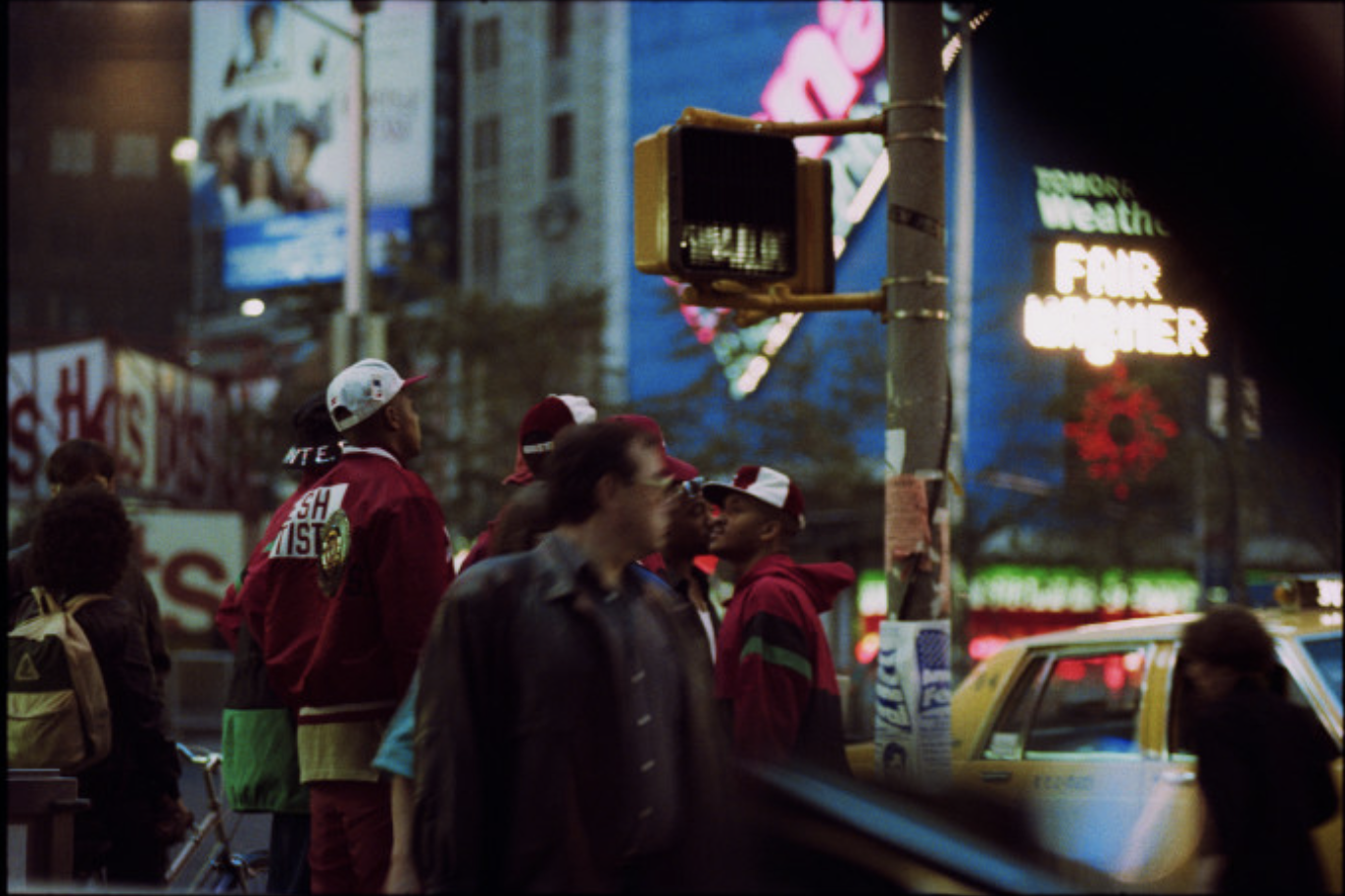


Relying on generative gaps, these landscapes result from Henson mining his archive of negatives and manipulating them to produce a finished print. Sometimes, they are composed by a principle of magnification, with Henson honing in on details, and sometimes, they are created through areas of black being expanded to make the scene more cinematic and foreboding. Like silence in a film or the pause in a pulse, the black suggests the things you can’t see.
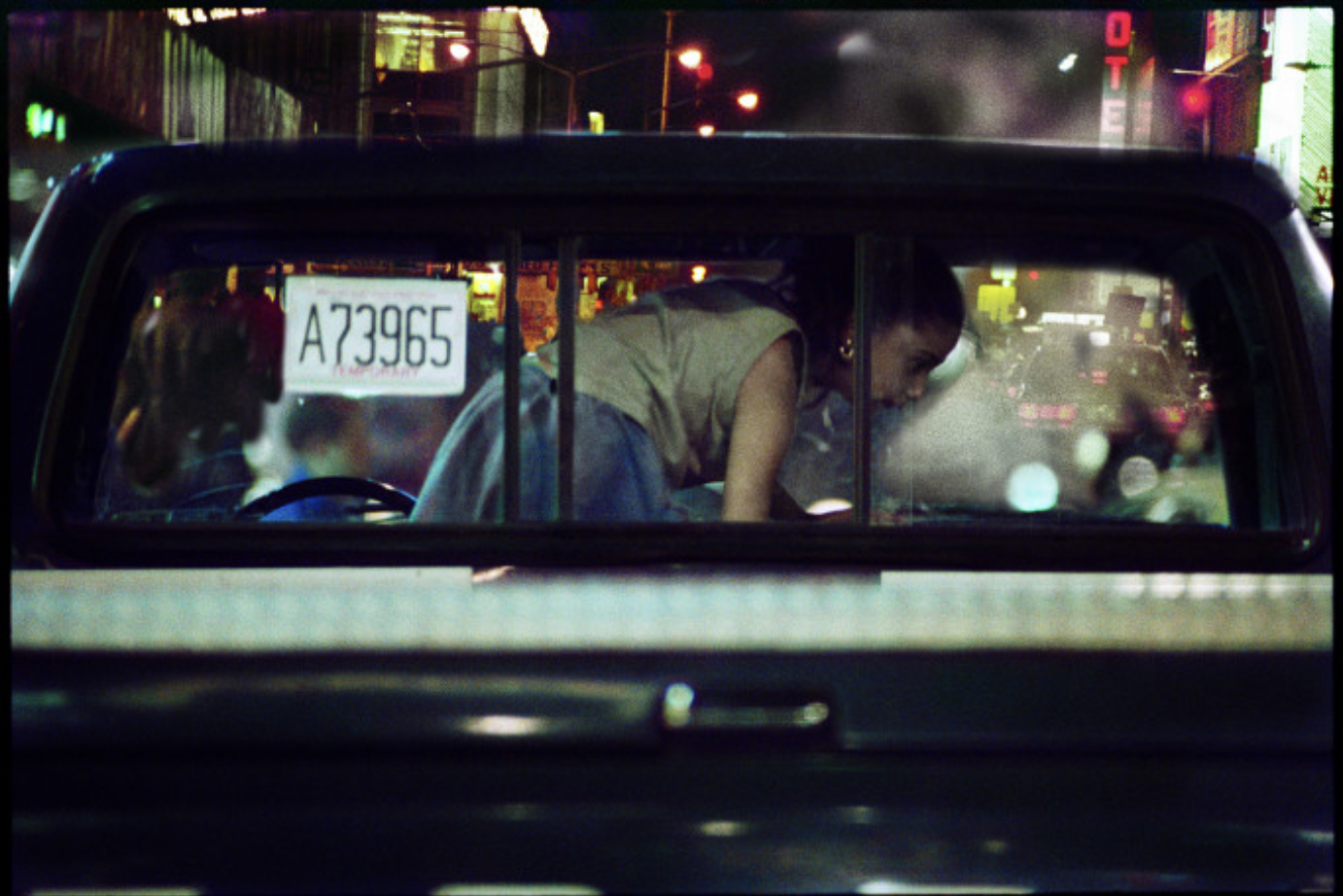


