The New Worlds Of Wine
Changing weather and emerging fortunes are conspiring to create promising vineyards in wholly unexpected places. But where will your next bombshell bottle come from?
Related articles
The world of wine has always operated on its own schedule—greatness takes time. It generally requires many seasons for a vineyard to mature to the point at which the vines produce wine with serious ageing potential. In the big picture, some European regions have spent a millennium or more refining the taste profiles of their bottlings.
But the combination of rapidly evolving technology, emerging international economies and the progressing effects of climate change has scrambled the traditional map and fast-forwarded the timeline. There’s now good wine from Virginia, Israel and Brazil, but some countries we know and love—including our very own Australia —have regions that are likely to struggle to continue producing the excellent wine we’re used to because of heat, drought and fires. But amid the chaos some happy surprises, with a number of previously overlooked countries and areas set to ascend.
Georgia
Georgian wine may present the perfect blend of storied past and exciting future. “It’s an ancient tradition, at least 8,000 years old,” says John Wurdeman, an American wunderkind impresario of Georgian grapes. But history isn’t what’s motivating the newest fans in the US. “American hipster wine bars are serving orange wines from there, made in clay pots, to rebel against the status quo Bordeaux and Napa wines they think are boring.” True enough—the bottles are popping up at places like wine bar Ten Bells on New York’s Lower East Side, as well as at the Michelin-starred Washington, D.C., restaurant Maydān.
Wurdeman cofounded Pheasant’s Tears, a boutique natural winery that makes 15 or 16 different bottlings every year. It’s the Georgian winery with perhaps the most US snob appeal, but it’s not alone; wine imports from Georgia to the US almost doubled this past year over 2018. Wurdeman employs the most distinct tradition of the country, fermenting all his wines in qvevri, the traditional clay pots that are buried in the ground.
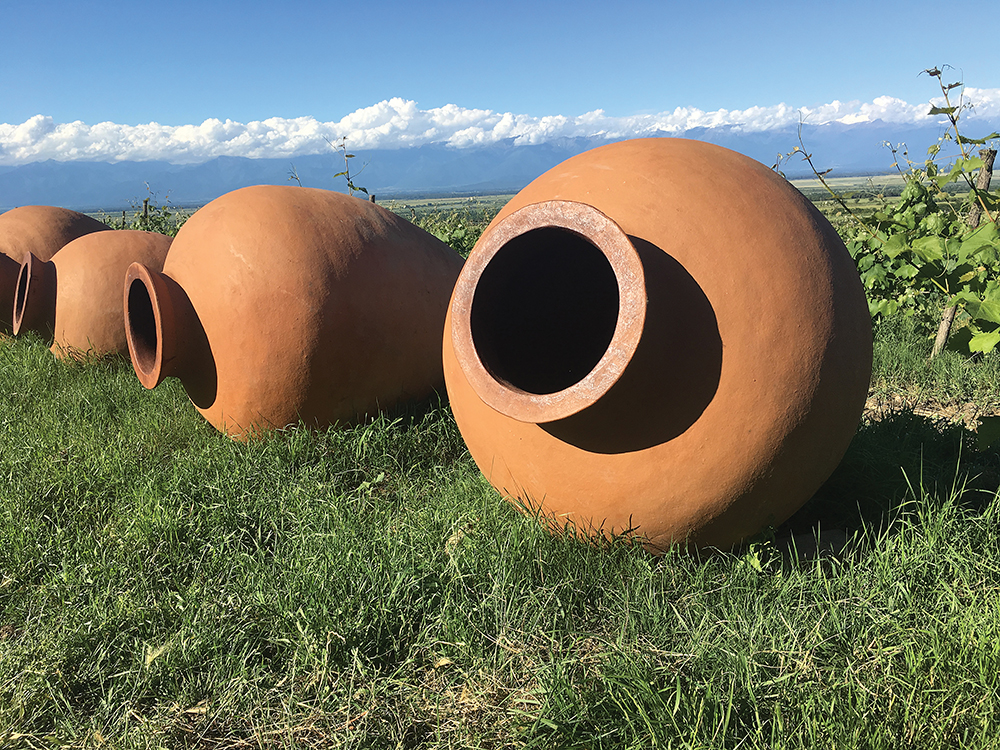

The old ways are part of Georgia’s unique story, but so are modern winemaking techniques—even though it has taken a while to shake off the stagnation of 70 years under Soviet domination, which did no favours for the wine industry.
“It’s not an easy history” is how Wurdeman puts it. Lisa Granik, who holds a prestigious master-of-wine title and wrote a book on Georgian wine, travels there often and says that, slowly, “Georgia is entering the modern world.”
Since the country has some 500 varieties of grapes, you can give up now on getting a handle on the full range of Georgian offerings, but among white, you’ll see Mtsvane, Kisi and Rkatsiteli grapes; among reds, Saperavi, which Granik calls the “Syrah of Georgia.” But, says Wurdeman, “if people try one Georgian wine, it’s often orange, since so many of our grapes lend themselves to that expression.”
His Pheasant’s Tears 2018 Mtsvane Amber Wine is an example of the quirky, intense and appealing style, which more people are discovering. It’s no wonder that Granik says, “In a generation, we’ll see more varieties and better quality. The best Georgian wines are yet to come.”
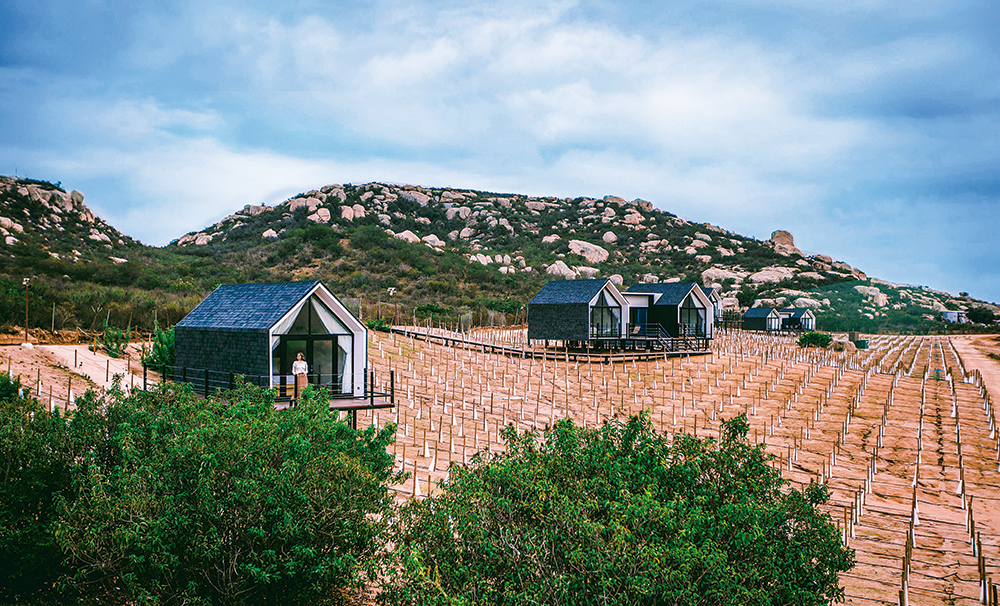
Valle de Guadalupe, Mexico
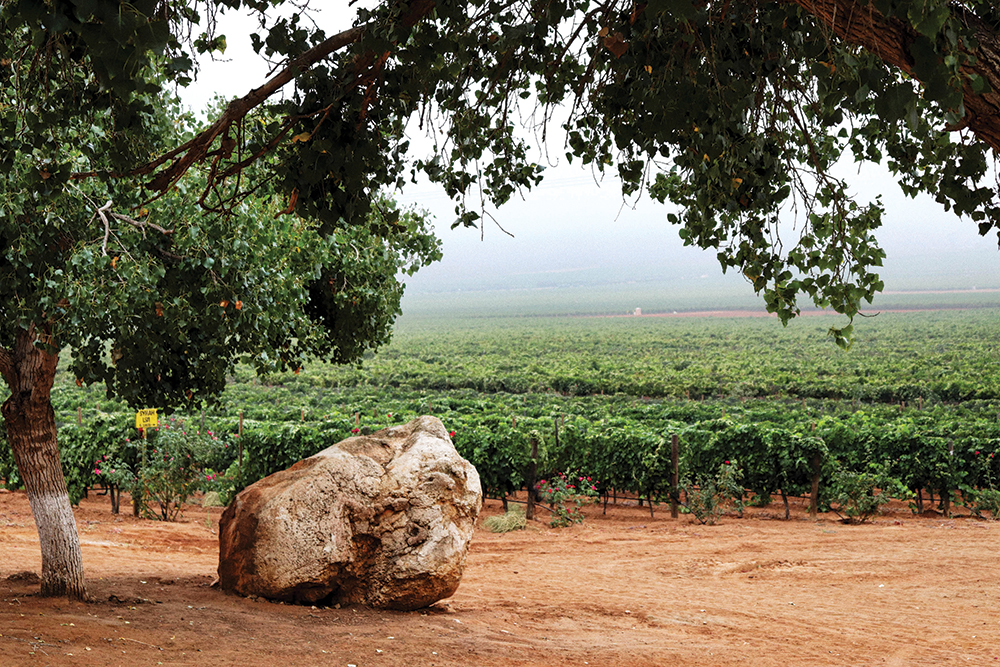
In the past five years, the idea of wine from Mexico went from crazy-sounding to very enticing. A mere 110-kilometre drive south of the US-Mexico border on the Baja Peninsula is the Valle de Guadalupe, where some 150 wineries, mostly small operations, have sprouted up to take advantage of wine-friendly conditions. The region produces 90 per cent of the country’s wines.
Most well-established wine regions have rules and customs governing what gets made, but Guadalupe is in a position to experiment and see what works.
“It reminds me of Paso Robles 15 years ago,” says Tomás Bracamontes, who has become a major importer of the wines through his company, La Competencia Imports. “There are no rules. You can do anything you want. Some people are making Pinot Noir and others Rhône blends.” Bracamontes’s money is on the white grape Chenin Blanc as far as up-and-comers go, and “Tempranillo is doing really well,” he adds, referring to Spain’s great red export.

The wineries may be small, but they’ve caught the eye of industry power players. Lourdes Martinez Ojeda became a talked-about winemaker with her work for Bodegas Henri Lurton, a Valle de Guadalupe venture of Bordeaux’s renowned Lurton family (they make Château Brane-Cantenac and many others).
“Having this great Bordeaux family down there has really helped,” says Jeff Harding, the beverage director at the Waverly Inn in New York.
Harding, who visited the region last year, quickly became a fan, putting Guadalupe wines on his list. He compares the climate to some familiar California regions.
“It’s hot in the day, but it’s between two mountain ranges, so it cools right down at night. It’s comparable to Napa.” (Others say the torrid climate of the Priorat area in Spain is closer to the mark.)
Harding’s primary recommendation is about taste: “Bigger, riper fruit” is the overall profile compared to other places. “They’re approachable and great to drink,” he adds, “and it doesn’t hurt that they go great with Mexican food. Without a doubt, we’ll be seeing more of these wines in 20 years.” Keen to try something you won’t get anywhere else? Sample the natural-style bottlings from La Casa Vieja: Made from the original rootstock—some of the vines are 120 years old—the wines are funky, fascinating and distinct.
Okanagan Valley, British Columbia
The emerging Canadian region making the biggest impression on global palates is the Okanagan Valley in British Columbia, the southern portion of which lies just across the border from Washington State. And the valley will be only more influential in the coming years.
It’s a long, skinny area oriented on a north-south axis: In the north, it’s cooler, and Pinot Noir and Riesling grapes thrive; in the south, much hotter and a home to Bordeaux red grapes such as Merlot and Cabernet Sauvignon. “There are so many places that make good Cab, but I loved the Riesling from Martin’s Lane,” says James Tidwell, master sommelier and co-founder of Texsom, an influential conference of sommeliers. “I brought some back from my trip—and I never do that.”
The region’s prime mover is Anthony von Mandl, owner of Martin’s Lane, Mission Hill winery and three other properties that he calls the “Iconic Wineries” of BC. “They’re all managed independently,” says von Mandl, “in the same way LVMH has 75 fashion brands.” Among the best of Mission Hill’s wines is the 2012 Oculus, a silky and rewarding Bordeaux-style blend. Another in von Mandl’s portfolio, CheckMate 2015 Little Pawn Chardonnay, scored 100 points from well-regarded Canadian critic John Schreiner; it also happened to nab the vote of former vice president Al Gore, who ordered two cases before that review was out. The irony of Gore’s connoisseurship does not escape von Mandl: “Little did he know it was enabled by climate change.”

England
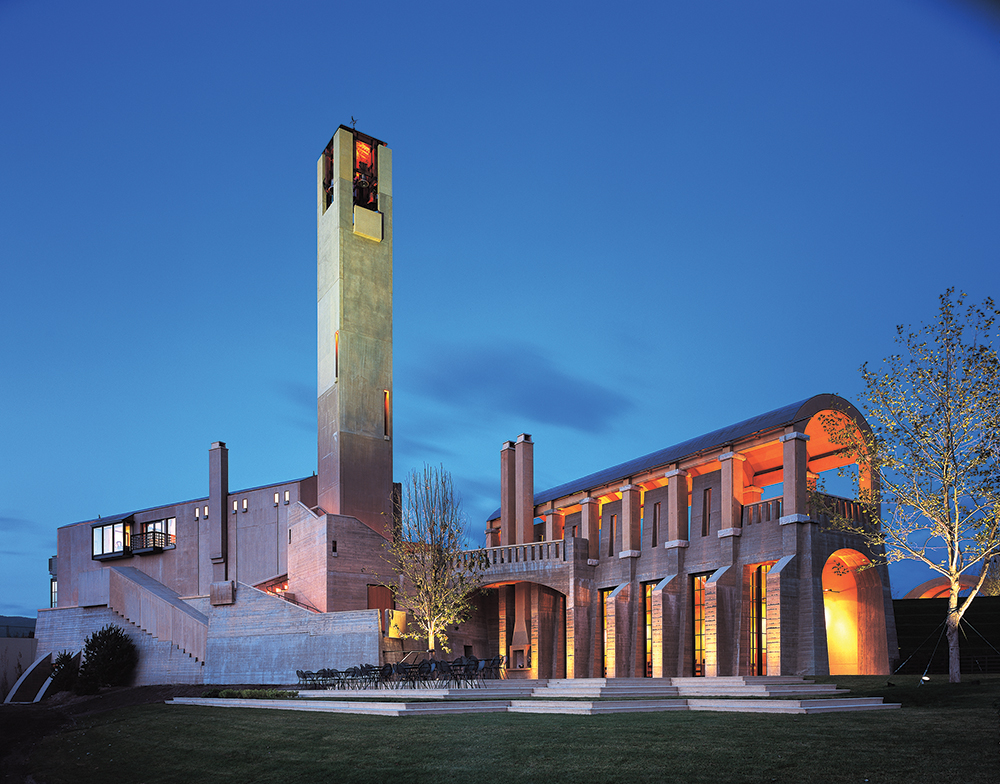
Over the past 30 years the bubblies have popped up in various parts of southern England, where climate change has created perfect conditions for making sparkling wine. The vintners explicitly model their businesses after Champagne, planting that region’s three grapes: Chardonnay, Pinot Noir and Pinot Meunier.
Hampshire’s Hambledon Vineyard, founded in 1952 and acquired in 1999 by former investment banker Ian Kellett, started selling sparkling wine in 2014.
“He saw the potential in the chalky soils here, just like in Champagne,” says Hambledon’s education manager, Katrina Smith. She adds that the winery’s bubblies are in a “broader, richer style” than those of similar English wineries, and that all the grapes come from nearby estate vineyards that Hambledon owns, giving the winery more control over the product.
The chief winemaker of another sparkling winery, Nyetimber, cautions against too simplistic a view regarding warming temperatures. “It’s really climate chaos,” states Cherie Spriggs. “In 2012 we didn’t harvest a single grape. It was the coldest conditions since we’ve been keeping records.”
It’s the cooler-than-most conditions that are generally why people like these wines and it helps explain Nyetimber’s elegant drops (its Blanc de Blancs is superb), which have been winning blind tastings against Champagne, which is deeply satisfying for Spriggs: “That’s our benchmark.”
India
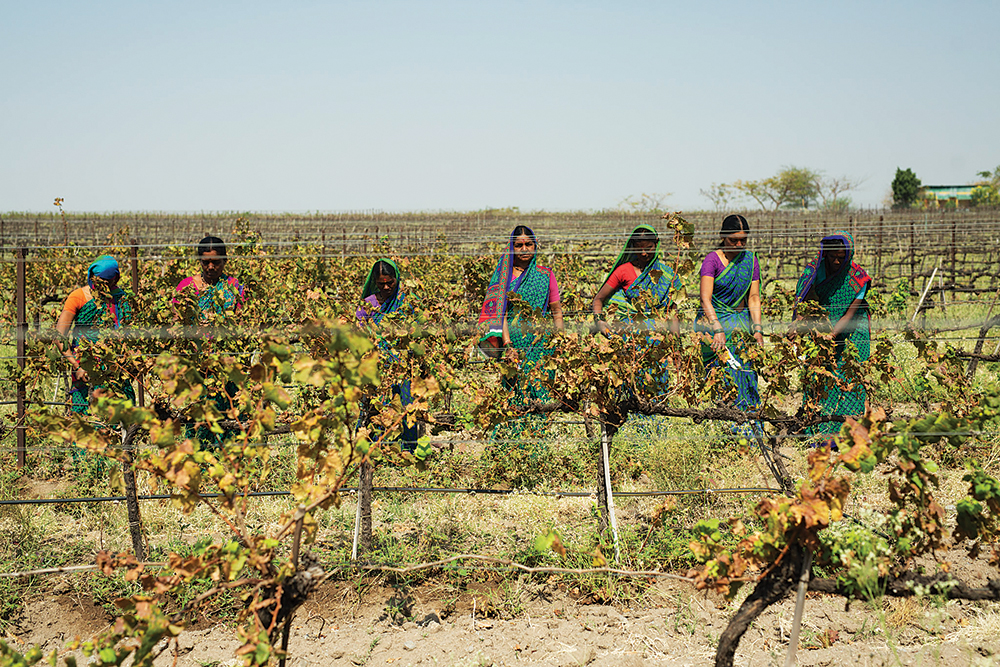