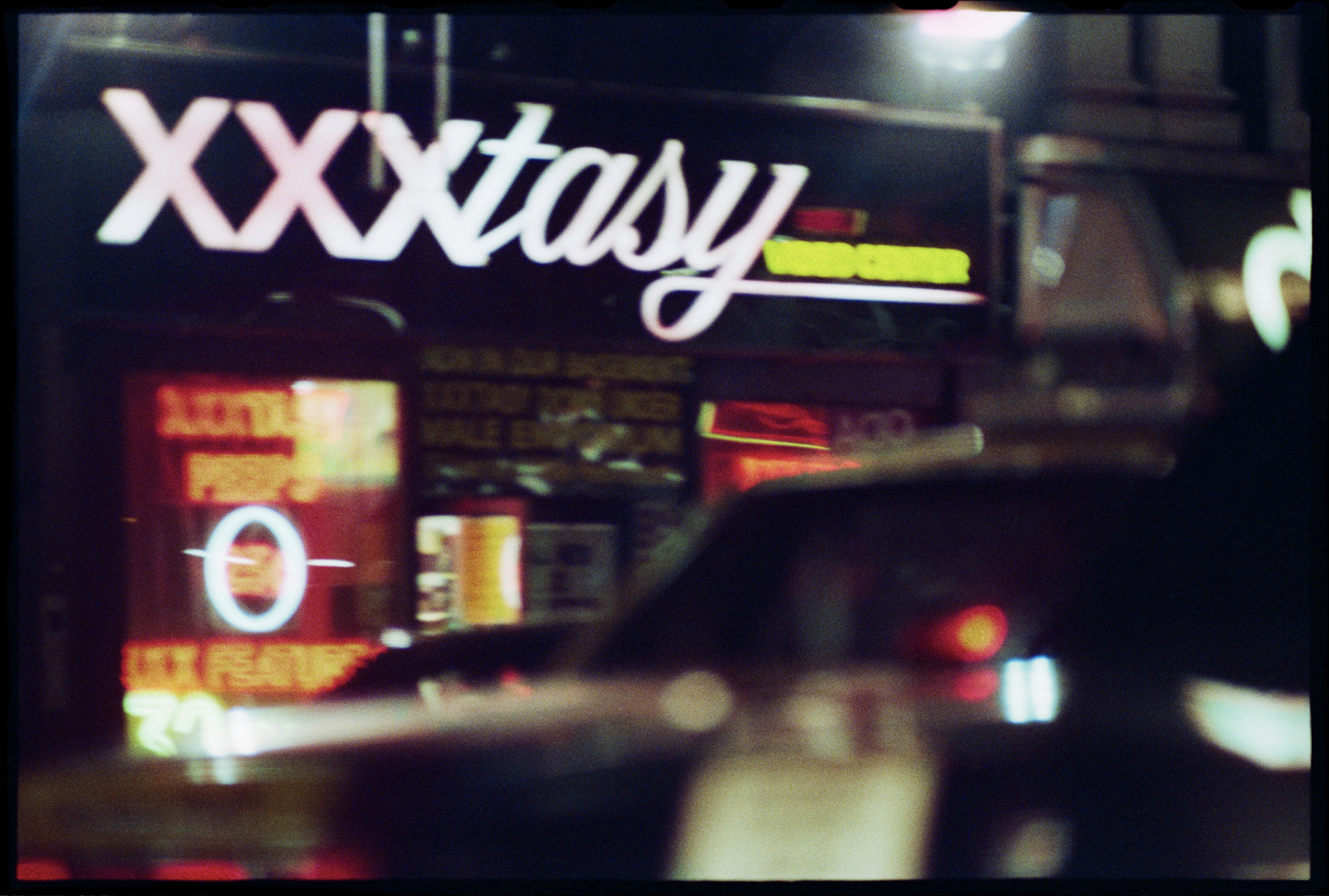
Henson’s illustrious career has spanned four decades and was memorably marred by controversy over a series of nude adolescent photographs shown in 2008, which made him front-page news for weeks. This series of portraits made Henson the subject of a police investigation during which no offence was found.
In recent years, Henson has been a sharp critic of cancel culture, encouraging artists to contribute something that will have lasting value and add to the conversation, rather than tearing down the past.
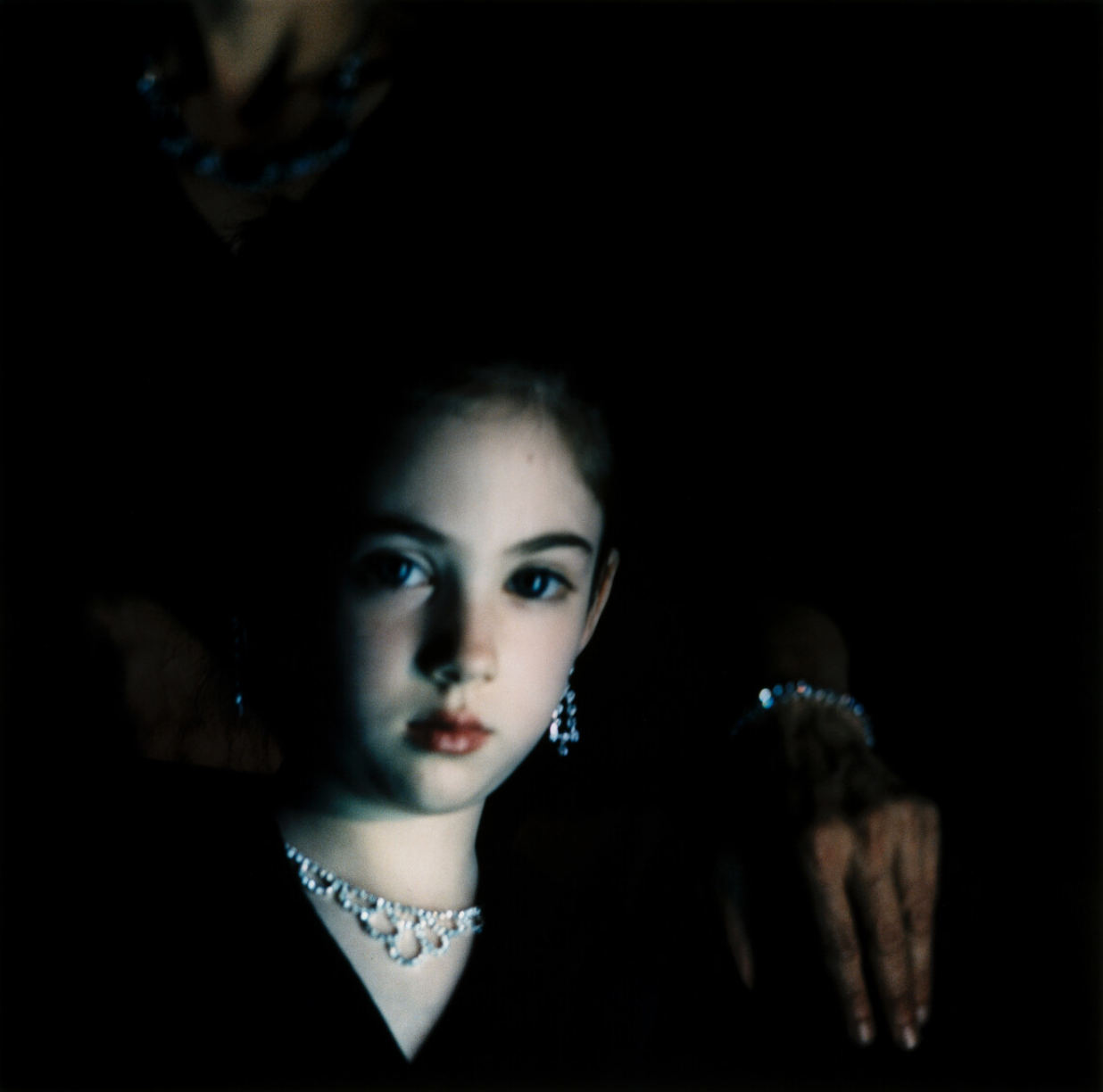