Despite ancient traditions of winemaking, India’s more a beer-and-spirits kind of country. But thanks to some wealthy entrepreneurs, things are starting to happen when it comes to premium wine.
Pharmaceutical tycoons Krishna Prasad and Uma Chigurupati established Krsma Estates in 2008 in Hampi Hills, a hot, dry inland area, which Prasad cheerfully concedes is “not a wine region.” But in his travels he stumbled upon a farmer who was growing wine grapes there and realised how good the conditions were. Krsma now produces three wines a year including a fairly classic Cabernet Sauvignon that’s been commended at international wine competitions. Now making 5,000 cases a year, Prasad notes that his “ego” dictates that the wine be exported too. “It’s a passion and a hobby for me,” he says, “not a business.”
Founder of Fratelli Vineyards’ Sette label, Kapil Sekhri, has similar inspirations. But he’s taken a decidedly cooperative approach: He makes Fratelli’s wines in India, with grapes from the Maharashtra region not too far from Mumbai, but he does it in partnership with Tuscan winemakers Piero Masi and the Secci family. And the wines have been praised by the respected British critic Jancis Robinson.
Sekhri also partners with French-born, Napa-based winemaker and entrepreneur Jean-Charles Boisset, to make three Indian wines under the J’noon label, the best of which is the white, a blend of Chardonnay and Sauvignon Blanc.
This story comes from our latest Autumn 2020 issue. To purchase a copy or to sign up to an annual subscription of Robb Report Australia & New Zealand click here. To stay in touch with all the latest news click here.
Subscribe to the Newsletter
Recommended for you
Bill Henson Show Opens at Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery
Dark, grainy and full of shadows Bill Henson’s latest show draws on 35 mm colour film shot in New York City in 1989.
April 20, 2024
Forever Leather
Furnishings wrapped or accented with classic, cognac-coloured hide create a patina that works with any aesthetic.
April 17, 2024
You may also like.
By Zeb Daemen
18/04/2024
You may also like.
Bill Henson Show Opens at Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery
Dark, grainy and full of shadows Bill Henson’s latest show draws on 35 mm colour film shot in New York City in 1989.
Bill Henson is one of Australia’s best-known contemporary photographers. When a show by this calibre of artist opens here, the art world waits with bated breath to see what he will unveil.
This time, he presents a historically important landscape series that chronicles a time in New York City that no longer exists. It’s a nostalgic trip back in time, a nocturnal odyssey through the frenetic, neon-lit streets of a long-lost America.
Known for his chiaroscuro style, Henson’s cinematic photographs often transform his subject into ambiguous objects of beauty. This time round, the show presents a mysterious walk through the streets of Manhattan, evoking a seedy, yet beautiful vision of the city.
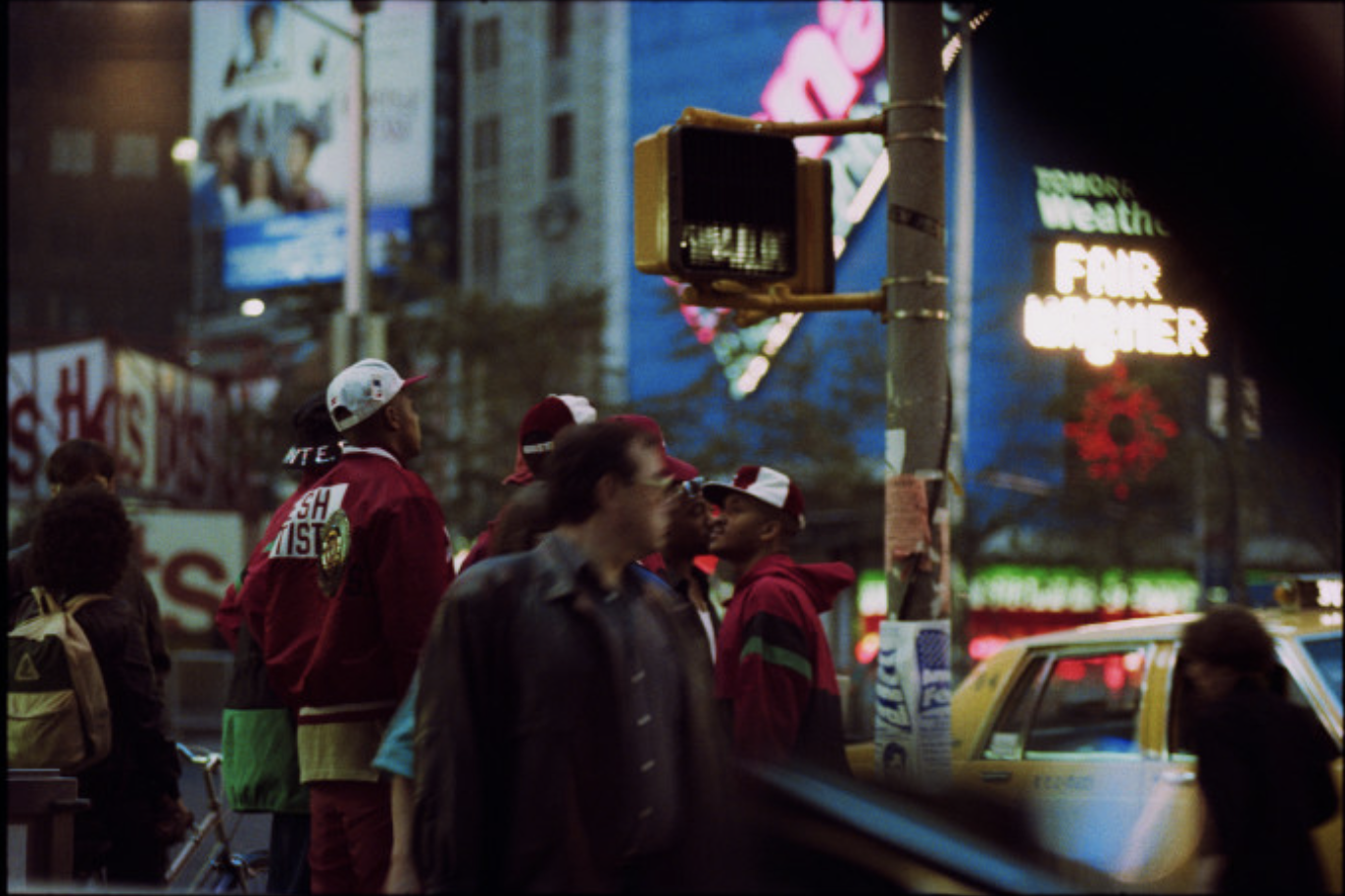
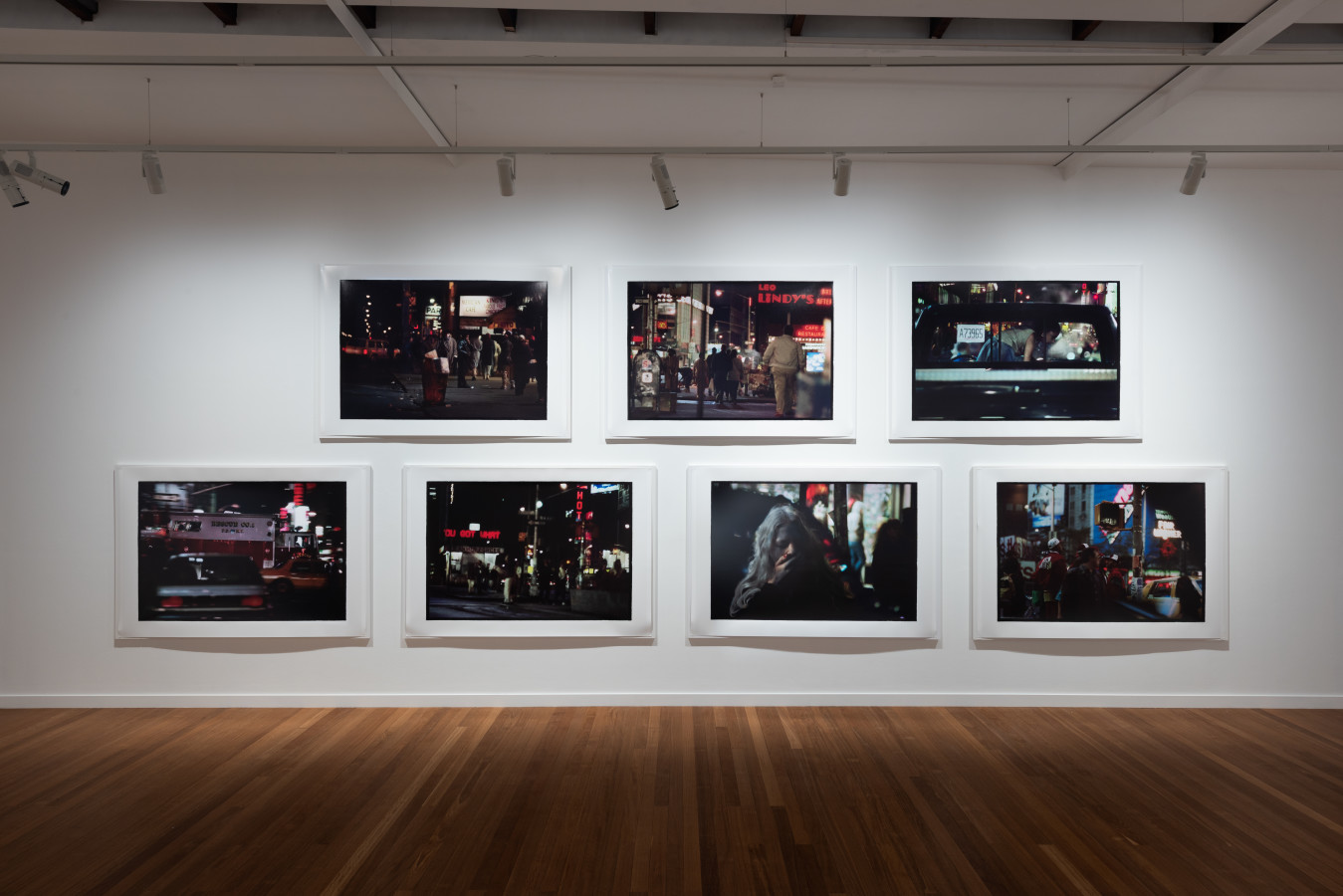


Relying on generative gaps, these landscapes result from Henson mining his archive of negatives and manipulating them to produce a finished print. Sometimes, they are composed by a principle of magnification, with Henson honing in on details, and sometimes, they are created through areas of black being expanded to make the scene more cinematic and foreboding. Like silence in a film or the pause in a pulse, the black suggests the things you can’t see.
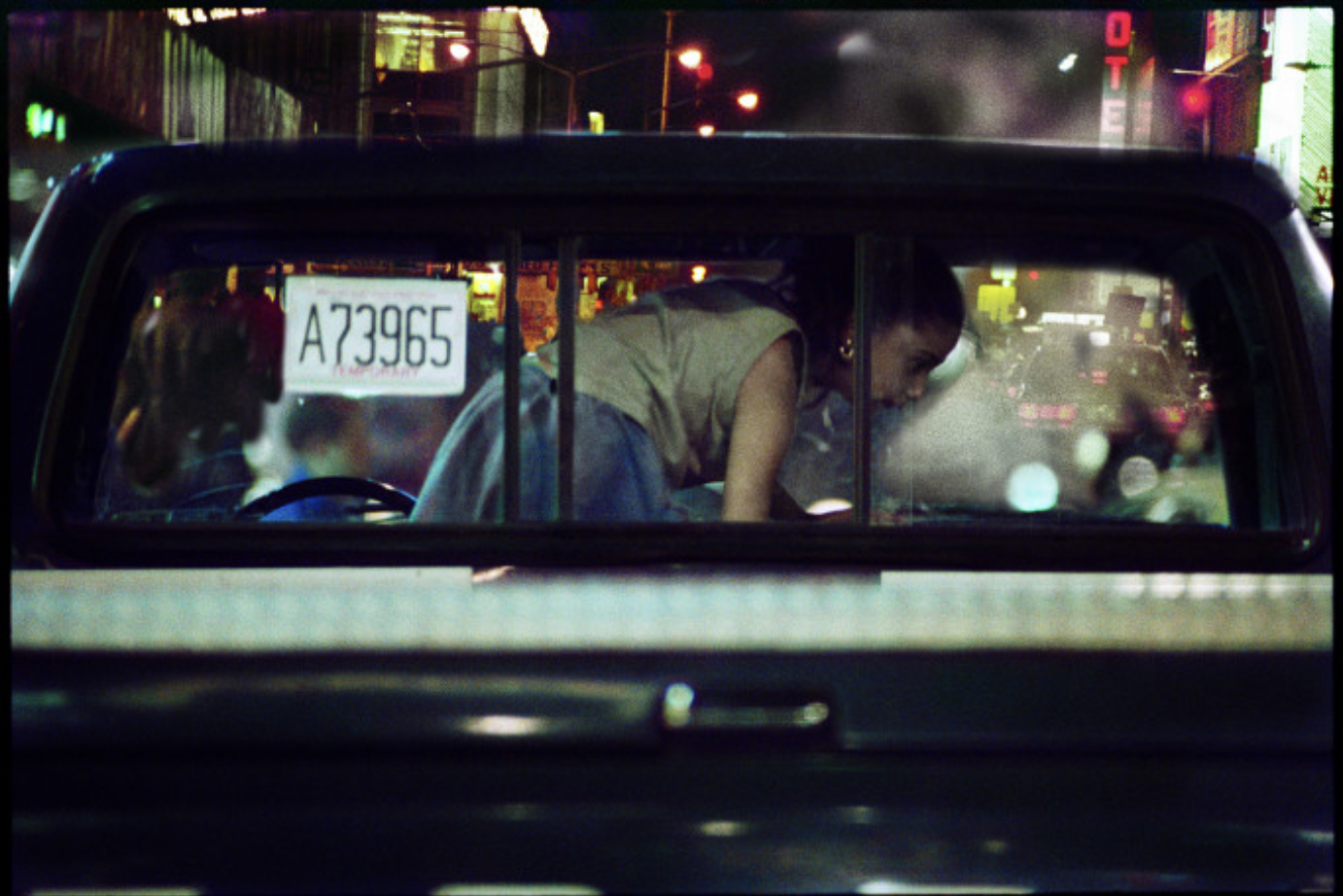