His work deals with the liminal space between the mystical and the real, the seen and unseen, the boundary between youth and adulthood.
His famous Paris Opera Project, 1990-91, pictured above, is similarly intense as the current show, dwelling on the border between the painterly and the cinematic.
Bill Henson’s ‘The Liquid Night’ runs until 11 May 2024 at Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery.
Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery, 8 Soudan Ln, Paddington NSW; roslynoxley9.com.au
You may also like.
Watch of the Week: the Piaget Altiplano Ultimate Concept Tourbillon
The new release claims the throne as the world’s thinnest Tourbillon.
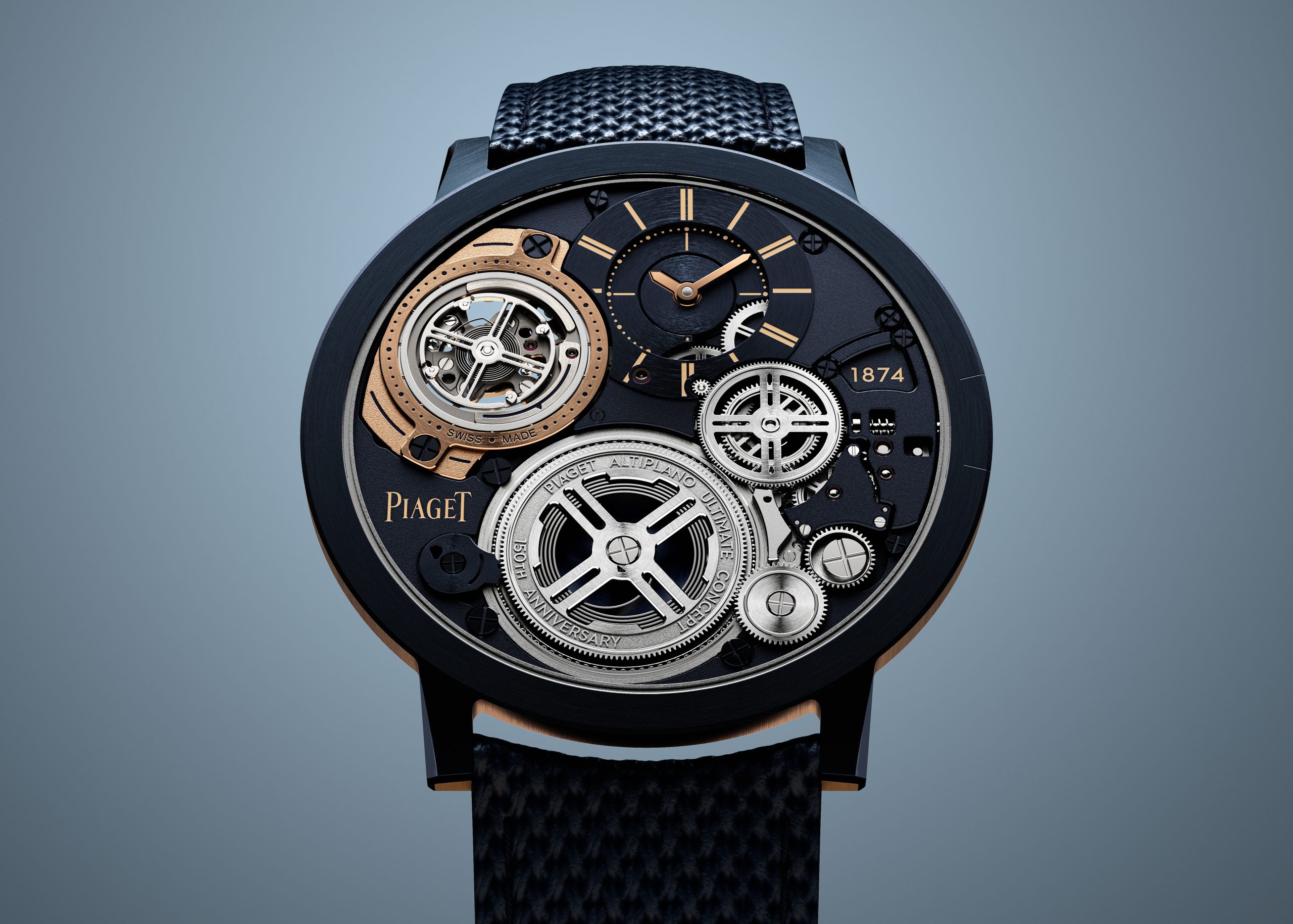
Piaget, the watchmaker’s watchmaker, has once again redefined the meaning of “ultra-thin” thanks to its newest masterpiece, the Altiplano Ultimate Concept Tourbillon—the world’s thinnest tourbillon watch.
In the world of high-watchmaking where thin is never thin enough—look at the ongoing battle between Piaget, Bulgari, and Richard Mille for the honours—Piaget caused a furore at Watches & Wonders in Geneva when it unveiled its latest feat to coincide with the Maison’s 150th year anniversary.
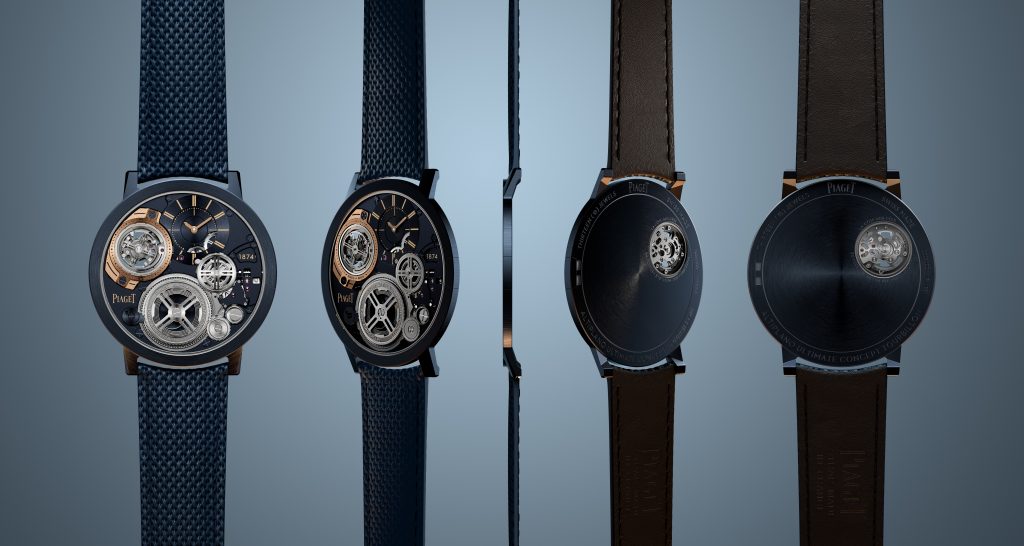

Piaget claims that the new Altiplano is “shaped by a quest for elegance and driven by inventiveness”, and while this might be true, it’s clear that the Maison’s high-watchmaking divisions in La Côte-aux-Fées and Geneva are also looking to end the conversation around who owns the ultra-thin watchmaking category.
The new Altiplano pushes the boundaries of horological ingenuity 67 years after Piaget invented its first ultra-thin calibre—the revered 9P—and six years after it presented the world’s then-thinnest watch, the Altiplano Ultimate Concept. Now, with the release of this unrivalled timepiece at just 2mm thick—the same as its predecessor, yet now housing the beat of a flying tourbillon, prized by watchmaking connoisseurs—you can’t help but marvel at its ultra-thin mastery, whether the timepiece is to your liking or not.
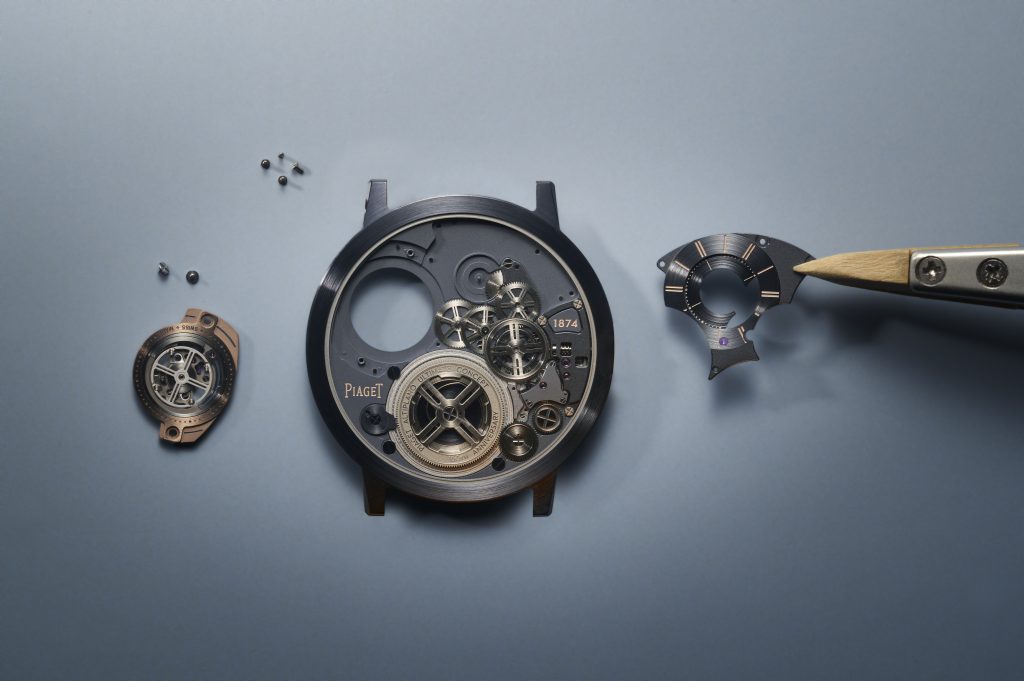

In comparison, the Bulgari Octo Finissimo Tourbillon was 3.95mm thick when unveiled in 2020, which seems huge on paper compared to what Piaget has been able to produce. But to craft a watch as thin and groundbreaking as its predecessor, now with an added flying tourbillon complication, the whole watchmaking process had to be revalued and reinvented.
“We did far more than merely add a tourbillon,” says Benjamin Comar, Piaget CEO. “We reinvented everything.”
After three years of R&D, trial and error—and a redesign of 90 percent of the original Altiplano Ultimate Concept components—the 2024 version needs to be held and seen to be believed. The end product certainly isn’t a watch for the everyday watch wearer—although Piaget will tell you otherwise—but in many ways, the company didn’t conjure a timepiece like the Altiplano as a profit-seeking exercise. Instead, overcoming such an arduous and technical watchmaking feat proves that Piaget can master the flying tourbillon in such a whimsical fashion and, in the process, subvert the current state-of-the-art technical principles by making an impactful visual—and technical—statement.
The only question left to ask is, what’s next, Piaget?