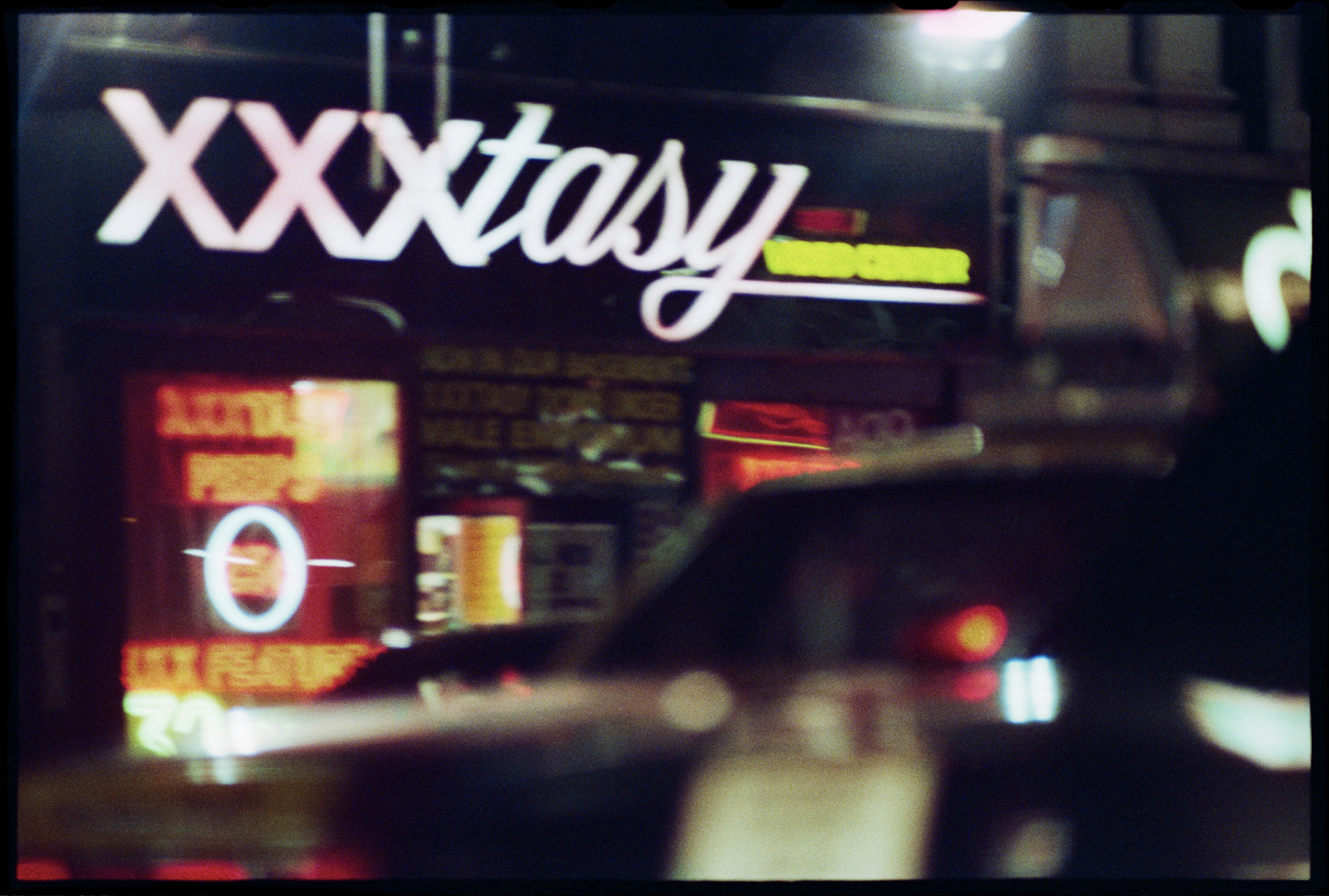
Henson’s illustrious career has spanned four decades and was memorably marred by controversy over a series of nude adolescent photographs shown in 2008, which made him front-page news for weeks. This series of portraits made Henson the subject of a police investigation during which no offence was found.
In recent years, Henson has been a sharp critic of cancel culture, encouraging artists to contribute something that will have lasting value and add to the conversation, rather than tearing down the past.
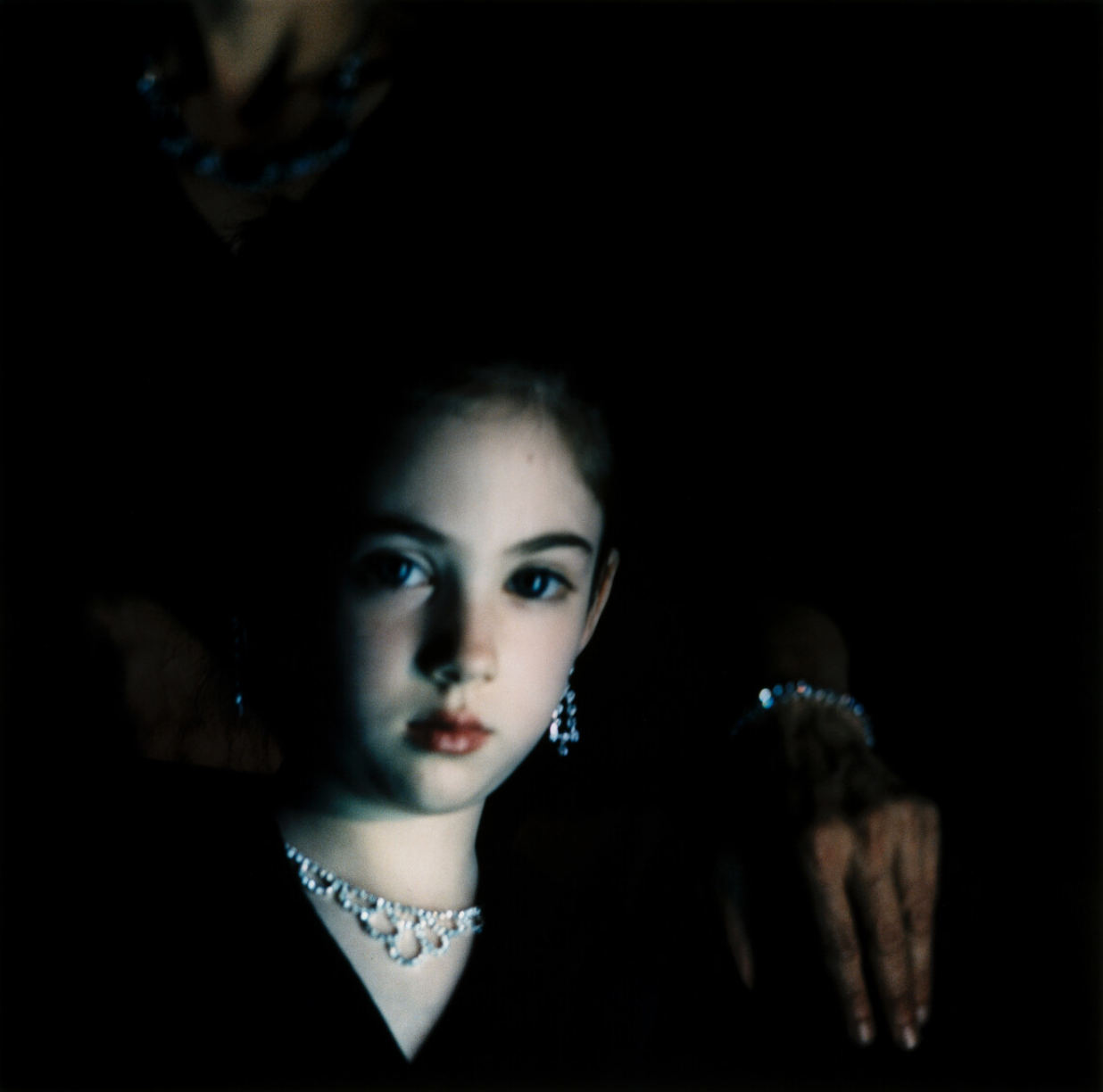

His work deals with the liminal space between the mystical and the real, the seen and unseen, the boundary between youth and adulthood.
His famous Paris Opera Project, 1990-91, pictured above, is similarly intense as the current show, dwelling on the border between the painterly and the cinematic.
Bill Henson’s ‘The Liquid Night’ runs until 11 May 2024 at Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery.
Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery, 8 Soudan Ln, Paddington NSW; roslynoxley9.com.au
You may also like.
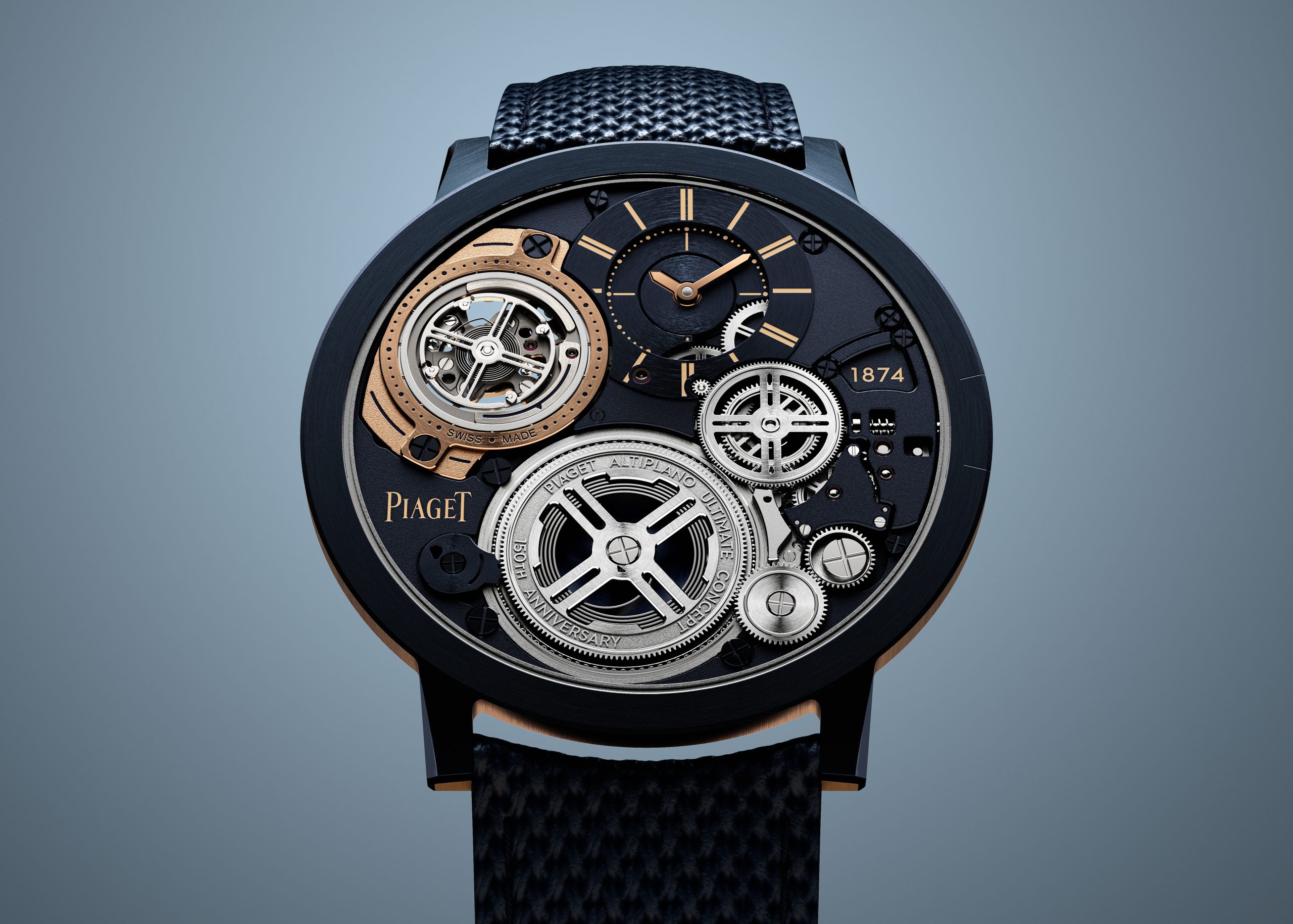
Watch of the Week: the Piaget Altiplano Ultimate Concept Tourbillon
The new release claims the throne as the world’s thinnest Tourbillon.
Piaget, the watchmaker’s watchmaker, has once again redefined the meaning of “ultra-thin” thanks to its newest masterpiece, the Altiplano Ultimate Concept Tourbillon—the world’s thinnest tourbillon watch.
In the world of high-watchmaking where thin is never thin enough—look at the ongoing battle between Piaget, Bulgari, and Richard Mille for the honours—Piaget caused a furore at Watches & Wonders in Geneva when it unveiled its latest feat to coincide with the Maison’s 150th year anniversary.
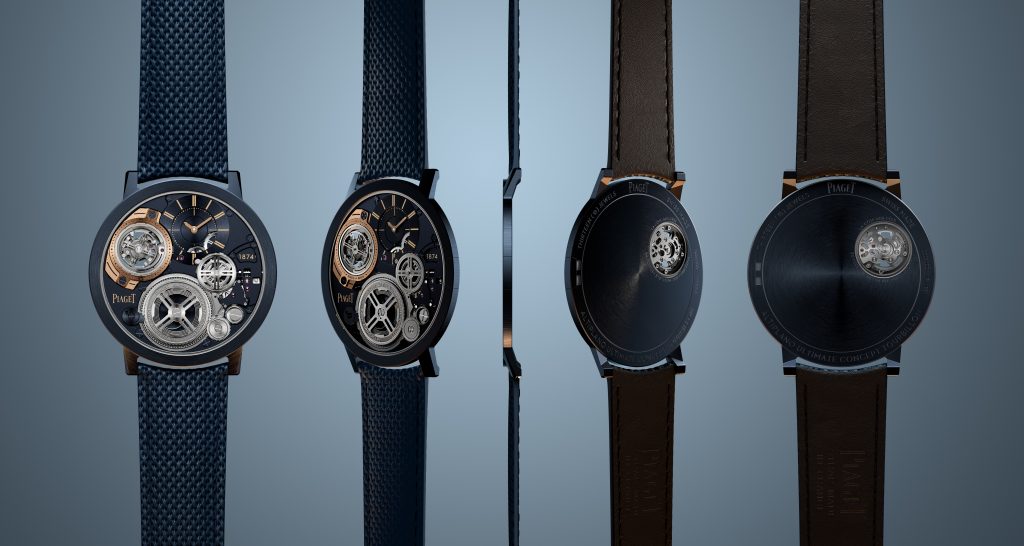

Piaget claims that the new Altiplano is “shaped by a quest for elegance and driven by inventiveness”, and while this might be true, it’s clear that the Maison’s high-watchmaking divisions in La Côte-aux-Fées and Geneva are also looking to end the conversation around who owns the ultra-thin watchmaking category.
The new Altiplano evidently pushes the boundaries of horological ingenuity 67 years after Piaget invented its first ultra-thin calibre—the revered 9P—and six years after it presented the world’s then-thinnest watch, the Altiplano Ultimate Concept. Now, debuting this unrivalled timepiece at just 2mm thick—the same thinness as its predecessor, yet now housing the beat of a flying tourbillon, prized by watchmaking connoisseurs—you can’t help but marvel at its ultra-thin mastery, whether the timepiece is to your liking or not.

In comparison, the Bulgari Octo Finissimo Tourbillon was 3.95mm thick when unveiled in 2020, which seems huge on paper compared to what Piaget has been able to produce. But to craft a watch as thin and groundbreaking as its predecessor, now with an added flying tourbillon complication, the whole watchmaking process had to be revalued and reinvented.
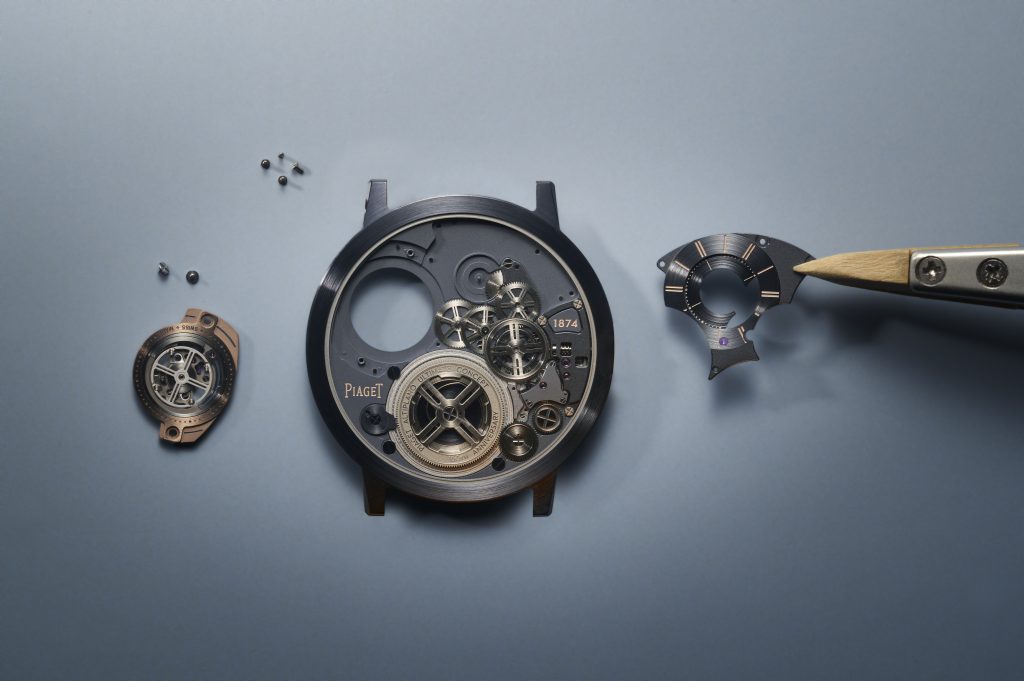
“We did far more than merely add a tourbillon,” says Benjamin Comar, Piaget CEO. “We reinvented everything.”
After three years of R&D, trial and error—and a redesign of 90 percent of the original Altiplano Ultimate Concept components—the 2024 version needs to be held and seen to be believed. The end product certainly isn’t a watch for the everyday watch wearer—although Piaget will tell you otherwise—but in many ways, the company didn’t conjure a timepiece like the Altiplano as a profit-seeking exercise. Instead, overcoming such an arduous and technical watchmaking feat proves that Piaget can master the flying tourbillon in such a whimsical fashion and, in the process, subvert the current state-of-the-art technical principles by making an impactful visual—and technical—statement.
The only question left to ask is, what’s next, Piaget?

—
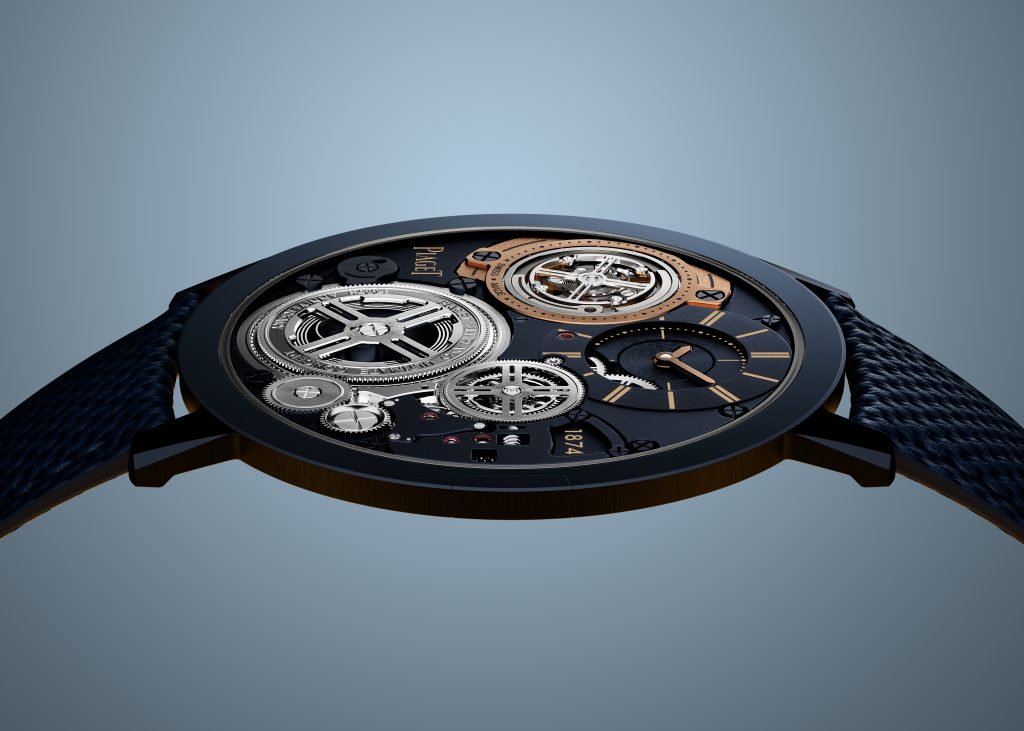
Model: Altiplano Ultimate Concept Tourbillon 150th Anniversary
Diameter: 41.5 mm
Thickness: 2 mm (crystal included)
Material: M64BC cobalt alloy, blue PVD -treated
Dial: Monobloc dial; polished round and baton indices, Bâton-shaped hand for the minutes Monobloc disc with a hand for the hours
Water resistance: 20m
Movement: Calibre 970P-UC, one-minute peripheral tourbillon
Winding: Hand-wound
Functions: hours, minutes, and small seconds (time-only)
Power reserve: 40 hours
Availability: Limited production, not numbered
Price: Price on request
You may also like.
Polar Opposites
A journey north to one of the harshest, remotest spots on Earth couldn’t be more luxurious.
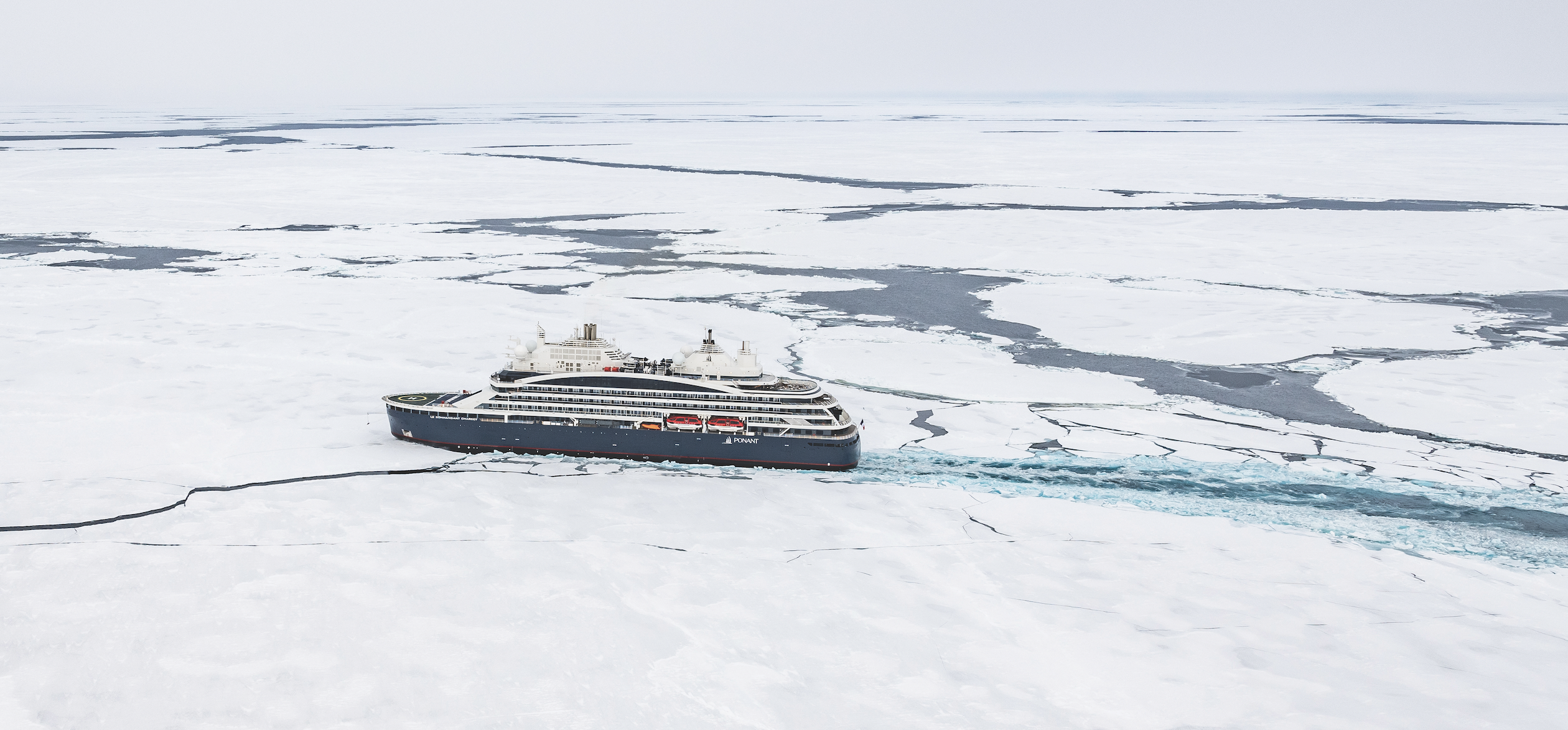
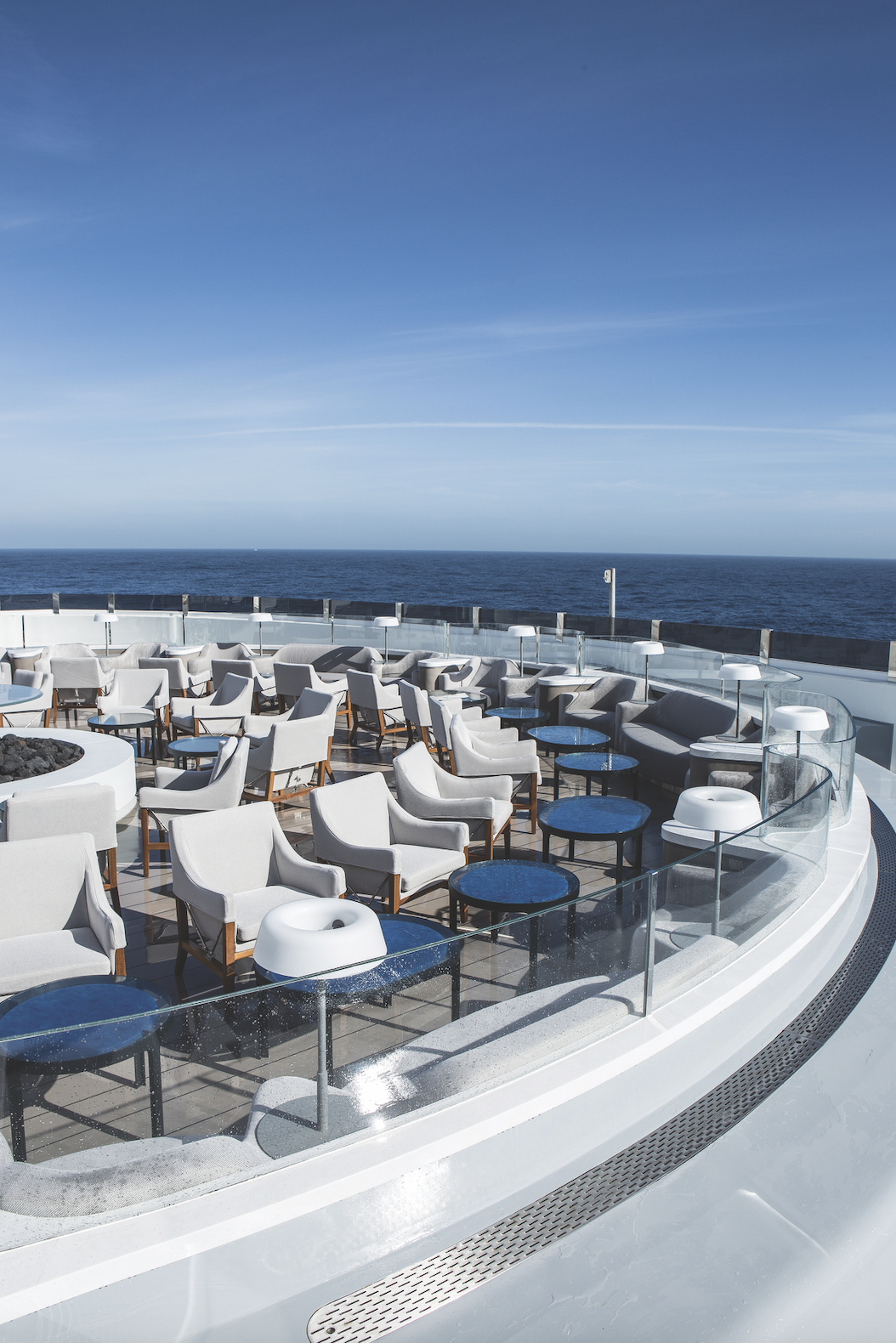
A century ago, an expedition to the North Pole involved dog sleds and explorers in heavy, fur-lined clothes, windburned and famished after weeks of trudging across ice floes, finally planting their nations’ flags in the barren landscape. These days, if you’re a tourist, the only way to reach 90 degrees north latitude, the geographic North Pole, is aboard Le Commandant Charcot, a six-star hotel mated to a massive, 150-metre ice-breaking hull.
My wife, Cathy, and I are among the first group of tourists aboard Ponant’s new expedition icebreaker, the world’s only Polar Class 2–rated cruise ship (of seven levels of ice vessel, second only to research and military vessels in ability to manoeuvre in Arctic conditions). Our arrival on July 14 couldn’t be more different from explorer Robert Peary’s on April 6, 1909. On that date, he reported, he staked a small American flag—sewed by his wife—into the Pole, joined by four Inuits and his assistant, Matthew Henson, a Black explorer from Maine who was with Peary on his two previous Arctic expeditions. (Peary’s claim of being first to the Pole was quickly disputed by another American, Frederick Cook, who insisted he’d spent two days there a year earlier. Scholars now view both claims with skepticism.)
Our 300-plus party’s landing, on Bastille Day, features the captain of the French ship driving around in an all-terrain vehicle with massive wheels and an enormous tricolour flag on the back, guests dressed in stylish orange parkas celebrating on the ice, and La Marseillaise, France’s national anthem, blaring from loudspeakers. After an hour of taking selfies and building snow igloos in the icescape, with temperatures in the relatively balmy low 30s, we head back into our heated sanctuary for mulled wine and freshly baked croissants. Mission accomplished. Flags planted. Now, lunch.
As a kid, I was fascinated by stories of adventurers trying to reach the North Pole without any means of rescue. In the 19th century, most of their attempts ended in disaster—ships getting trapped in the ice, a hydrogen balloon crashing, even cannibalism. It wasn’t until Cook and Peary reportedly set foot there that the race to the North Pole was really on. Norwegian Roald Amundsen, the first to reach the South Pole, in 1911, is credited with being the first to document a trip over the North Pole, which he did in 1926 in the airship Norge. In 1977, the nuclear-powered icebreaker Arktika became the first surface vessel to make it to the North Pole. Since then, only 18 other ships have completed the voyage.

Visiting the North Pole seemed about as likely for me as walking on the Moon. It wasn’t even on my bucket list. Then came Le Commandant Charcot, which was named after France’s most beloved polar explorer and reportedly cost about US$430 million (around $655 million) to build. The irony of visiting one of the planet’s most remote and inhospitable points while travelling in the lap of luxury doesn’t escape me or anyone else I speak with on the voyage. Danie Ferreira, from Cape Town, South Africa, describes it as “an ensemble of contradictions bordering on the absurd”. Ferreira, who is on board with his wife, Suzette, is a veteran of early-explorer-style high-Arctic journeys, months-long treks involving dog sleds and real toil and suffering. He booked this trip to obtain an official North Pole stamp for an upcoming two-volume collection of his photographs, Out in the Cold, documenting his polar adventures. “Reserving the cabin felt like a betrayal of my expeditionary philosophy,” he says with a laugh.
Then, like the rest of us, he embraces the contradictions. “This is like the first time I saw the raw artistry of Cirque du Soleil,” he explains. “Everything is beyond my wildest expectations, unrelatable to anything I’ve experienced.”

The 17-day itinerary launches from the Norwegian settlement of Longyearbyen, Svalbard, the northernmost town in the Arctic Circle, and heads 1,186 nautical miles to the North Pole, then back again. As a floating hotel, the vessel is exceptional: 123 balconied staterooms and suites, the most expensive among them duplexes with butler service (prices range from around $58,000 to $136,000 per person, double occupancy); a spa with a sauna, massage therapists, and aestheticians; a gym and heated indoor pool. The boat weighs more than 35,000 tons, enabling it to break ice floes like “a chocolate bar into little pieces, rather than slice through them”, according to Captain Patrick Marchesseau. Six-metre-wide stainless-steel propellers, he adds, were designed to “chew ice like a blender”.
Marchesseau, a tall, lanky, 40-ish mariner from Brittany, impeccable in his navy uniform but rocking royal-blue boat shoes, proves to be a charming host. Never short of a good quip, he’s one of three experienced ice captains who alternate at the helm of Charcot throughout the year. He began piloting Ponant ships through drifting ice floes in Antarctica in 2009, when he took the helm of Le Diamant, Ponant’s first expedition vessel. “An epic introduction,” Marchesseau calls those early voyages, but the isolated, icebound North Pole aboard a larger, more complicated vessel is potentially an even thornier challenge. “We’ll first sail east where the ice is less concentrated and then enter the pack at 81 degrees,” he tells a lecture hall filled with passengers on day one. “We don’t plan to stop until we get to the North Pole.”
Around us, the majority of the other 101 guests are older French couples; there are also a few extended families, some other Europeans, mostly German and Dutch, as well as 10 Americans. Among the supporting cast are six research scientists and 221 staff, including 18 naturalist guides from a variety of countries.
The first six days are more about the journey than the destination. Cathy and I settle into our comfortable stateroom, enjoy the ocean views from our balcony, make friends with other guests and naturalists, frequent the spa, and indulge in the contemporary French cuisine at Nuna, which is often jarred by ice passing under the hull, as well as at the more casual Sila (Inuit for “sky”). There are the usual cruise events: the officers’ gala, wine pairings, daily French pastries, Broadway-style shows, opera singers and concert pianists. Initially, I worry about “Groundhog Day” setting in, but once we hit patchy ice floes on day two, it’s clear that the polar party is on. The next day, we’re ensconced in the ice pack.
Veterans of Arctic journeys immediately feel at home. Ferreira, often found on the observation deck 15 metres above the ice with his long-lensed cameras, is in his element snapping different patterns and colours of the frozen landscape. “It feels like combining low-level flying with an out-of-body experience,” he says. “Whenever the hull shudders against the ice, I have a reality check.”

“I came back because I love this ice,” adds American Gin Millsap, who with her husband, Jim, visited the North Pole in 2015 aboard the Russian nuclear icebreaker Fifty Years of Victory, which for obvious reasons is no longer a viable option for Americans and many Europeans. “I love the peace, beauty and calmness.”
It is easy to bliss out on the endless barren vistas, constantly morphing into new shapes, contours and shades of white as the weather moves from bright sunshine to howling snowstorms—sometimes within the course of a few hours. I spend a lot of time on the cold, windswept bow, looking at the snow patterns, ridges and rivers flowing within the pale landscape as the boat crunches through the ice. It feels like being in a black-and-white movie, with no colours except the turquoise bottoms of ice blocks overturned by the boat. Beautiful, lonely, mesmerising.
Rather than a solid landmass, the Arctic ice pack is actually millions of square kilometres of ice floes, slowly pushed around by wind and currents. The size varies according to season: this past winter, the ice was at its fifth-lowest level on record, encompassing 14.6 million square kilometres, while during our cruise it was 4.7 million square kilometres, the 10th-lowest summer number on record. There are myriad ice types—young ice, pancake ice, ice cake, brash ice, fast ice—but the two that our ice pilot, Geir-Martin Leinebø, cares about are first-year ice and old ice. The thinness of the former provides the ideal route to the Pole, while the denseness of the aged variety can result in three-to-eight-metre-high ridges that are potentially impassable. Leinebø is no novice: in his day job, he’s the captain of Norway’s naval icebreaker, KV Svalbard, the first Norwegian vessel to reach the North Pole, in 2019.

It’s not a matter of just pointing the boat due north and firing up the engine. Leinebø zigzags through the floes. A morning satellite feed and special software aid in determining the best route; the ship’s helicopter sometimes scouts 65 or so kilometres ahead, and there’s a sonar called the Sea Ice Monitoring System (SIMS). But mostly Leinebø uses his eyes. “You look for the weakest parts of the ice—you avoid the ridges because that means thickness and instead look for water,” he says. “If the ‘water sky’ in the distance is dark, it’s reflecting water like a mirror, so you head in that direction.”
Everyone on the bridge is surprised by the lack of multi-year ice, but with more than a hint of disquietude. Though we don’t have to ram our way through frozen ridges, the advance of climate change couldn’t be more apparent. Environmentalists call the Arctic ice sheet the canary in the coal mine of the planet’s climate change for good reason: it is happening here first. “It’s not right,” mutters Leinebø. “There’s just too much open water for July. Really scary.”
The Arctic ice sheet has shrunk to about half its 1985 size, and as both mariners and scientists on board note, the quality of the ice is deteriorating. “It’s happening faster than our models predicted,” says Marisol Maddox, senior arctic analyst at the Polar Institute of the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars. “We’re seeing major events like Greenland’s ice sheet melting and sliding into the ocean—that wasn’t forecasted until 2070.” The consensus had been that the Arctic would be ice-free by 2050, but many scientists now expect that day to come in the 2030s.
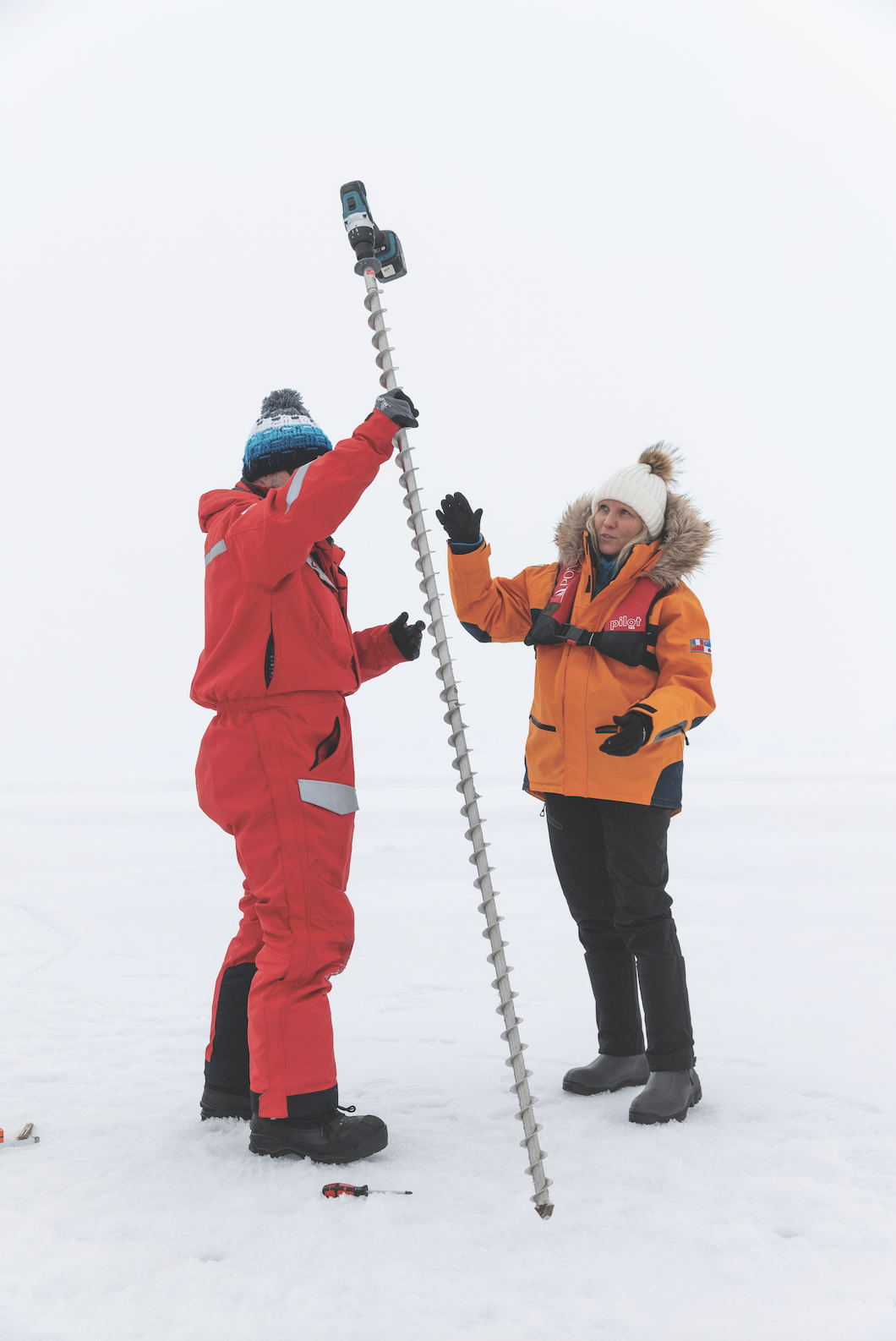
That deterioration, it turns out, is why the three teams of scientists are on the voyage—two studying the ice and the other assessing climate change’s impact on plankton. As part of its commitment to sustainability, Ponant has designed two research labs—one wet and one dry—on a lower deck. “We took the advice of many scientists for equipping these labs,” says Hugues Decamus, Charcot’s chief engineer, clearly proud of the nearly US$12 million facilities.
The combined size of the labs, along with a sonar room, a dedicated server for the scientists, and a meteorological station on the vessel’s top deck, totals 130 square metres—space that could have been used for revenue generation. Ponant also has two staterooms reserved for scientists on each voyage and provides grants for travel expenses. The line doesn’t cherrypick researchers but instead asks the independent Arctic Research Icebreaker Consortium (ARICE) to choose participants based on submissions.