—
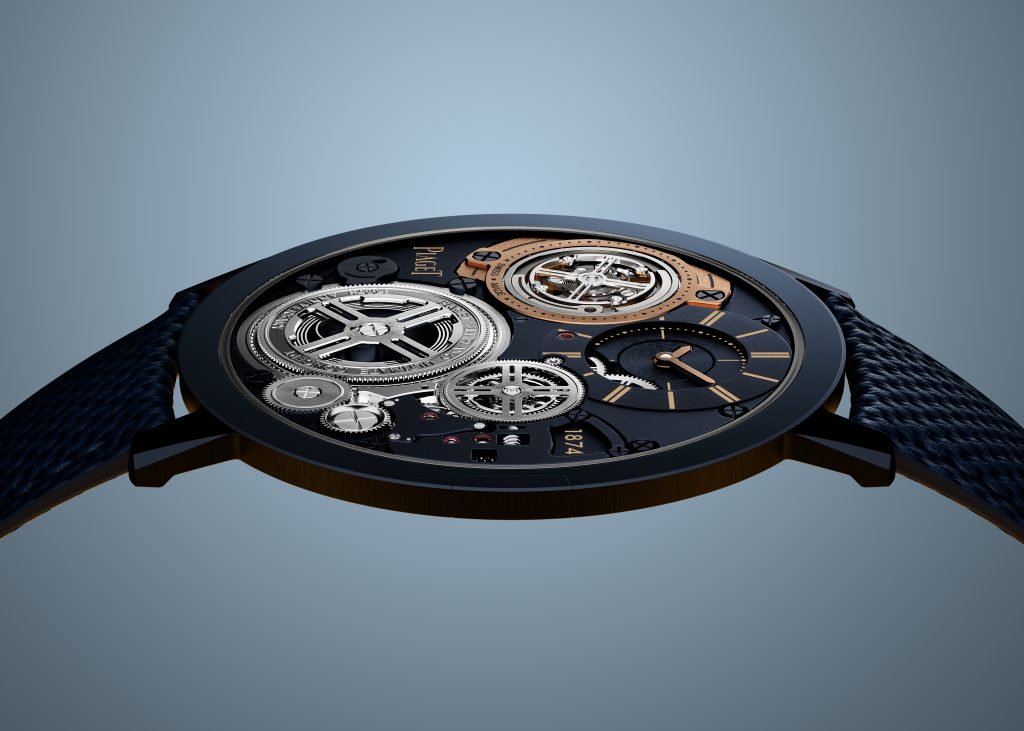
Model: Altiplano Ultimate Concept Tourbillon 150th Anniversary
Diameter: 41.5 mm
Thickness: 2 mm (crystal included)
Material: M64BC cobalt alloy, blue PVD -treated
Dial: Monobloc dial; polished round and baton indices, Bâton-shaped hand for the minutes Monobloc disc with a hand for the hours
Water resistance: 20m
Movement: Calibre 970P-UC, one-minute peripheral tourbillon
Winding: Hand-wound
Functions: hours, minutes, and small seconds (time-only)
Power reserve: 40 hours
Availability: Limited production, not numbered
Price: Price on request
You may also like.
18/04/2024
By Jay Cheses
17/04/2024
Polar Opposites
A journey north to one of the harshest, remotest spots on Earth couldn’t be more luxurious.
A century ago, an expedition to the North Pole involved dog sleds and explorers in heavy, fur-lined clothes, windburned and famished after weeks of trudging across ice floes, finally planting their nations’ flags in the barren landscape. These days, if you’re a tourist, the only way to reach 90 degrees north latitude, the geographic North Pole, is aboard Le Commandant Charcot, a six-star hotel mated to a massive, 150-metre ice-breaking hull.
My wife, Cathy, and I are among the first group of tourists aboard Ponant’s new expedition icebreaker, the world’s only Polar Class 2–rated cruise ship (of seven levels of ice vessel, second only to research and military vessels in ability to manoeuvre in Arctic conditions). Our arrival on July 14 couldn’t be more different from explorer Robert Peary’s on April 6, 1909. On that date, he reported, he staked a small American flag—sewed by his wife—into the Pole, joined by four Inuits and his assistant, Matthew Henson, a Black explorer from Maine who was with Peary on his two previous Arctic expeditions. (Peary’s claim of being first to the Pole was quickly disputed by another American, Frederick Cook, who insisted he’d spent two days there a year earlier. Scholars now view both claims with skepticism.)
Our 300-plus party’s landing, on Bastille Day, features the captain of the French ship driving around in an all-terrain vehicle with massive wheels and an enormous tricolour flag on the back, guests dressed in stylish orange parkas celebrating on the ice, and La Marseillaise, France’s national anthem, blaring from loudspeakers. After an hour of taking selfies and building snow igloos in the icescape, with temperatures in the relatively balmy low 30s, we head back into our heated sanctuary for mulled wine and freshly baked croissants. Mission accomplished. Flags planted. Now, lunch.
As a kid, I was fascinated by stories of adventurers trying to reach the North Pole without any means of rescue. In the 19th century, most of their attempts ended in disaster—ships getting trapped in the ice, a hydrogen balloon crashing, even cannibalism. It wasn’t until Cook and Peary reportedly set foot there that the race to the North Pole was really on. Norwegian Roald Amundsen, the first to reach the South Pole, in 1911, is credited with being the first to document a trip over the North Pole, which he did in 1926 in the airship Norge. In 1977, the nuclear-powered icebreaker Arktika became the first surface vessel to make it to the North Pole. Since then, only 18 other ships have completed the voyage.
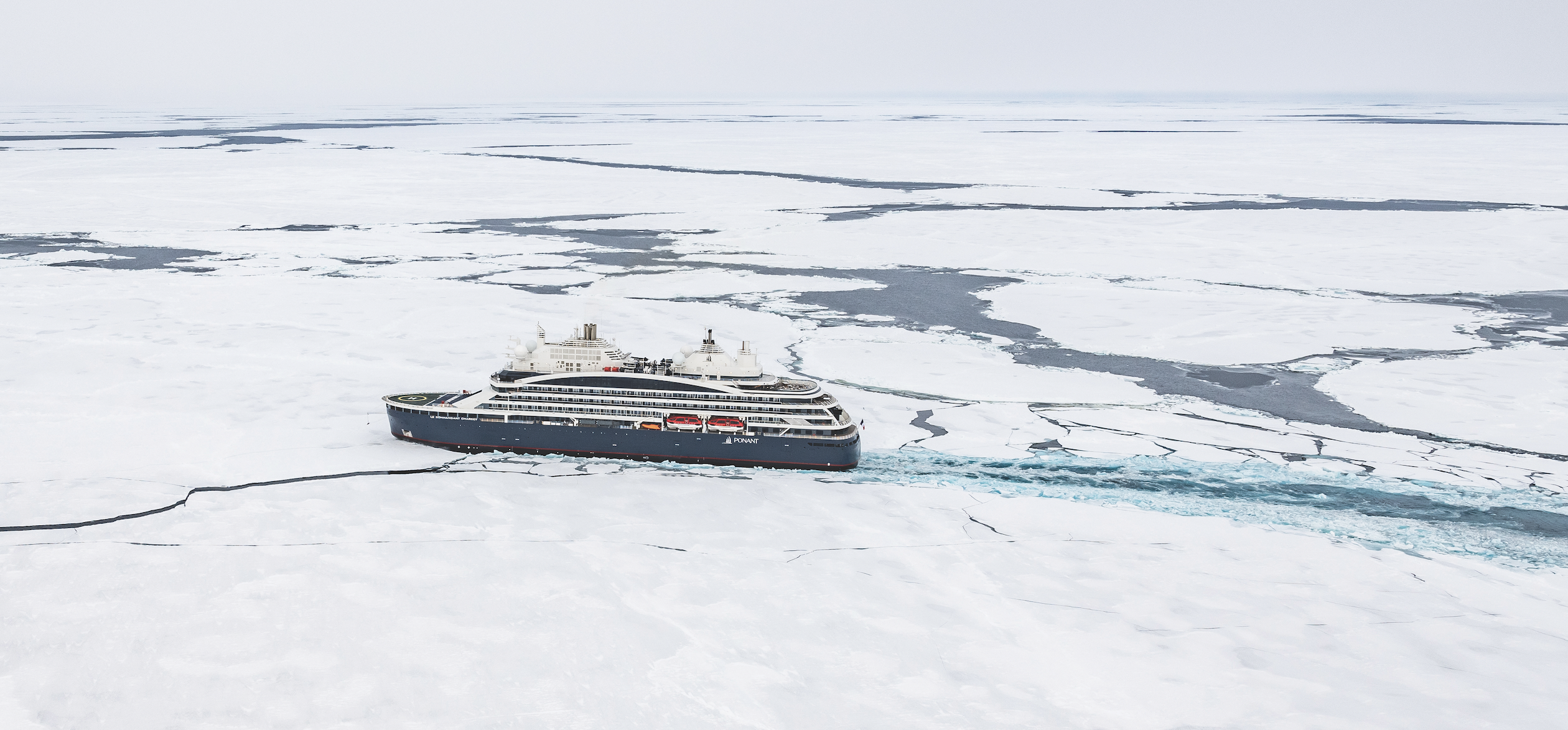