The idea, says the vessel’s science officer on this voyage, Daphné Buiron, is to make the process transparent and minimise the appearance of greenwashing. “Yes, this alliance may deliver a positive public image for the company, but this ship shows we do real science on board,” she says. The labs will improve over time, adds Decamus, as the ship amasses more sophisticated equipment.
Research scientists and tourist vessels don’t typically mix. The former, wary of becoming mascots for the cruise lines’ sustainability marketing efforts, and cognisant of the less-than-pristine footprint of many vessels, tend to be wary. The cruise lines, for their part, see scientists as potentially high maintenance when paying customers should be the priority. But there seemed to be a meeting of the minds, or at least a détente, on Le Commandant Charcot.
“We discuss this a lot and are aware of the downsides, but also the positives,” says Franz von Bock und Polach, head of the institute for ship structural design and analysis at Hamburg University of Technology, specialising in the physics of sea ice. Not only does Charcot grant free access to these remote areas, but the ship will also collect data on the same route multiple times a year with equipment his team leaves on board, offering what scientists prize most: repeatability. “One transit doesn’t have much value,” he says. “But when you measure different seasons, regions and years, you build up a more complex picture.” So, more than just a research paper: forecasts of ice conditions for long-term planning by governments as the Arctic transforms.
Nils Haëntjens, from the University of Maine, is analysing five-millilitre drops of water on a high-tech McLane IFCB microscope. “The instrument captures more than 250,000 images of phytoplankton along the latitudinal transect,” he says. Charcot has doors in the wet lab that allow the scientists to take water samples, and in the bow, inlets take in water without contaminating it. Two freezers can preserve samples for further research back in university labs.
Even though the boat won’t stop, the captain and chief engineer clearly want to make the science missions work. Marchesseau dispatches the helicopter with the researchers and their gear 100 kilometres ahead, where they take core samples and measurements. I spot them in their red snowsuits, pulling sleds on an ice floe, as the boat passes. Startled to see living-colour humans on the ice after days of monochrome, I feel a pang of jealousy as I head for a caviar tasting.
The only other humans we encounter on the journey north are aboard Fifty Years of Victory, the Russian icebreaker. The 160-metre orange- and-black leviathan reached the North Pole a day earlier—its 59th visit—and is on its way back to Murmansk. It’s a classic East meets West moment: the icebreaker, launched just after the collapse of the Soviet Union, meeting the new standard of polar luxury.
The evening before Bastille Day, Le Commandant Charcot arrives at the North Pole. Because of the pinpoint precision of the GPS, Marchesseau has to navigate back and forth for about 20 minutes—with a bridge full of passengers hushing each other so as not to distract him—until he finds 90 degrees north. That final chaotic approach to the top of the world in the grey, windswept landscape looks like a kid’s Etch A Sketch on the chartplotter, but it is met with rousing cheers. The next morning, with good visibility and light winds, we spill out onto the ice for the celebration, followed by a polar plunge.
As guests pose in front of flags and mile markers for major cities, the naturalist guides, armed with rifles, establish a wide perimeter to guard against polar bears. The fearless creatures are highly intelligent, with razor-sharp teeth, hooked claws and the ability to sprint at 40 km/h. Males average about three metres tall and weigh around 700 kilos. They are loners that will kill anything—including other bears and even their own cubs. Cathy and I walk around the far edges of the perimeter to enjoy some solitude. Looking out over the white landscape, I know this is a milestone. But it feels odd that getting here didn’t involve any sweat or even a modicum of discomfort.

The rest of the week is an entirely different trip. On the return south, we see a huge male polar bear ambling on the ice, looking over his shoulder at us. It is our first sighting of the Arctic’s apex predator, and everyone crowds the observation lounge with long-lensed cameras. The next day, we see another male, this one smaller, running away from the ship. “They have many personalities,” says Steiner Aksnes, head of the expedition team, who has led scientists and film crews in the Arctic for 25 years. We see a dozen on the return to Svalbard, where 3,000 are scattered across the archipelago, outnumbering human residents.
The last five days we make six stops on different islands, travelling by Zodiac from Charcot to various beaches. On Lomfjorden, as we look on a hundred yards from shore, a mother polar bear protects her two cubs while a young male hovers in the background. On a Zodiac ride off Alkefjellet, the air is alive with birds, including tens of thousands of Brünnich’s guillemots as well as glaucous gulls and kittiwakes, which nest in that island’s cliffs, while a young male polar bear munches on a ring seal, chin glistening red.
On this part of the trip, the expedition team, mostly 30-something, free-spirited scientists whose areas of expertise range from botany to alpine trekking to whales, lead hikes across different landscapes. The jam-packed schedule sometimes involves three activities per day and includes following the reindeer on Palanderbukta, seeing a colony of 200 walruses on Kapp Lee, hiking the black tundra of Burgerbukta (boasting 3.8-cm-tall willows—said to be the smallest trees in the world and the largest on Svalbard—plus mosquitoes!), watching multiple species of whales breaching offshore, and kayaking the ice floes of Ekmanfjorden. Svalbard is a protected wilderness area, and the cruise lines tailor their schedules so vessels don’t overlap, giving visitors the impression they are setting foot on virgin land.
Chances to experience that sense of discovery and wonder, even slightly stage-managed ones, are dwindling along with the ice sheet and endangered wildlife. If a stunning trip to a frozen North Pole is on your bucket list, the time to go is now.

PARADIGM SHIP
For those studying polar ice, a berth aboard Le Commandant Charcot is like a winning lottery ticket. “This cruise ship is one of the few resources scientists can use, because nothing else can get there,” says G. Mark Miller, CEO of research-vessel builder Greenwater Marine Sciences Offshore (GMSO) and a former ship captain for the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). “Then factor in 80 percent of scientists who want to go to sea, can’t, because of the shortage of research vessels.”
Both Ponant and Viking have designed research labs aboard new expedition vessels as part of their sustainability initiatives. “Remote areas like Antarctica need more data—the typical research is just single data points,” says Damon Stanwell-Smith, Ph.D., head of science and sustainability at Viking. “Every scientist says more information is needed.” The twin sisterships Viking Octantis and Viking Polaris, which travel to Antarctica, Patagonia, the Great Lakes and Canada, have identical 35-square-metre labs, separated into wet and dry areas and fitted out with research equipment. In hangars below are military-grade rigid-hulled inflatables and two six-person yellow submersibles (the pair on Octantis are named John and Paul, while Polaris’s are George and Ringo). Unlike Ponant, Viking doesn’t have an independent association choose scientists for each voyage. Instead, it partners with the University of Cambridge, the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, and NOAA, which send their researchers to work with Viking’s onboard science officers.

“Some people think marine research is sticking some kids on a ship to take measurements,” says Stanwell-Smith. “But we know we can do first-rate science—not spin.” Other cruise lines are also embracing sustainability initiatives, with coral-reef-restoration projects and water-quality measurements, usually in partnership with universities. Just about every vessel has “citizen-scientist” research programs allowing guests the opportunity to count birds or pick up discarded plastic on beaches. So far, Ponant and Viking are the only lines with serious research labs. Ponant is adding science officers to other vessels in its fleet. As part of the initiatives, scientists deliver onboard lectures and sometimes invite passengers to assist in their research.

Given the shortage of research vessels, Stanwell-Smith thinks this passenger-funded system will coexist nicely with current NGO- and government-owned ships. “This could be a new paradigm for exploring the sea,” he says. “Maybe the next generation of research vessels will look like ours.”
You may also like.
By Jay Cheses
17/04/2024
Shifting into Neutral
How to Rock a Neutral Selection of Menswear This Autumn.
Model, designer and international jet-setter Johannes Huebl dons autumn’s most refined looks and shares his style insights gleaned from years in front of the camera. Styled by Alex Badia and photographed by Feb Daemen in Barcelona, Huebel’s simple advice rings true.
“I like a natural colour palette and wear monochrome a lot. I tend to stick to no more than two textures in an outfit: a cashmere overshirt and corduroy trousers, for example,” says Huebel, reflecting on his signature style which is captured well in this Autumnal photoshoot.
“Attitude—and a fashionably relaxed mindset— is the secret to wearing clothes like these. The comfort and quality put me at ease.”
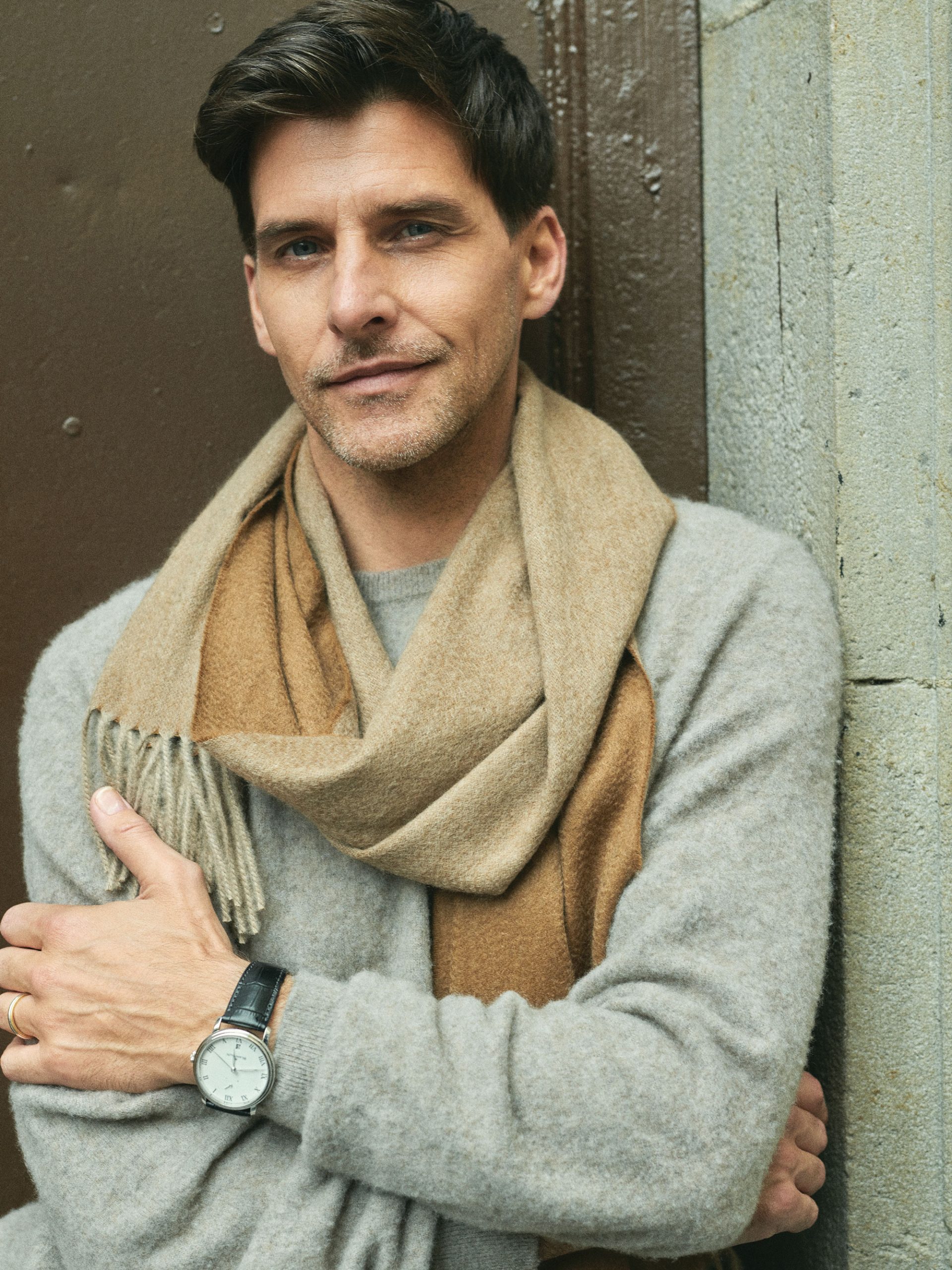

Massimo Alba hand-brushed-cashmere sweater, $1,440; Begg & Co cashmere scarf, $870; preowned Blancpain Villeret watch $34,720
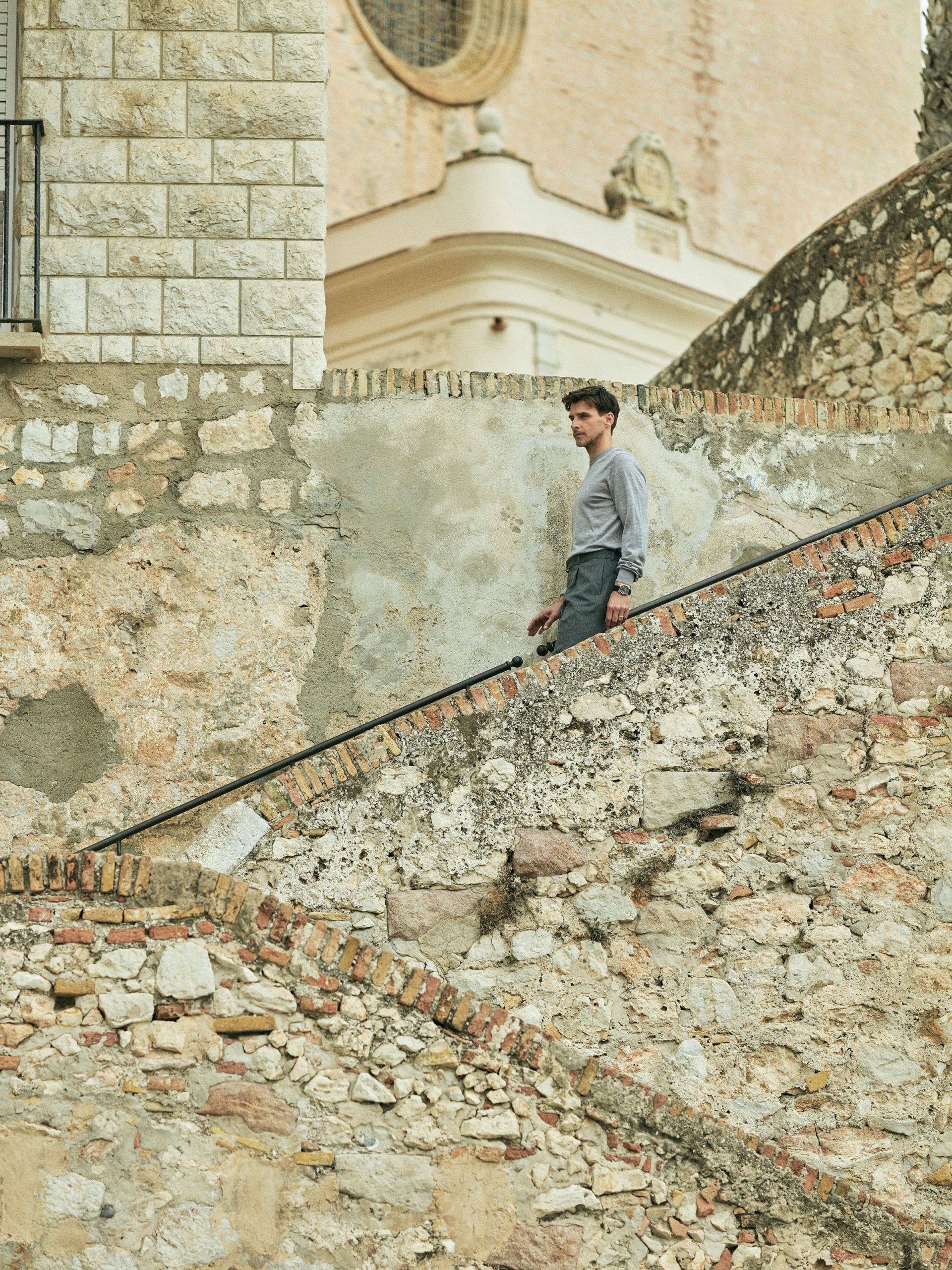