Visiting the North Pole seemed about as likely for me as walking on the Moon. It wasn’t even on my bucket list. Then came Le Commandant Charcot, which was named after France’s most beloved polar explorer and reportedly cost about US$430 million (around $655 million) to build. The irony of visiting one of the planet’s most remote and inhospitable points while travelling in the lap of luxury doesn’t escape me or anyone else I speak with on the voyage. Danie Ferreira, from Cape Town, South Africa, describes it as “an ensemble of contradictions bordering on the absurd”. Ferreira, who is on board with his wife, Suzette, is a veteran of early-explorer-style high-Arctic journeys, months-long treks involving dog sleds and real toil and suffering. He booked this trip to obtain an official North Pole stamp for an upcoming two-volume collection of his photographs, Out in the Cold, documenting his polar adventures. “Reserving the cabin felt like a betrayal of my expeditionary philosophy,” he says with a laugh.
Then, like the rest of us, he embraces the contradictions. “This is like the first time I saw the raw artistry of Cirque du Soleil,” he explains. “Everything is beyond my wildest expectations, unrelatable to anything I’ve experienced.”
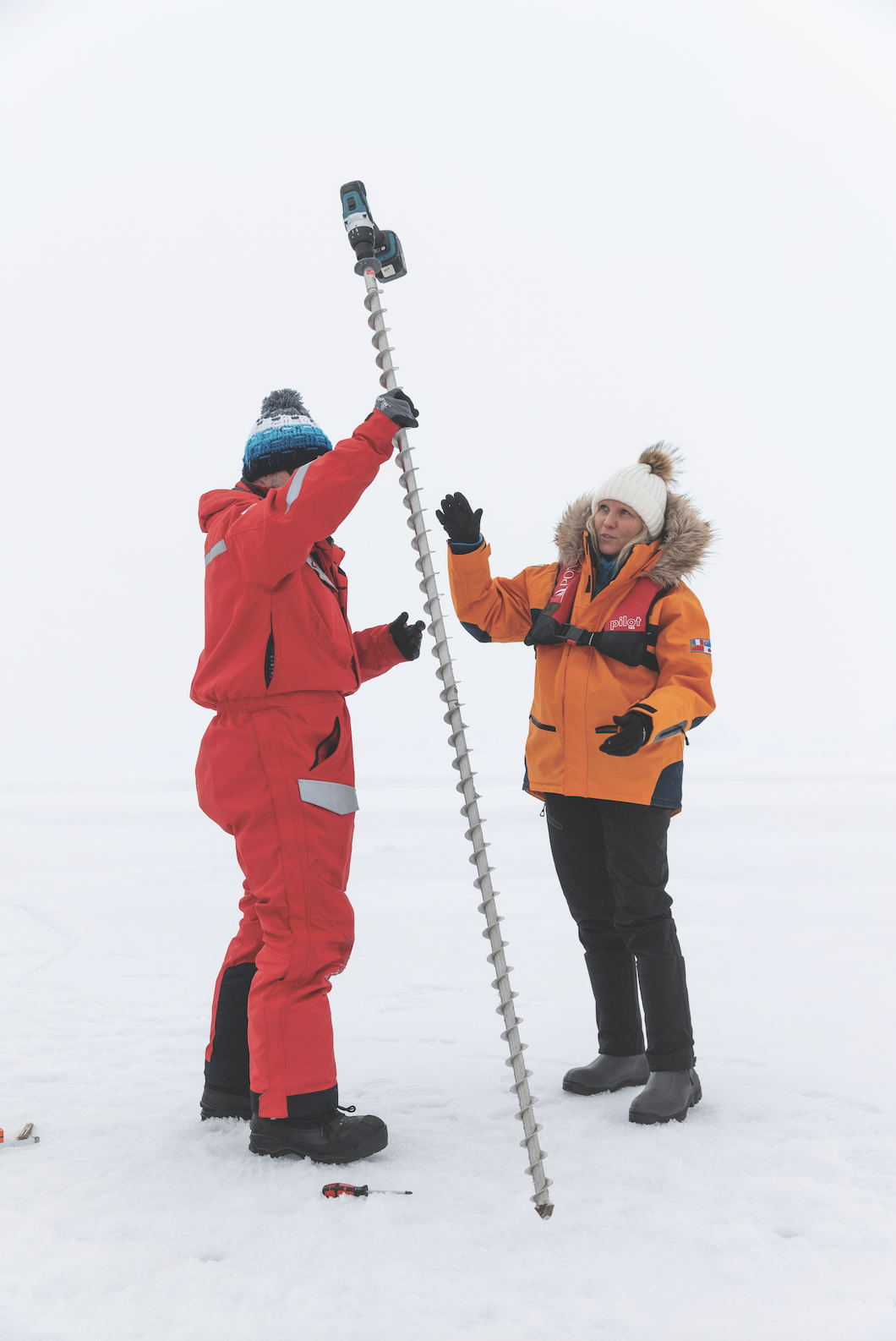

The 17-day itinerary launches from the Norwegian settlement of Longyearbyen, Svalbard, the northernmost town in the Arctic Circle, and heads 1,186 nautical miles to the North Pole, then back again. As a floating hotel, the vessel is exceptional: 123 balconied staterooms and suites, the most expensive among them duplexes with butler service (prices range from around $58,000 to $136,000 per person, double occupancy); a spa with a sauna, massage therapists, and aestheticians; a gym and heated indoor pool. The boat weighs more than 35,000 tons, enabling it to break ice floes like “a chocolate bar into little pieces, rather than slice through them”, according to Captain Patrick Marchesseau. Six-metre-wide stainless-steel propellers, he adds, were designed to “chew ice like a blender”.
Marchesseau, a tall, lanky, 40-ish mariner from Brittany, impeccable in his navy uniform but rocking royal-blue boat shoes, proves to be a charming host. Never short of a good quip, he’s one of three experienced ice captains who alternate at the helm of Charcot throughout the year. He began piloting Ponant ships through drifting ice floes in Antarctica in 2009, when he took the helm of Le Diamant, Ponant’s first expedition vessel. “An epic introduction,” Marchesseau calls those early voyages, but the isolated, icebound North Pole aboard a larger, more complicated vessel is potentially an even thornier challenge. “We’ll first sail east where the ice is less concentrated and then enter the pack at 81 degrees,” he tells a lecture hall filled with passengers on day one. “We don’t plan to stop until we get to the North Pole.”
Around us, the majority of the other 101 guests are older French couples; there are also a few extended families, some other Europeans, mostly German and Dutch, as well as 10 Americans. Among the supporting cast are six research scientists and 221 staff, including 18 naturalist guides from a variety of countries.
The first six days are more about the journey than the destination. Cathy and I settle into our comfortable stateroom, enjoy the ocean views from our balcony, make friends with other guests and naturalists, frequent the spa, and indulge in the contemporary French cuisine at Nuna, which is often jarred by ice passing under the hull, as well as at the more casual Sila (Inuit for “sky”). There are the usual cruise events: the officers’ gala, wine pairings, daily French pastries, Broadway-style shows, opera singers and concert pianists. Initially, I worry about “Groundhog Day” setting in, but once we hit patchy ice floes on day two, it’s clear that the polar party is on. The next day, we’re ensconced in the ice pack.
Veterans of Arctic journeys immediately feel at home. Ferreira, often found on the observation deck 15 metres above the ice with his long-lensed cameras, is in his element snapping different patterns and colours of the frozen landscape. “It feels like combining low-level flying with an out-of-body experience,” he says. “Whenever the hull shudders against the ice, I have a reality check.”

“I came back because I love this ice,” adds American Gin Millsap, who with her husband, Jim, visited the North Pole in 2015 aboard the Russian nuclear icebreaker Fifty Years of Victory, which for obvious reasons is no longer a viable option for Americans and many Europeans. “I love the peace, beauty and calmness.”
It is easy to bliss out on the endless barren vistas, constantly morphing into new shapes, contours and shades of white as the weather moves from bright sunshine to howling snowstorms—sometimes within the course of a few hours. I spend a lot of time on the cold, windswept bow, looking at the snow patterns, ridges and rivers flowing within the pale landscape as the boat crunches through the ice. It feels like being in a black-and-white movie, with no colours except the turquoise bottoms of ice blocks overturned by the boat. Beautiful, lonely, mesmerising.
Rather than a solid landmass, the Arctic ice pack is actually millions of square kilometres of ice floes, slowly pushed around by wind and currents. The size varies according to season: this past winter, the ice was at its fifth-lowest level on record, encompassing 14.6 million square kilometres, while during our cruise it was 4.7 million square kilometres, the 10th-lowest summer number on record. There are myriad ice types—young ice, pancake ice, ice cake, brash ice, fast ice—but the two that our ice pilot, Geir-Martin Leinebø, cares about are first-year ice and old ice. The thinness of the former provides the ideal route to the Pole, while the denseness of the aged variety can result in three-to-eight-metre-high ridges that are potentially impassable. Leinebø is no novice: in his day job, he’s the captain of Norway’s naval icebreaker, KV Svalbard, the first Norwegian vessel to reach the North Pole, in 2019.

It’s not a matter of just pointing the boat due north and firing up the engine. Leinebø zigzags through the floes. A morning satellite feed and special software aid in determining the best route; the ship’s helicopter sometimes scouts 65 or so kilometres ahead, and there’s a sonar called the Sea Ice Monitoring System (SIMS). But mostly Leinebø uses his eyes. “You look for the weakest parts of the ice—you avoid the ridges because that means thickness and instead look for water,” he says. “If the ‘water sky’ in the distance is dark, it’s reflecting water like a mirror, so you head in that direction.”
Everyone on the bridge is surprised by the lack of multi-year ice, but with more than a hint of disquietude. Though we don’t have to ram our way through frozen ridges, the advance of climate change couldn’t be more apparent. Environmentalists call the Arctic ice sheet the canary in the coal mine of the planet’s climate change for good reason: it is happening here first. “It’s not right,” mutters Leinebø. “There’s just too much open water for July. Really scary.”
The Arctic ice sheet has shrunk to about half its 1985 size, and as both mariners and scientists on board note, the quality of the ice is deteriorating. “It’s happening faster than our models predicted,” says Marisol Maddox, senior arctic analyst at the Polar Institute of the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars. “We’re seeing major events like Greenland’s ice sheet melting and sliding into the ocean—that wasn’t forecasted until 2070.” The consensus had been that the Arctic would be ice-free by 2050, but many scientists now expect that day to come in the 2030s.
That deterioration, it turns out, is why the three teams of scientists are on the voyage—two studying the ice and the other assessing climate change’s impact on plankton. As part of its commitment to sustainability, Ponant has designed two research labs—one wet and one dry—on a lower deck. “We took the advice of many scientists for equipping these labs,” says Hugues Decamus, Charcot’s chief engineer, clearly proud of the nearly US$12 million facilities.
The combined size of the labs, along with a sonar room, a dedicated server for the scientists, and a meteorological station on the vessel’s top deck, totals 130 square metres—space that could have been used for revenue generation. Ponant also has two staterooms reserved for scientists on each voyage and provides grants for travel expenses. The line doesn’t cherrypick researchers but instead asks the independent Arctic Research Icebreaker Consortium (ARICE) to choose participants based on submissions.

The idea, says the vessel’s science officer on this voyage, Daphné Buiron, is to make the process transparent and minimise the appearance of greenwashing. “Yes, this alliance may deliver a positive public image for the company, but this ship shows we do real science on board,” she says. The labs will improve over time, adds Decamus, as the ship amasses more sophisticated equipment.
Research scientists and tourist vessels don’t typically mix. The former, wary of becoming mascots for the cruise lines’ sustainability marketing efforts, and cognisant of the less-than-pristine footprint of many vessels, tend to be wary. The cruise lines, for their part, see scientists as potentially high maintenance when paying customers should be the priority. But there seemed to be a meeting of the minds, or at least a détente, on Le Commandant Charcot.
“We discuss this a lot and are aware of the downsides, but also the positives,” says Franz von Bock und Polach, head of the institute for ship structural design and analysis at Hamburg University of Technology, specialising in the physics of sea ice. Not only does Charcot grant free access to these remote areas, but the ship will also collect data on the same route multiple times a year with equipment his team leaves on board, offering what scientists prize most: repeatability. “One transit doesn’t have much value,” he says. “But when you measure different seasons, regions and years, you build up a more complex picture.” So, more than just a research paper: forecasts of ice conditions for long-term planning by governments as the Arctic transforms.
Nils Haëntjens, from the University of Maine, is analysing five-millilitre drops of water on a high-tech McLane IFCB microscope. “The instrument captures more than 250,000 images of phytoplankton along the latitudinal transect,” he says. Charcot has doors in the wet lab that allow the scientists to take water samples, and in the bow, inlets take in water without contaminating it. Two freezers can preserve samples for further research back in university labs.
Even though the boat won’t stop, the captain and chief engineer clearly want to make the science missions work. Marchesseau dispatches the helicopter with the researchers and their gear 100 kilometres ahead, where they take core samples and measurements. I spot them in their red snowsuits, pulling sleds on an ice floe, as the boat passes. Startled to see living-colour humans on the ice after days of monochrome, I feel a pang of jealousy as I head for a caviar tasting.
The only other humans we encounter on the journey north are aboard Fifty Years of Victory, the Russian icebreaker. The 160-metre orange- and-black leviathan reached the North Pole a day earlier—its 59th visit—and is on its way back to Murmansk. It’s a classic East meets West moment: the icebreaker, launched just after the collapse of the Soviet Union, meeting the new standard of polar luxury.
The evening before Bastille Day, Le Commandant Charcot arrives at the North Pole. Because of the pinpoint precision of the GPS, Marchesseau has to navigate back and forth for about 20 minutes—with a bridge full of passengers hushing each other so as not to distract him—until he finds 90 degrees north. That final chaotic approach to the top of the world in the grey, windswept landscape looks like a kid’s Etch A Sketch on the chartplotter, but it is met with rousing cheers. The next morning, with good visibility and light winds, we spill out onto the ice for the celebration, followed by a polar plunge.
As guests pose in front of flags and mile markers for major cities, the naturalist guides, armed with rifles, establish a wide perimeter to guard against polar bears. The fearless creatures are highly intelligent, with razor-sharp teeth, hooked claws and the ability to sprint at 40 km/h. Males average about three metres tall and weigh around 700 kilos. They are loners that will kill anything—including other bears and even their own cubs. Cathy and I walk around the far edges of the perimeter to enjoy some solitude. Looking out over the white landscape, I know this is a milestone. But it feels odd that getting here didn’t involve any sweat or even a modicum of discomfort.

The rest of the week is an entirely different trip. On the return south, we see a huge male polar bear ambling on the ice, looking over his shoulder at us. It is our first sighting of the Arctic’s apex predator, and everyone crowds the observation lounge with long-lensed cameras. The next day, we see another male, this one smaller, running away from the ship. “They have many personalities,” says Steiner Aksnes, head of the expedition team, who has led scientists and film crews in the Arctic for 25 years. We see a dozen on the return to Svalbard, where 3,000 are scattered across the archipelago, outnumbering human residents.
The last five days we make six stops on different islands, travelling by Zodiac from Charcot to various beaches. On Lomfjorden, as we look on a hundred yards from shore, a mother polar bear protects her two cubs while a young male hovers in the background. On a Zodiac ride off Alkefjellet, the air is alive with birds, including tens of thousands of Brünnich’s guillemots as well as glaucous gulls and kittiwakes, which nest in that island’s cliffs, while a young male polar bear munches on a ring seal, chin glistening red.
On this part of the trip, the expedition team, mostly 30-something, free-spirited scientists whose areas of expertise range from botany to alpine trekking to whales, lead hikes across different landscapes. The jam-packed schedule sometimes involves three activities per day and includes following the reindeer on Palanderbukta, seeing a colony of 200 walruses on Kapp Lee, hiking the black tundra of Burgerbukta (boasting 3.8-cm-tall willows—said to be the smallest trees in the world and the largest on Svalbard—plus mosquitoes!), watching multiple species of whales breaching offshore, and kayaking the ice floes of Ekmanfjorden. Svalbard is a protected wilderness area, and the cruise lines tailor their schedules so vessels don’t overlap, giving visitors the impression they are setting foot on virgin land.
Chances to experience that sense of discovery and wonder, even slightly stage-managed ones, are dwindling along with the ice sheet and endangered wildlife. If a stunning trip to a frozen North Pole is on your bucket list, the time to go is now.