L.B.M 1911 wool sweater, $595; Officine Générale wool pants, $995.
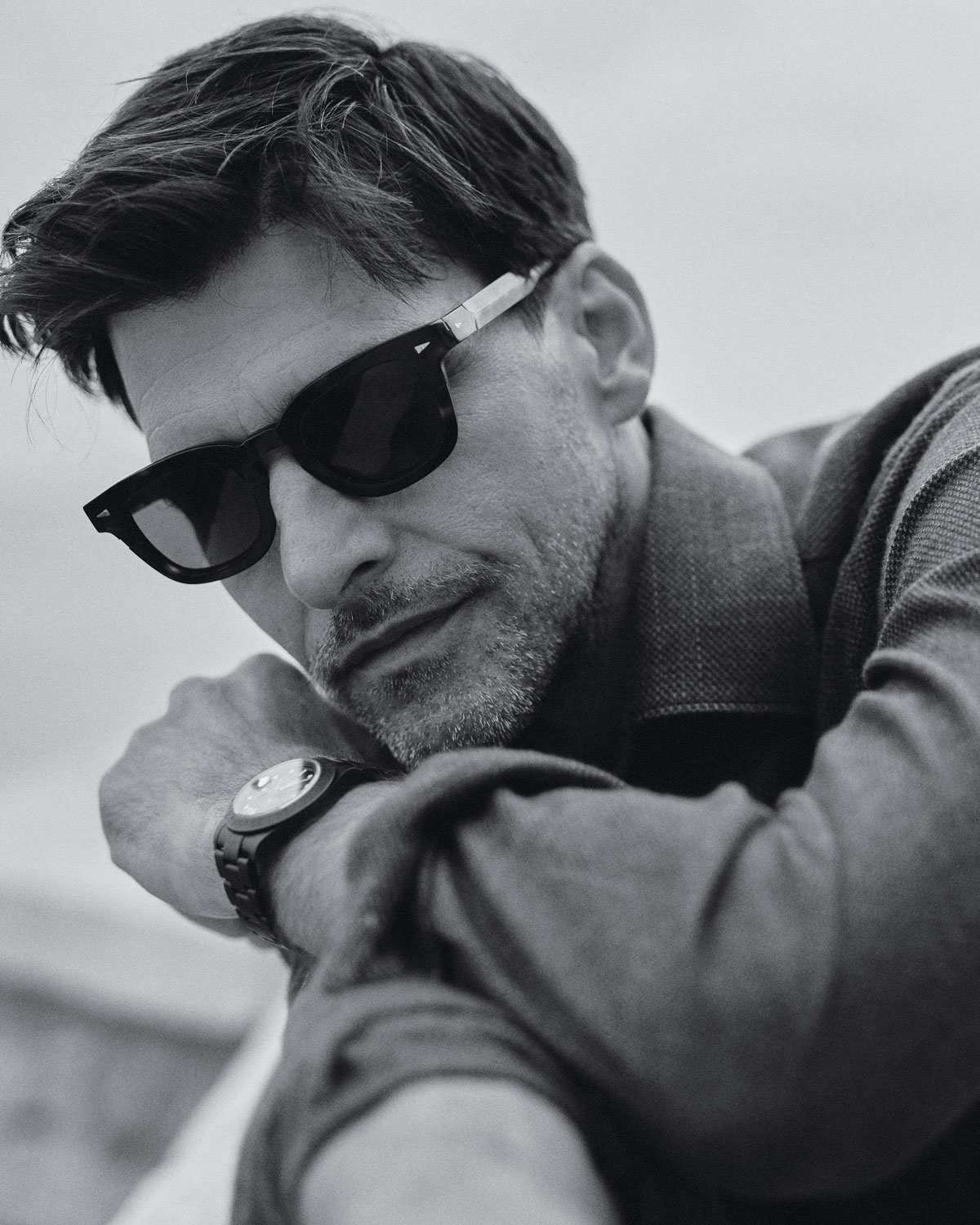

Kiton cashmere and silk overshirt, $10,065; Ahlem acetate sunglasses, $780; Rolex x Bamford Watch Department watch (model’s own)
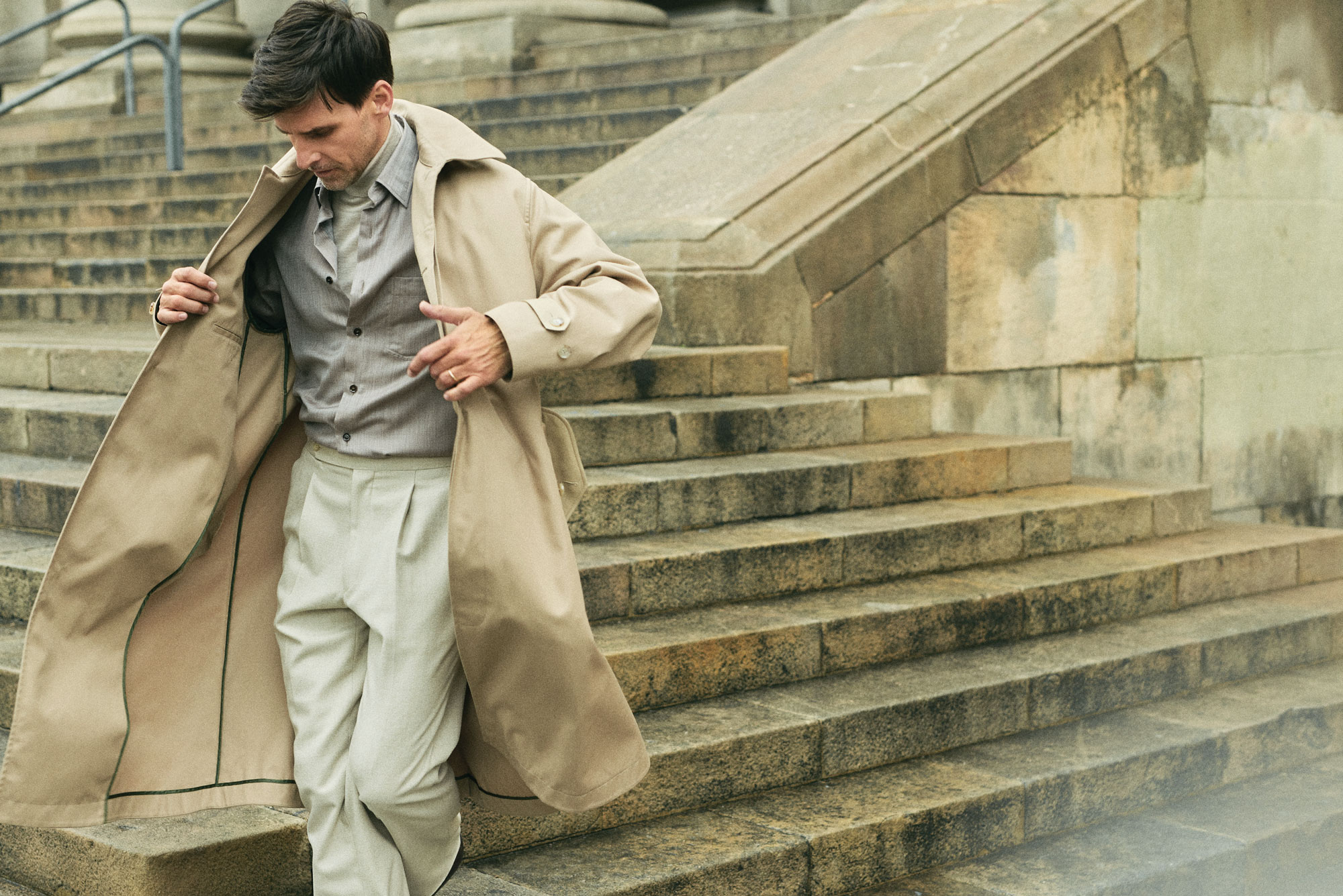

Bally cotton and poly trench, $3,605; Brioni cashmere and silk shirt, $5,895, and cashmere and silk turtleneck, $2,380: Stòffa wool pants, $795.
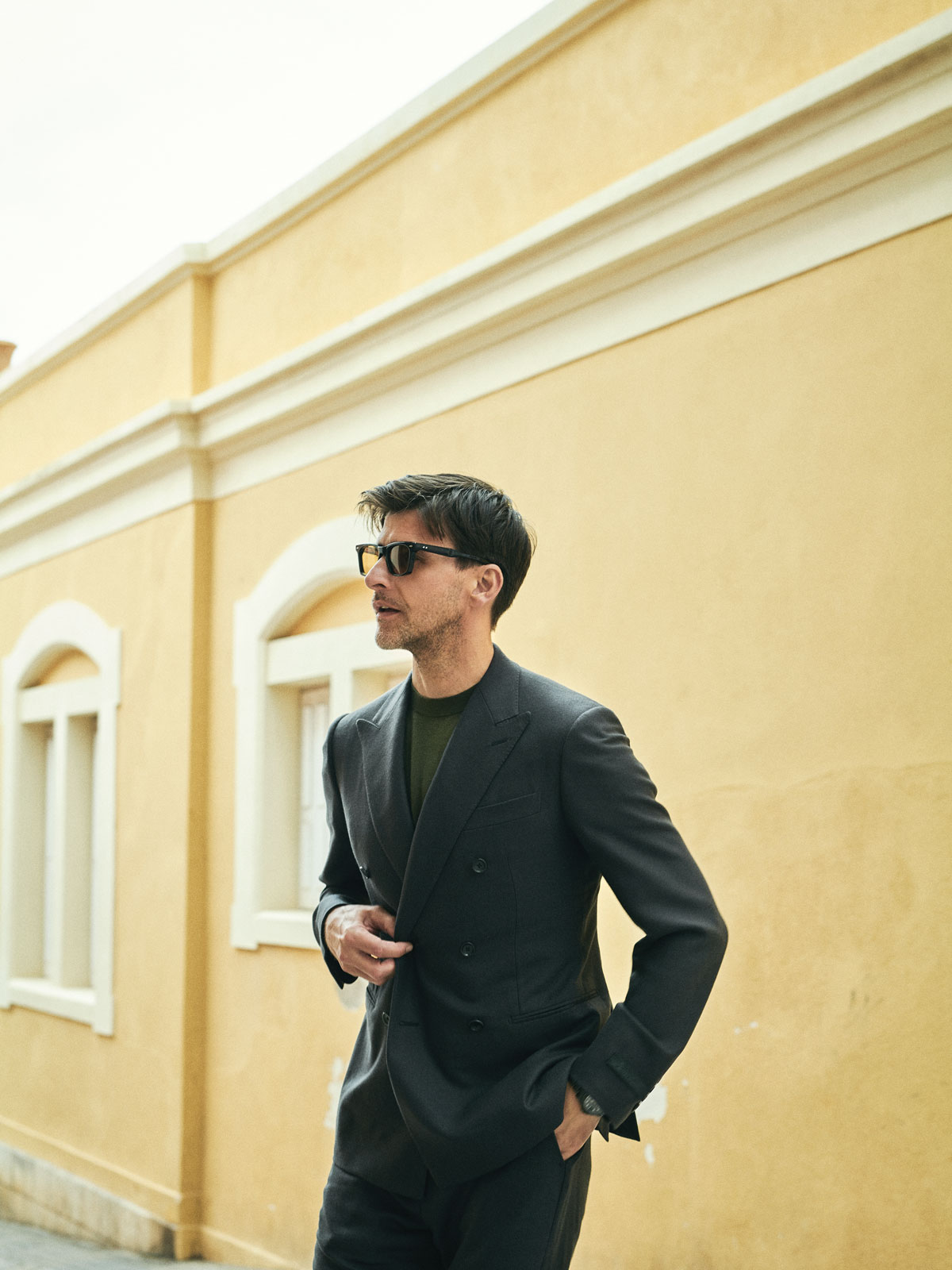

Louis Vuitton wool double- breasted Pont Neuf suit jacket, $5,215, and wool cigarette pants, $1,650; Connolly cashmere and silk T-shirt, $680; Jacques Marie Mage sunglasses, $1,210.
“My most valuable hacks: get your trousers hemmed so they fit right, avoid anything too tight, and align your colour palette. And don’t overthink it—a dark-navy suit never fails.”
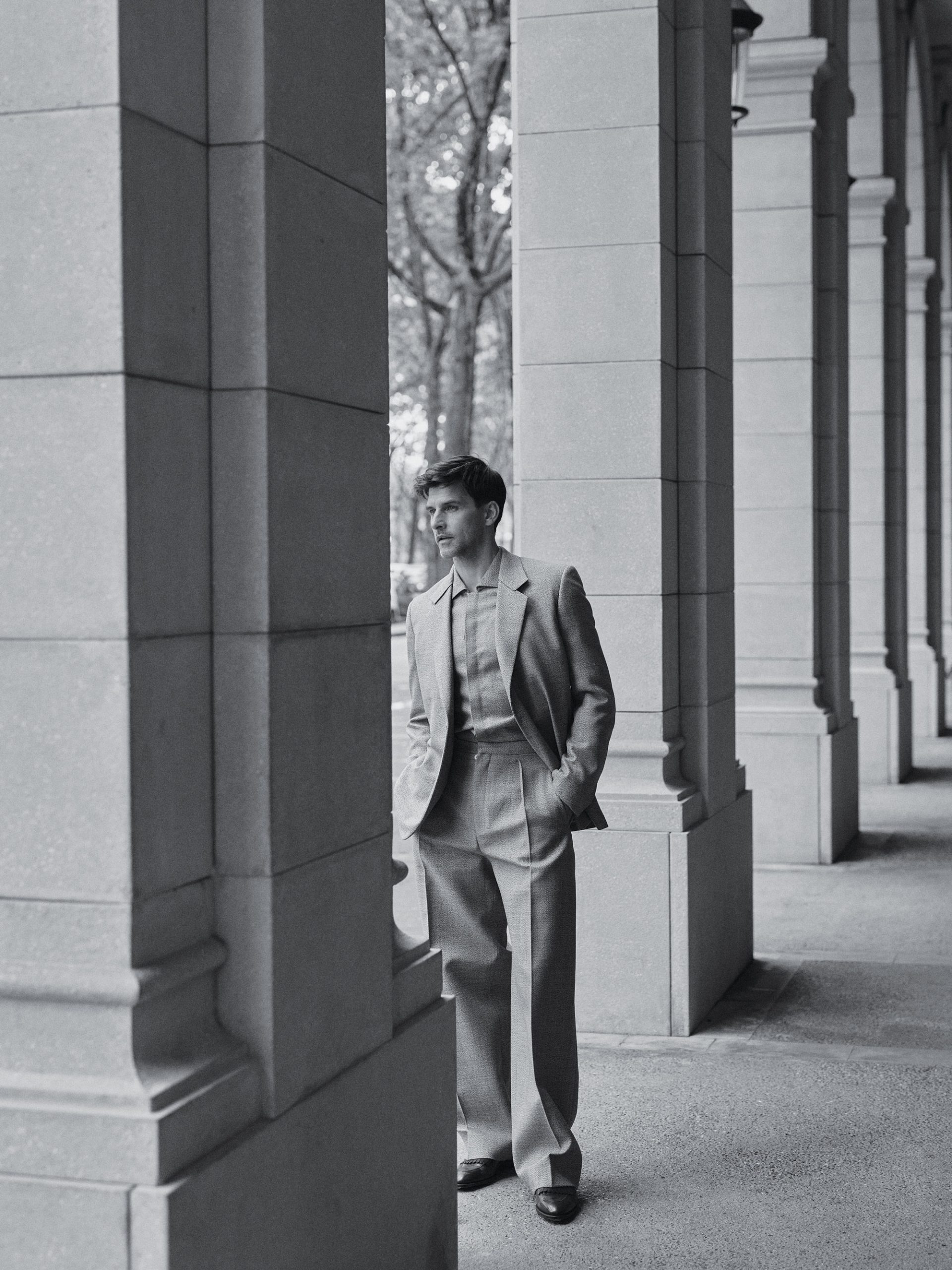

Altea technical-wool jacket, $1,300; Officine Générale cotton shirt, $430.
“Proportion and fit are all-important.I’ve learned that from designers and tailors over the last 20 years.”
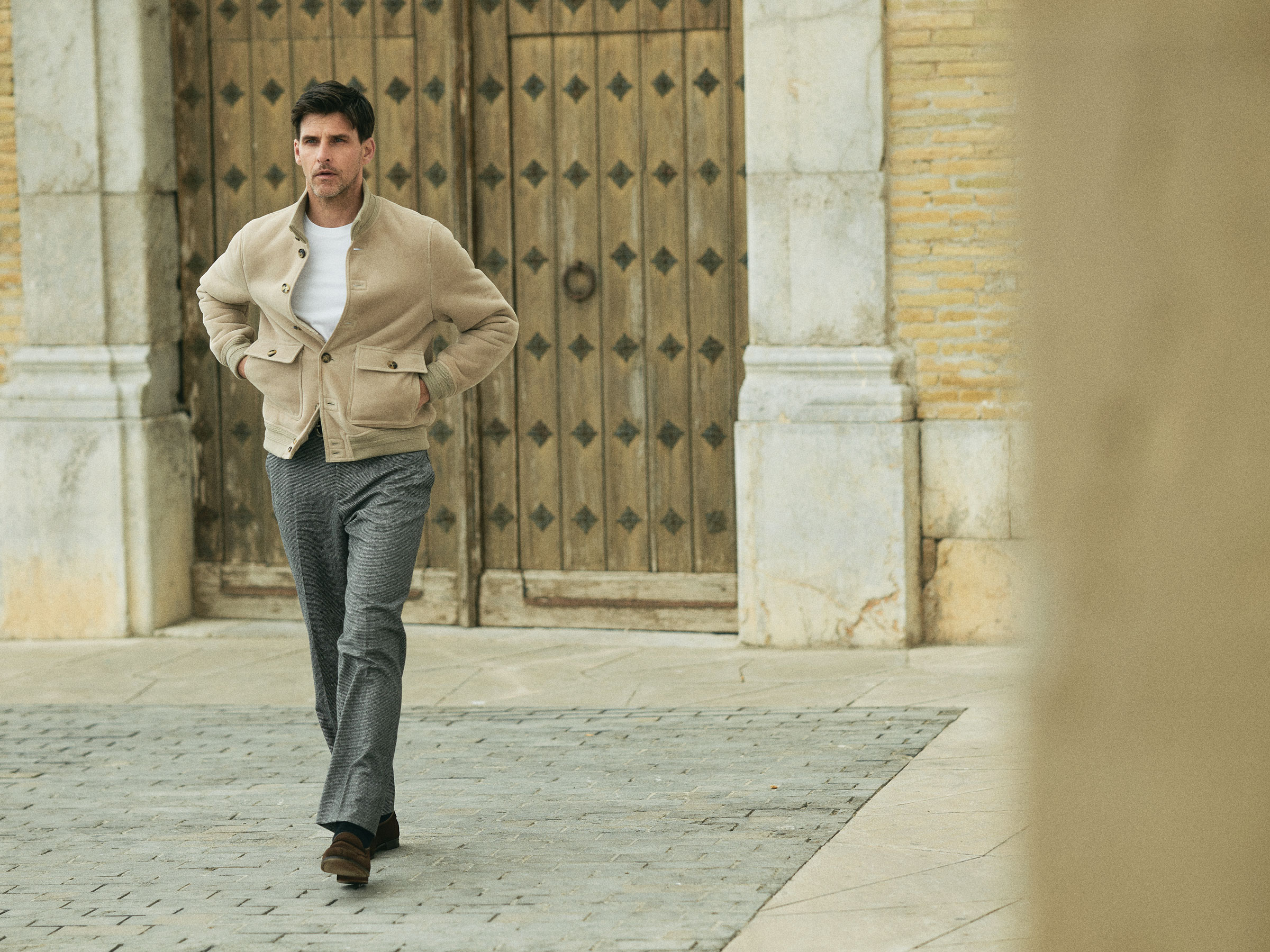

Valstar suede jacket, $4,050; Louis Vuitton cotton T-shirt, $855; Lardini wool and cashmere pants, $1,275; John Lobb suede loafers, $2,720.
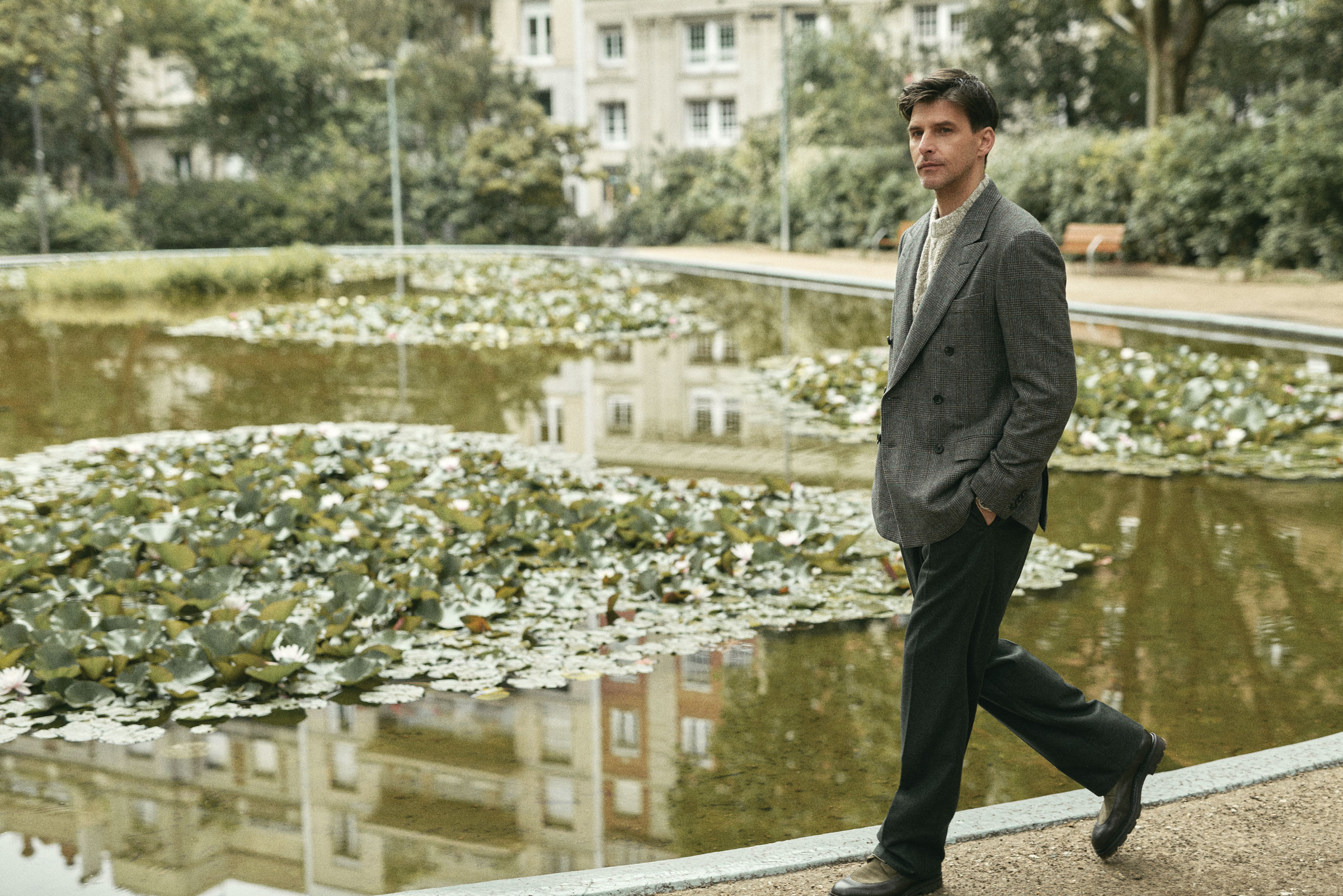

Loro Piana blazer, $7,560, sweater, $2,495, and pants, $2,190, all in cashmere and wool; John Lobb leather boots, $2,995.
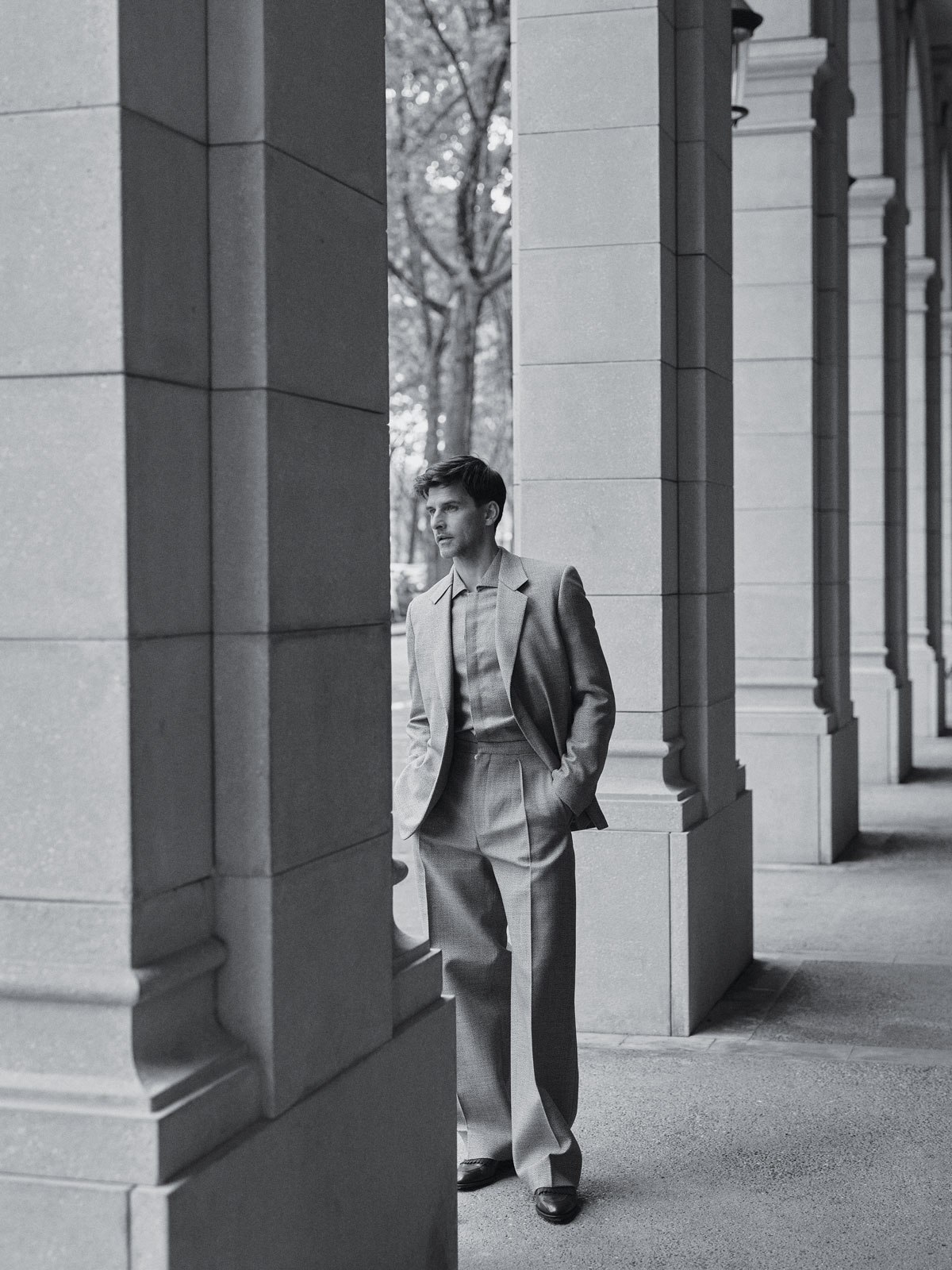

Zegna shetland-wool jacket, $5,215, shetland-wool shirt, $6,275, and pure-wool pleated trousers, $2,250; John Lobb suede loafers, $2,720.
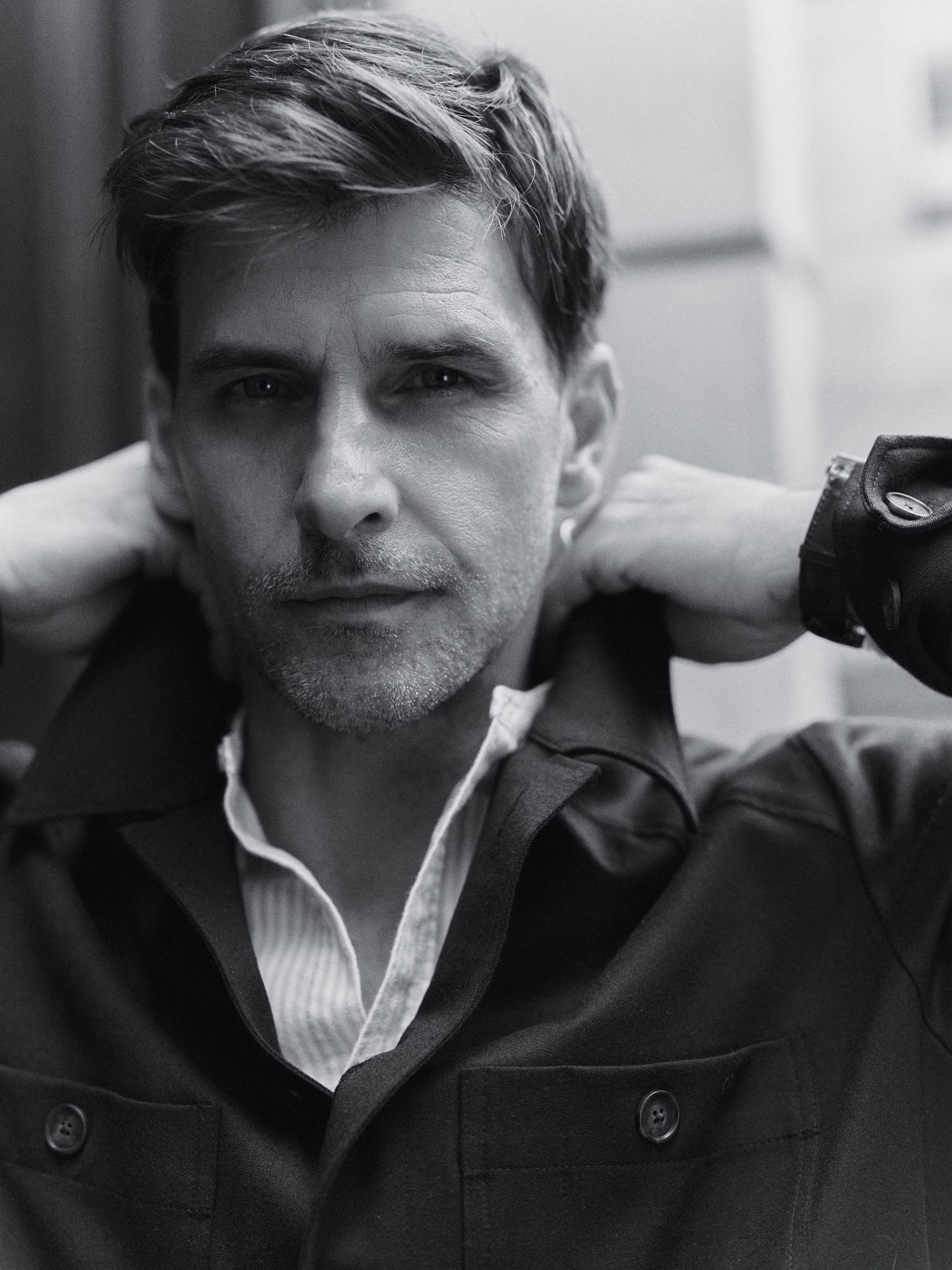

Altea technical-wool jacket, $1,300; Officine Générale cotton shirt, $430.

Model: Johannes Huebl
Senior market editor and casting: Luis Campuzano Hair and makeup artist: Mónica Marmo
Photo assistant: Paolo Caponetto
Executive producer: Rebecca Watson
Production assistants: Nikita Klepach, Marc Gejo Photo director: Irene Opezzo
You may also like.
17/04/2024
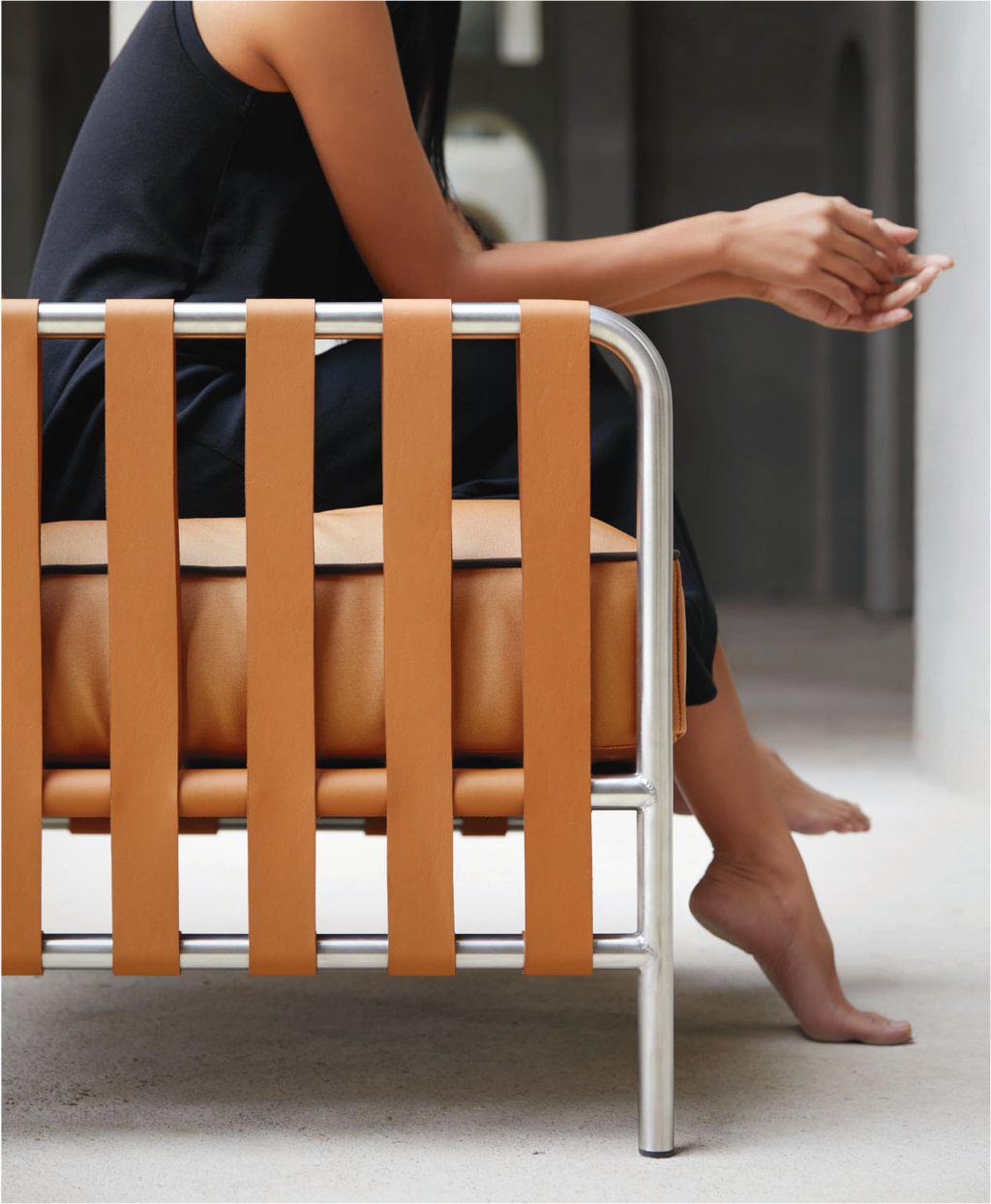
Forever Leather
Furnishings wrapped or accented with classic, cognac-coloured hide create a patina that works with any aesthetic.
Onsen, Gandia Blasco
As the textile industry makes technological advances, traditional outdoor furniture made from iron, wicker and teak seems ever so throwback-y and, dare we say, inconvenient and even uncomfortable. Gandia Blasco’s Mediterranean roots and architectural approach shine in its Onsen collection of garden furniture. Luxe synthetic-leather straps wrapping a tubular stainless-steel structure paired with long-wearing cushions in a similar shade lend new life to the idea of living with leather outdoors. From about $4,425; soft mat about $620, warm mat about $810; Onsen, Gandia Blasco
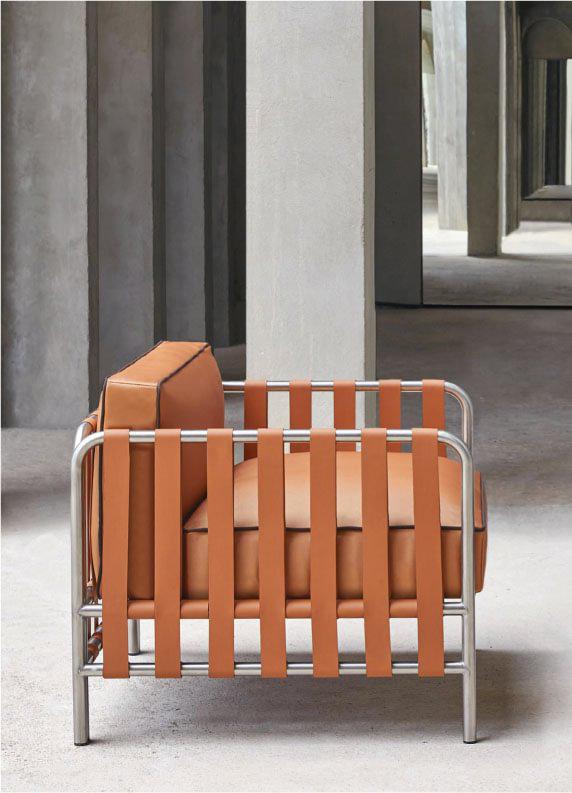