PARADIGM SHIP
For those studying polar ice, a berth aboard Le Commandant Charcot is like a winning lottery ticket. “This cruise ship is one of the few resources scientists can use, because nothing else can get there,” says G. Mark Miller, CEO of research-vessel builder Greenwater Marine Sciences Offshore (GMSO) and a former ship captain for the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). “Then factor in 80 percent of scientists who want to go to sea, can’t, because of the shortage of research vessels.”
Both Ponant and Viking have designed research labs aboard new expedition vessels as part of their sustainability initiatives. “Remote areas like Antarctica need more data—the typical research is just single data points,” says Damon Stanwell-Smith, Ph.D., head of science and sustainability at Viking. “Every scientist says more information is needed.” The twin sisterships Viking Octantis and Viking Polaris, which travel to Antarctica, Patagonia, the Great Lakes and Canada, have identical 35-square-metre labs, separated into wet and dry areas and fitted out with research equipment. In hangars below are military-grade rigid-hulled inflatables and two six-person yellow submersibles (the pair on Octantis are named John and Paul, while Polaris’s are George and Ringo). Unlike Ponant, Viking doesn’t have an independent association choose scientists for each voyage. Instead, it partners with the University of Cambridge, the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, and NOAA, which send their researchers to work with Viking’s onboard science officers.

“Some people think marine research is sticking some kids on a ship to take measurements,” says Stanwell-Smith. “But we know we can do first-rate science—not spin.” Other cruise lines are also embracing sustainability initiatives, with coral-reef-restoration projects and water-quality measurements, usually in partnership with universities. Just about every vessel has “citizen-scientist” research programs allowing guests the opportunity to count birds or pick up discarded plastic on beaches. So far, Ponant and Viking are the only lines with serious research labs. Ponant is adding science officers to other vessels in its fleet. As part of the initiatives, scientists deliver onboard lectures and sometimes invite passengers to assist in their research.

Given the shortage of research vessels, Stanwell-Smith thinks this passenger-funded system will coexist nicely with current NGO- and government-owned ships. “This could be a new paradigm for exploring the sea,” he says. “Maybe the next generation of research vessels will look like ours.”
You may also like.
Forever Leather
Furnishings wrapped or accented with classic, cognac-coloured hide create a patina that works with any aesthetic.
Onsen, Gandia Blasco
As the textile industry makes technological advances, traditional outdoor furniture made from iron, wicker and teak seems ever so throwback-y and, dare we say, inconvenient and even uncomfortable. Gandia Blasco’s Mediterranean roots and architectural approach shine in its Onsen collection of garden furniture. Luxe synthetic-leather straps wrapping a tubular stainless-steel structure paired with long-wearing cushions in a similar shade lend new life to the idea of living with leather outdoors. From about $4,425; soft mat about $620, warm mat about $810; Onsen, Gandia Blasco
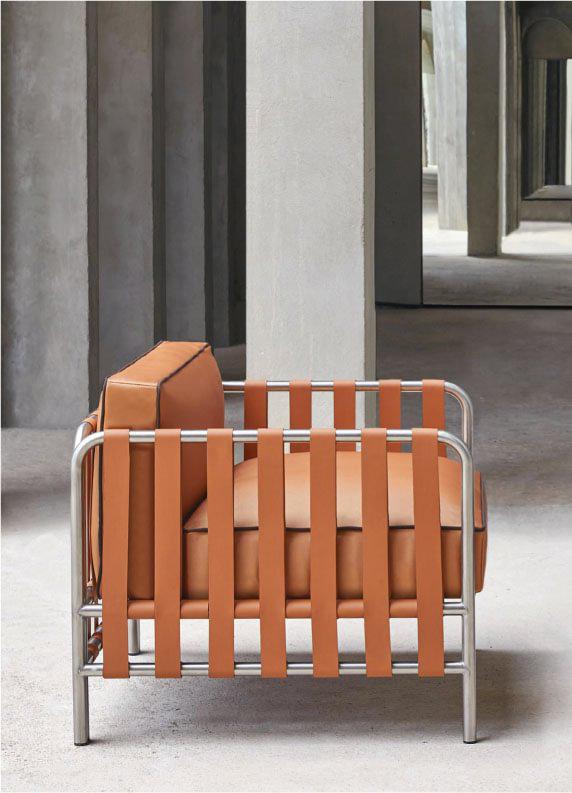

Gabri, Bolzan
The pared-down, leggy look of these tripod tables packs a functional punch without foregoing refinement. Designed by Matteo Zorzenoni for Bolzan and made in Italy, the Gabri’s leather-bound frames with subtle topstitching and semicircular notches recall desktop accessories of an analog age. The dark tops with touches of chalky veining are thoroughly of this century: made from neolith stone, they’re temperature-resistant and waterproof, so go ahead and place your martini where you will. Small, about $1,735; large, about $2,603; Bolzan.com
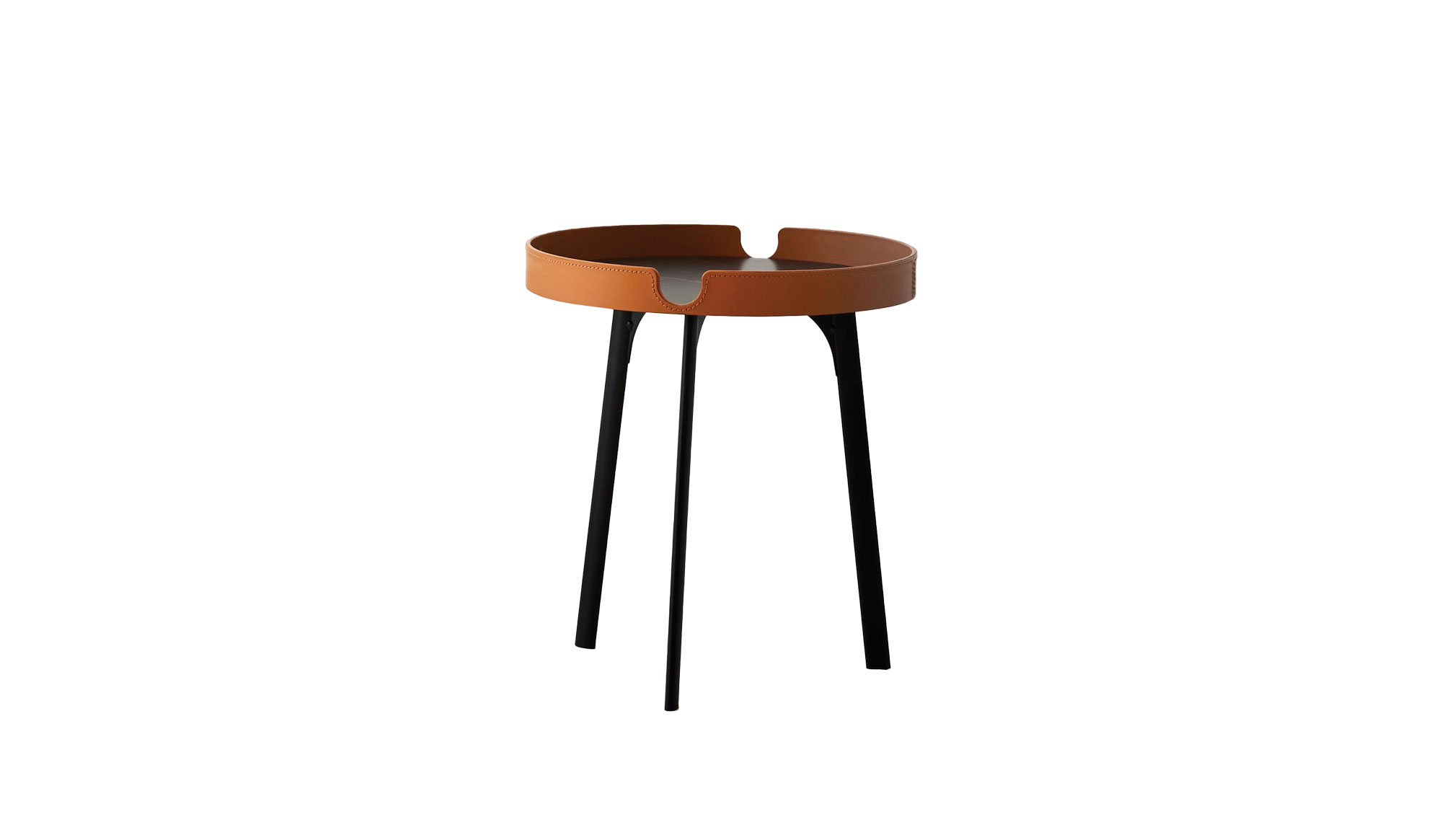