Gabri, Bolzan
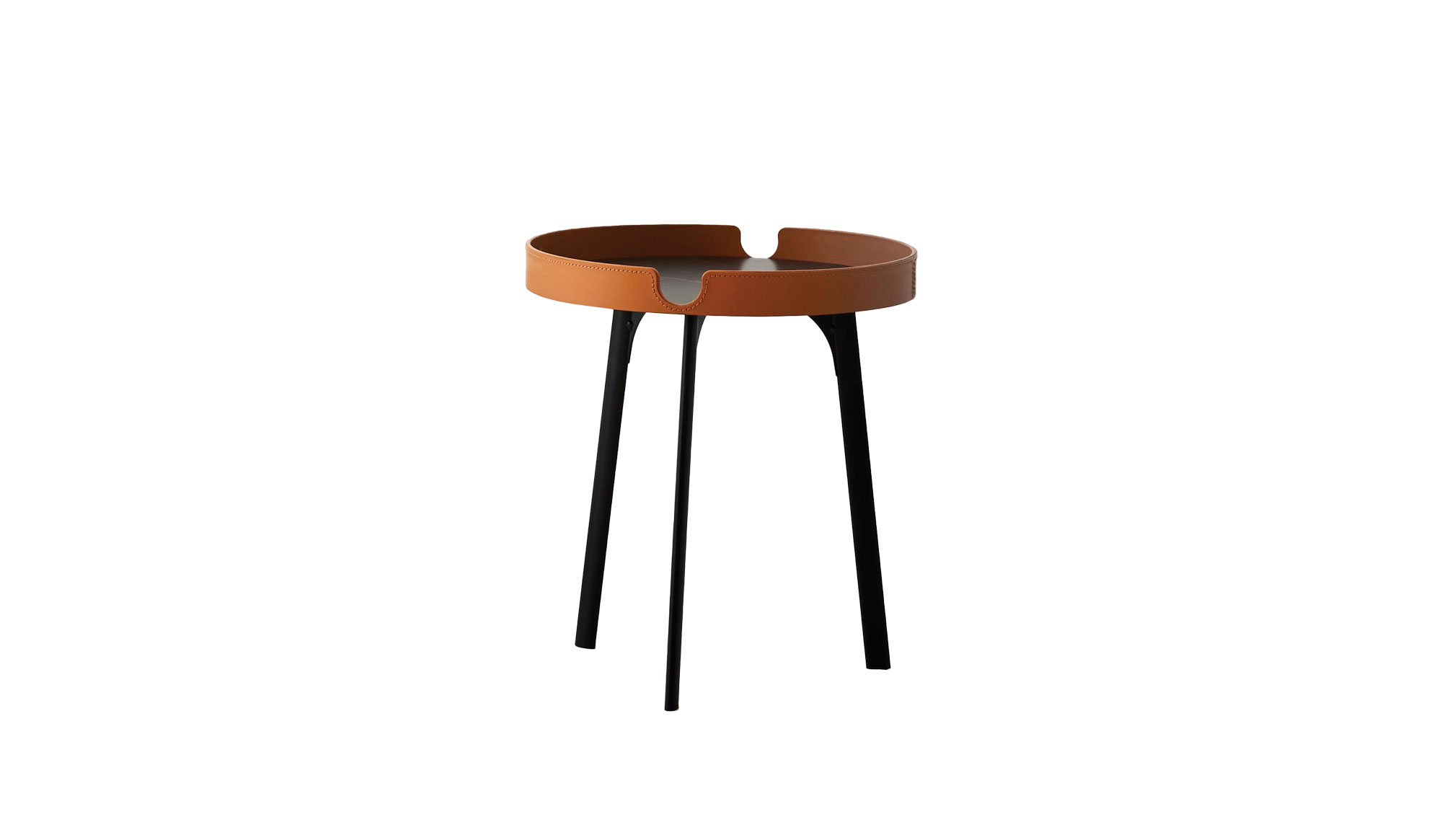
The pared-down, leggy look of these tripod tables packs a functional punch without foregoing refinement. Designed by Matteo Zorzenoni for Bolzan and made in Italy, the Gabri’s leather-bound frames with subtle topstitching and semicircular notches recall desktop accessories of an analog age. The dark tops with touches of chalky veining are thoroughly of this century: made from neolith stone, they’re temperature-resistant and waterproof, so go ahead and place your martini where you will. Small, about $1,735; large, about $2,603; Bolzan.com

Zenius Lines Giobagnara
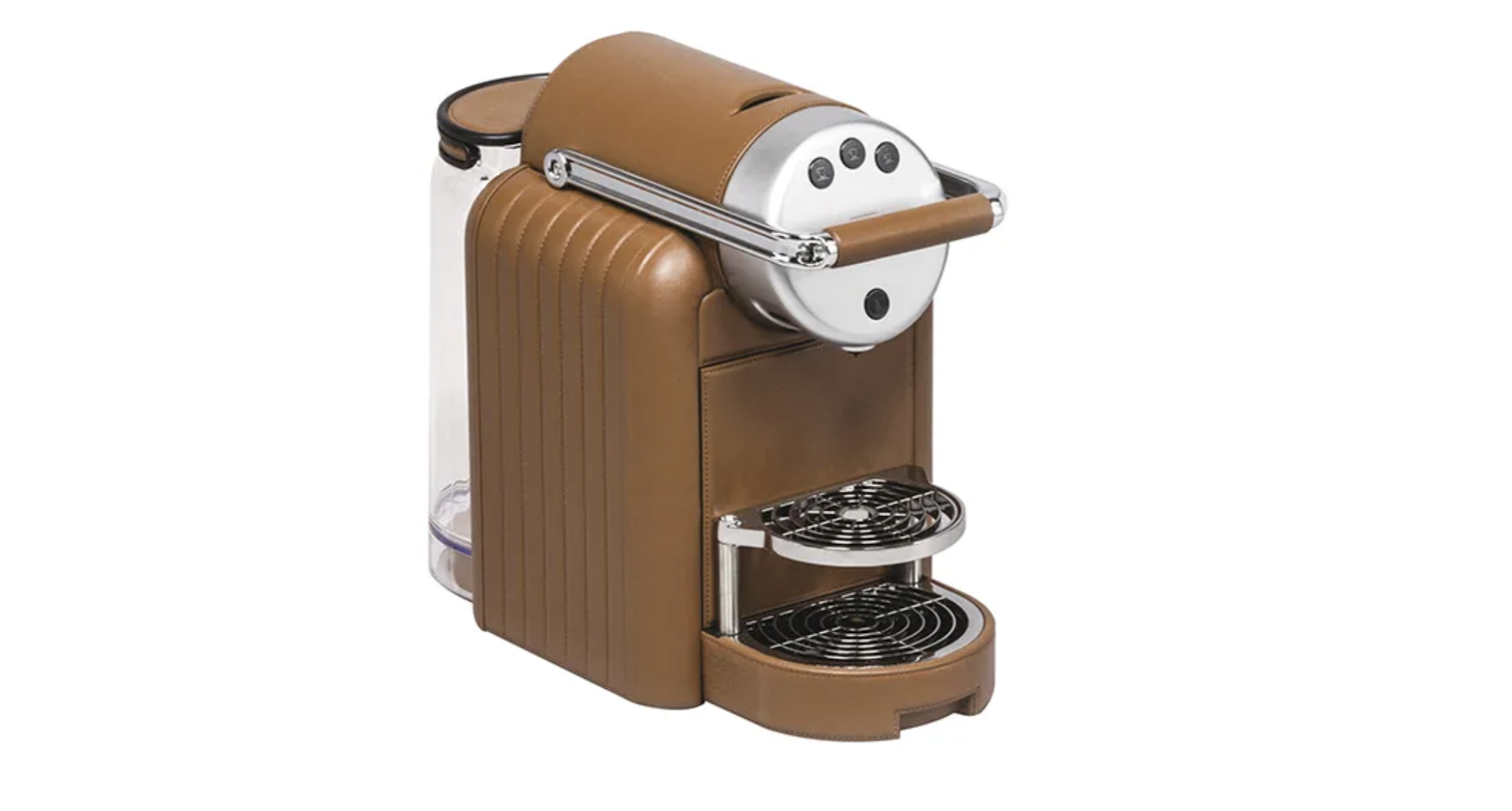
Giobagnara’s leather-encased Nespresso machine with vertical- or diamond-quilted detailing is genius in its unfussy application. The leather suits the product; the design channels the look of a luxury Italian sports car. The brand began with the Bagnara family producing household items in 1939, before moving into the luxury realm in the ’70s. Giorgio Bagnara changed its name to B. Home Interiors in 1999 and to the eponymous Giobagnara in 2014. If you like your home appliances with liberal leather detailing, it’s one to follow. About $7,900; Artemest.com

Vague, Tonucci Collection
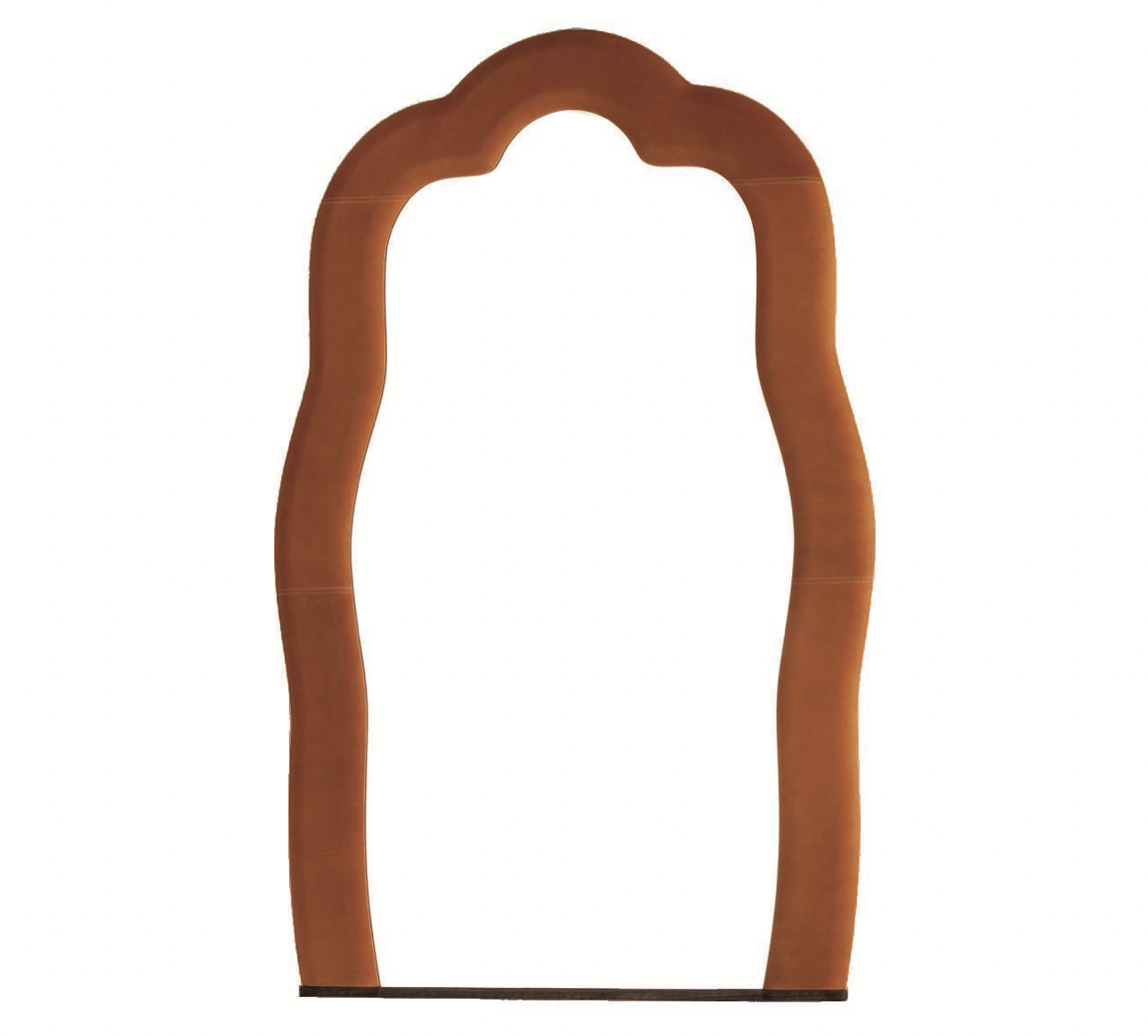
Fun house–meets-Baroque in this softly symmetrical, wall-mounted mirror that playfully beckons you into another dimension (and will bounce beautiful light around the room). Designed by Viola Tonucci, who took the reins of Tonucci Collection from her father last year, the thick, leather-covered frame introduces architectural interest and a hint of levity to a room, be it traditional or modern. About $8,050; Tonucci.com

DS-707, de Sede
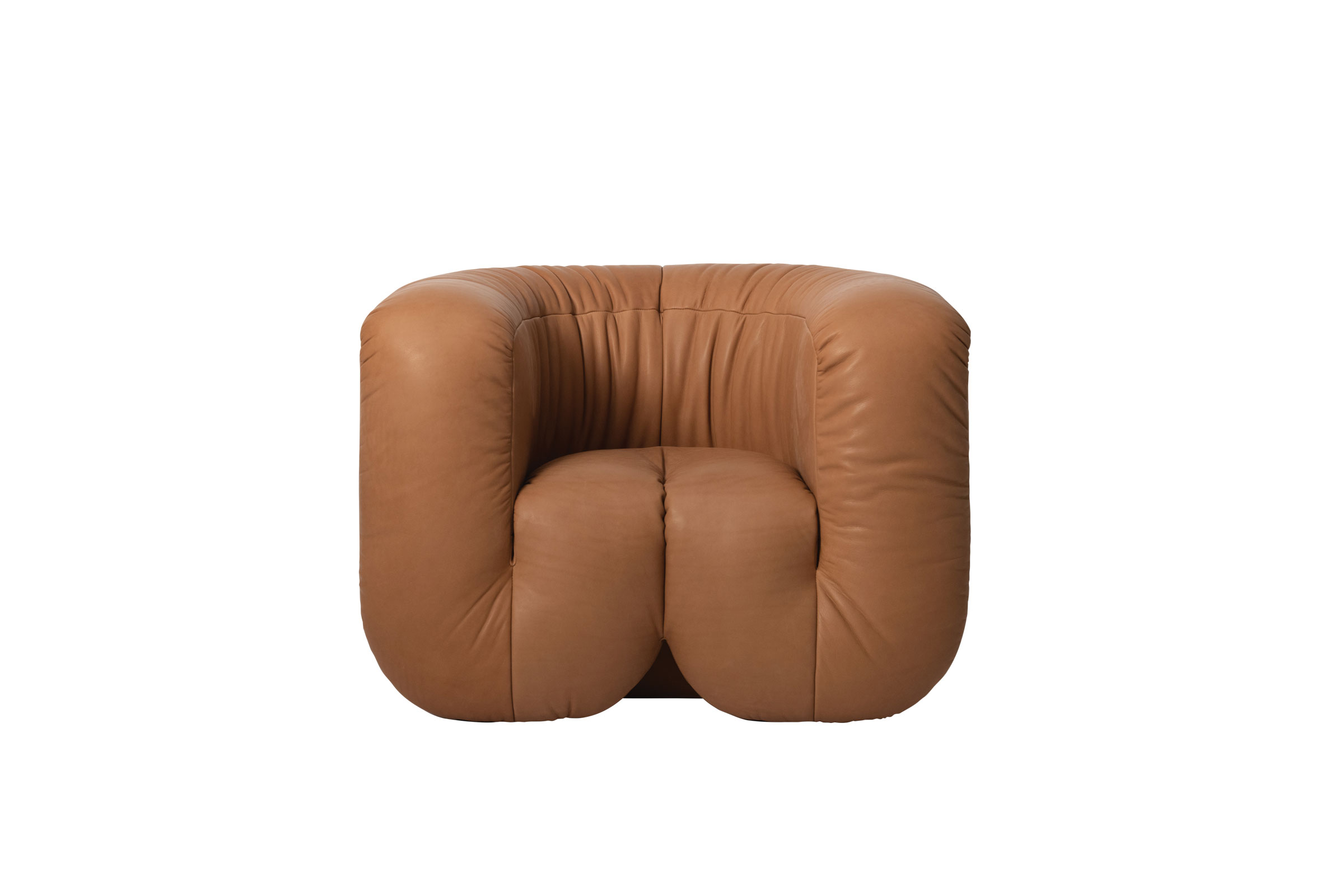
Given Philippe Malouin’s propensity for experimentation, it’s no wonder that Swiss furniture firm de Sede took a whole new approach in manufacturing Malouin’s DS-707 design. He began by noodling around with foam, folding it this way and that before settling on the serpentine shape. Although the silhouette made de Sede wary—creating it required the team to manipulate leather in a manner that could leave it less supple— the project prevailed with great success. The system itself invites experimentation as customers can configure the components to their heart’s content. From $30,450; deSede.com

You may also like.
18/04/2024


