Zenius Lines Giobagnara
Giobagnara’s leather-encased Nespresso machine with vertical- or diamond-quilted detailing is genius in its unfussy application. The leather suits the product; the design channels the look of a luxury Italian sports car. The brand began with the Bagnara family producing household items in 1939, before moving into the luxury realm in the ’70s. Giorgio Bagnara changed its name to B. Home Interiors in 1999 and to the eponymous Giobagnara in 2014. If you like your home appliances with liberal leather detailing, it’s one to follow. About $7,900; Artemest.com
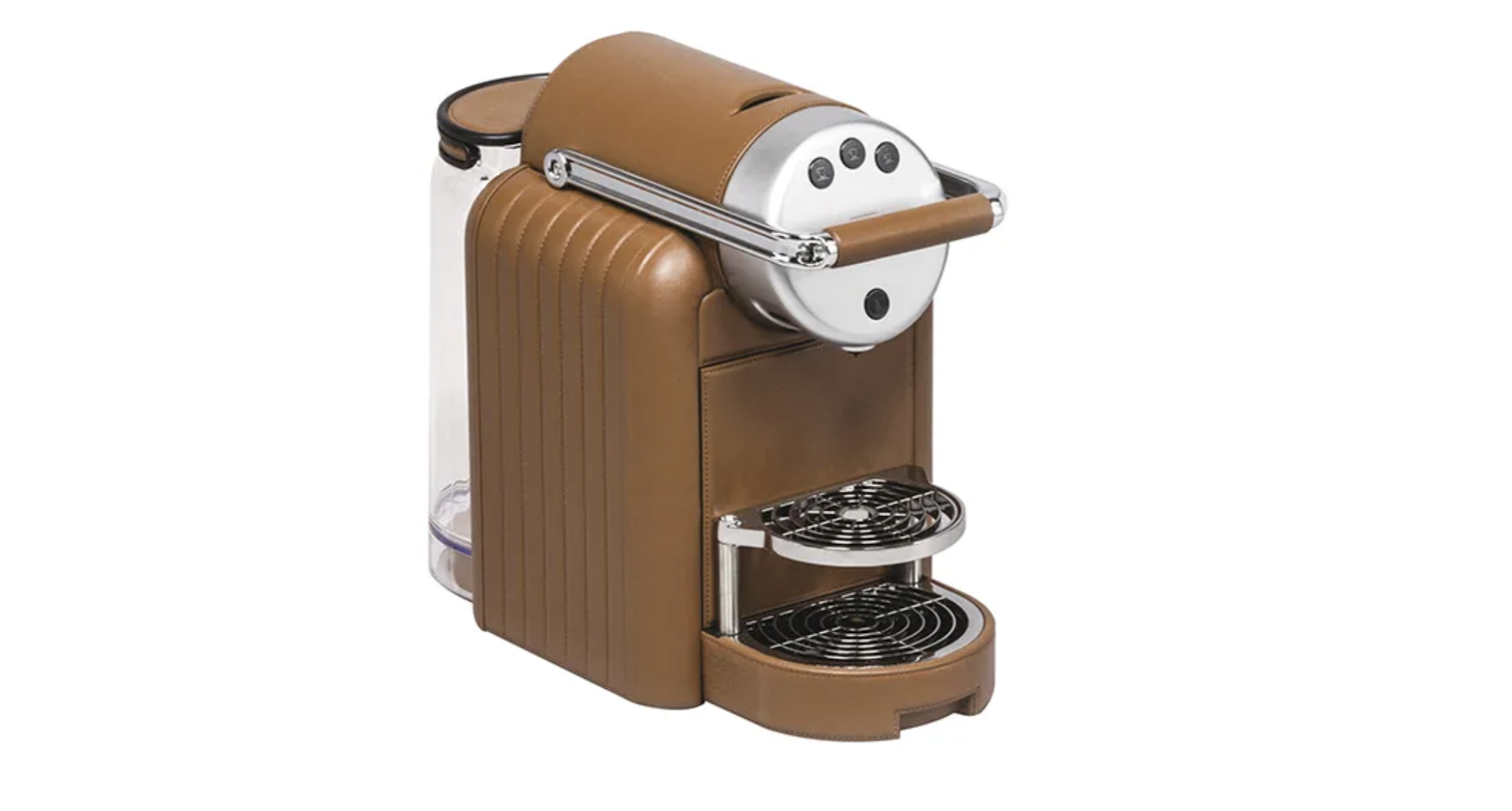

Vague, Tonucci Collection
Fun house–meets-Baroque in this softly symmetrical, wall-mounted mirror that playfully beckons you into another dimension (and will bounce beautiful light around the room). Designed by Viola Tonucci, who took the reins of Tonucci Collection from her father last year, the thick, leather-covered frame introduces architectural interest and a hint of levity to a room, be it traditional or modern. About $8,050; Tonucci.com
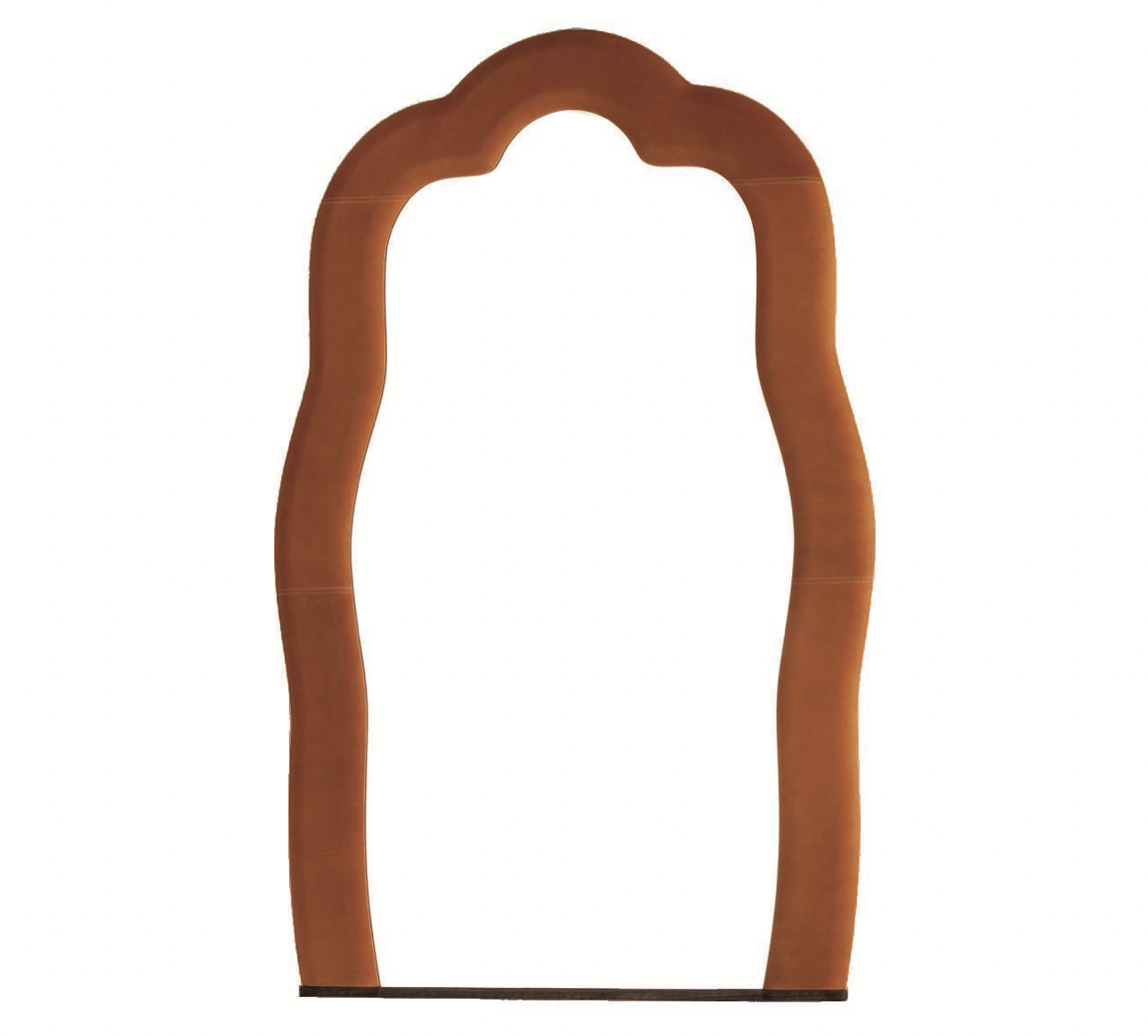

DS-707, de Sede
Given Philippe Malouin’s propensity for experimentation, it’s no wonder that Swiss furniture firm de Sede took a whole new approach in manufacturing Malouin’s DS-707 design. He began by noodling around with foam, folding it this way and that before settling on the serpentine shape. Although the silhouette made de Sede wary—creating it required the team to manipulate leather in a manner that could leave it less supple— the project prevailed with great success. The system itself invites experimentation as customers can configure the components to their heart’s content. From $30,450; deSede.com





















